一、概念
二叉搜索树又称二叉排序树,它或者是一棵空树,或者是具有以下性质的二叉树:
若它的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有节点的值都小于根节点的值
若它的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有节点的值都大于根节点的值
左<根<右
它的左右子树也分别为二叉搜索树
之所以又叫二叉排序树,是因为二叉搜索树中序遍历的结果是有序的
二、基础操作
1.查找find
基于二叉搜索树的特点,查找一个数并不难,若根节点不为空的情况下:
若根节点key==查找key,直接返回true
若根节点key>查找key,那得找到更小的,则往左子树查找
若根节点key<查找key,那得找到更大的,则往右子树查找
最多查找高度次,走到空为止,如果还没找到,则说明这个值不存在,返回false
bool find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
2.插入Insert
1.树为空,则直接插入,新增节点,直接插入root指针即可
2.树不为空,按二叉搜索树性质查找插入位置,插入新节点。
(注意:不能插入重复的元素,并且每次插入都是要定位到空节点的位置;我们先定义一个 cur从root开始,比较元素的大小:若插入的元素比当前位置元素小就往左走,比当前位置元素大就往右走,直到为空,相等就不能插入了;同时定义一个parent去记录当前 cur的前一个位置,最后判断cur是parent的左子树还是右子树即可)
bool Insert(const K& key)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(key);
if (parent->_key < key)
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
return true;
}
3.中序遍历InOrder
递归走起,同时由于_root是私有的,外部不能访问,我们可以在类内给中序提供一个方法即可,就不需要传参了
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
private:
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << " ";
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
Node* _root = nullptr;
4.删除erase
删除的情况比较多:
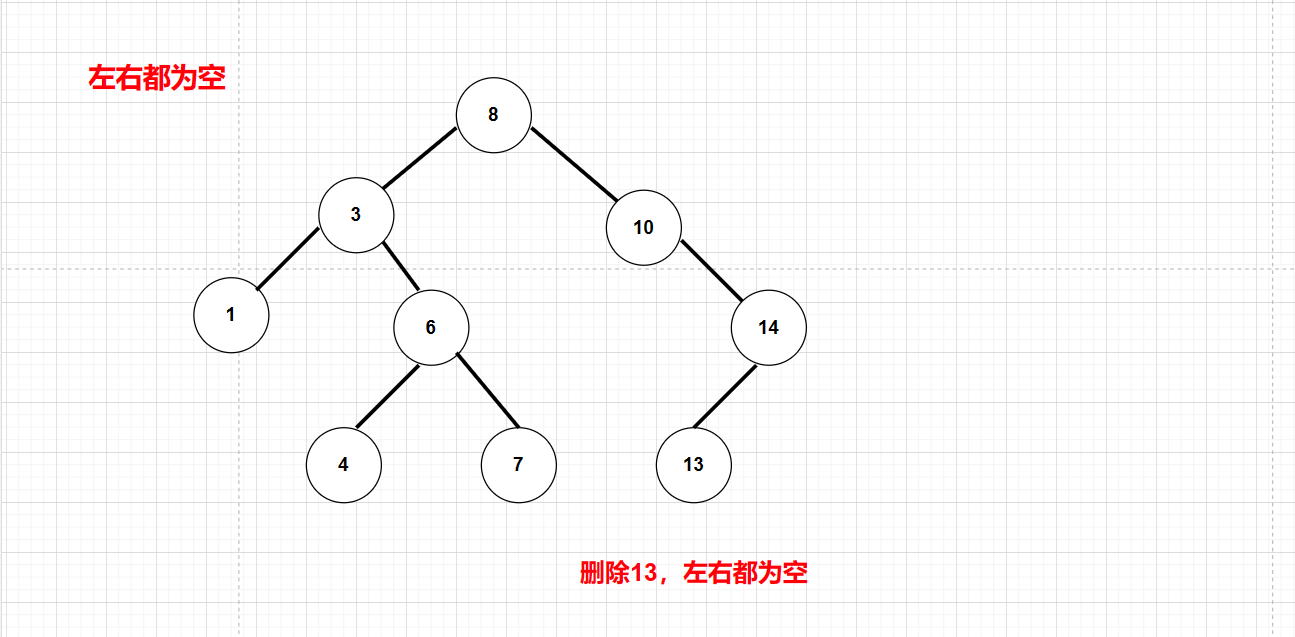
- 左右都为空:叶子结点,直接置空并链接到空指针
- 左为空或右为空:进行托孤:只有一个子节点,删除自己本身,并链接子节点和父节点(注意:如果父亲是空,也就是要删除根结点,此时根节点没有父亲,单独判断一下)
- 左右都不为空:找出替换节点:右子树最小节点**、**左子树最大节点。替换节点可以作为交换和删除进行交换,交换后删除交换节点、交换节点要么没有孩子,要么只有一个孩子可以直接删除
但是左右都为空可以纳入到左为空或右为空的情况

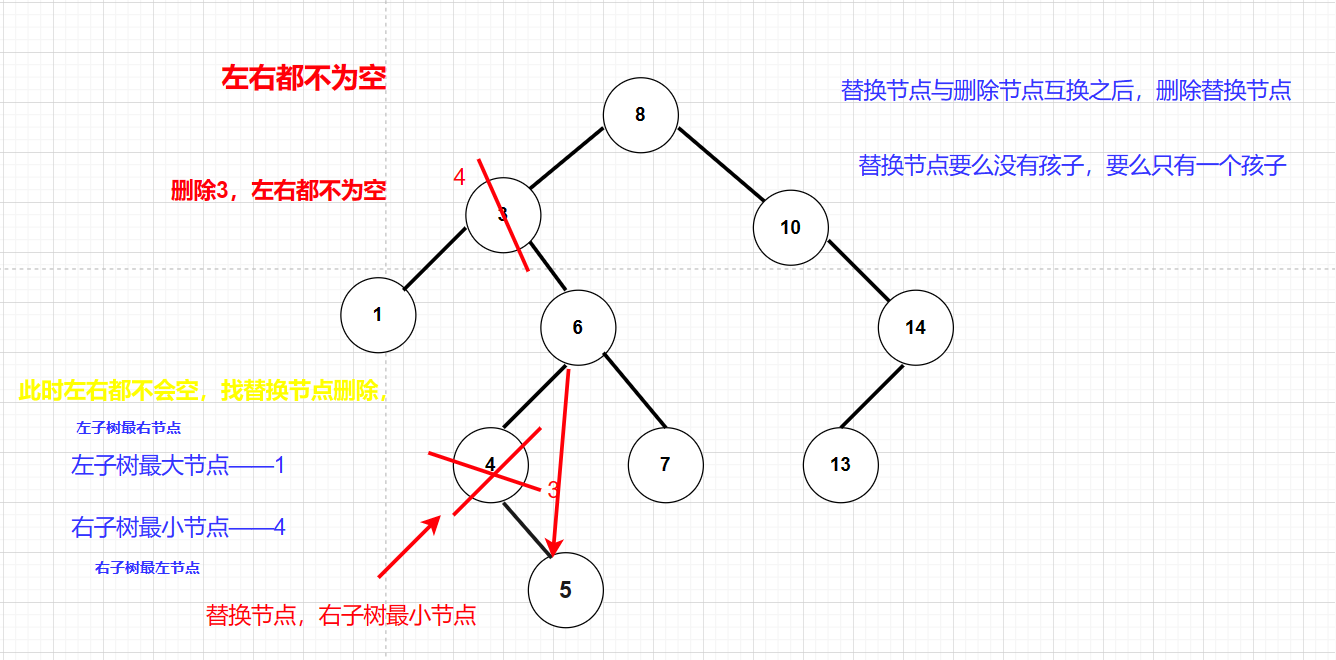
注意:
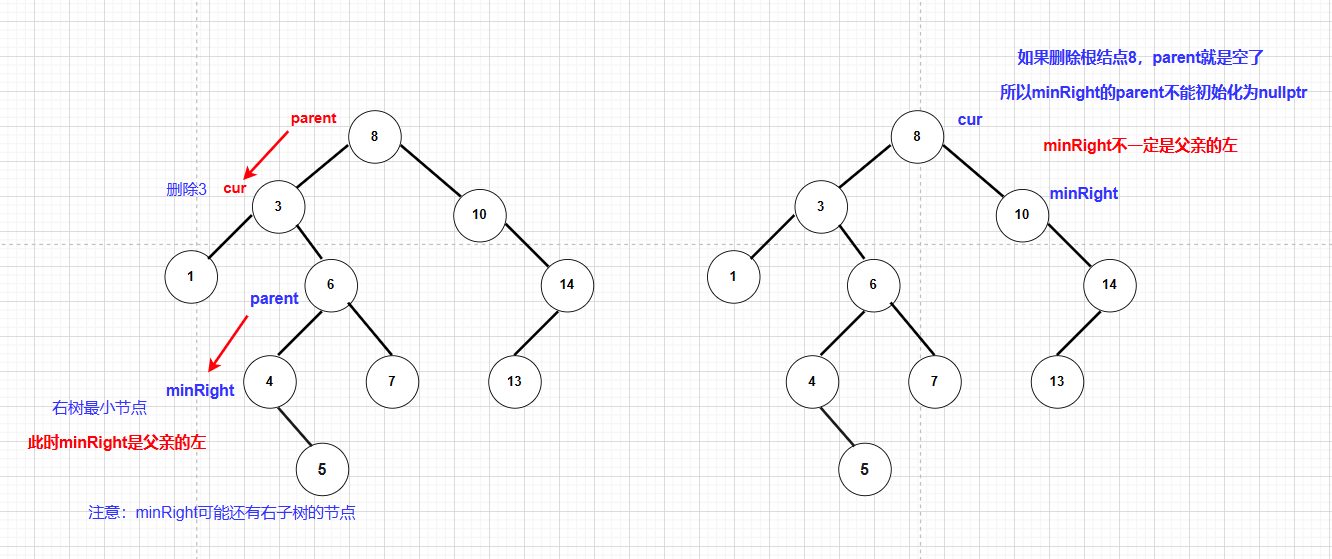
代码实现:
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
//左为空
if (cur->_left == nullptr)
{
//删除根结点
//if(parent==nullptr)
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_right;
}
else
{
if (parent->_left == cur)
{
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
}
delete cur;
}
//右为空
else if (cur->_right == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_left;
}
else
{
if (parent->_left == cur)
{
parent->_left = cur->_left;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
}
delete cur;
}
//左右都不为空,找替换节点
else
{
//不能初始化为nullptr
Node* parent = cur;
//右子树最小节点
Node* minRight = cur->_right;
while (minRight->_left)
{
parent = minRight;
minRight = minRight->_left;
}
cur->_key = minRight->_key;
//判断minRight是父亲的左还是右
if (minRight == parent->_left)
{
parent->_left = minRight->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_right = minRight->_right;
}
delete minRight;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
三、递归写法
1.递归查找
这个比较简单:苏醒把,递归时刻
bool _FindR(Node* root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr) return false;
else if (root->_key < key) return _FindR(root->_right, key);
else if (root->_key > key) return _FindR(root->_left, key);
else return true;
}
2.递归插入
最大的问题是插入之后跟父亲进行链接,如果直接给root是不可以的,因为root是栈帧里面的参数,只是局部变量:加上引用
bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
else if (root->_key < key)
return _InsertR(root->_right, key);
else if (root->_key > key)
return _InsertR(root->_left, key);
else
return false;
}
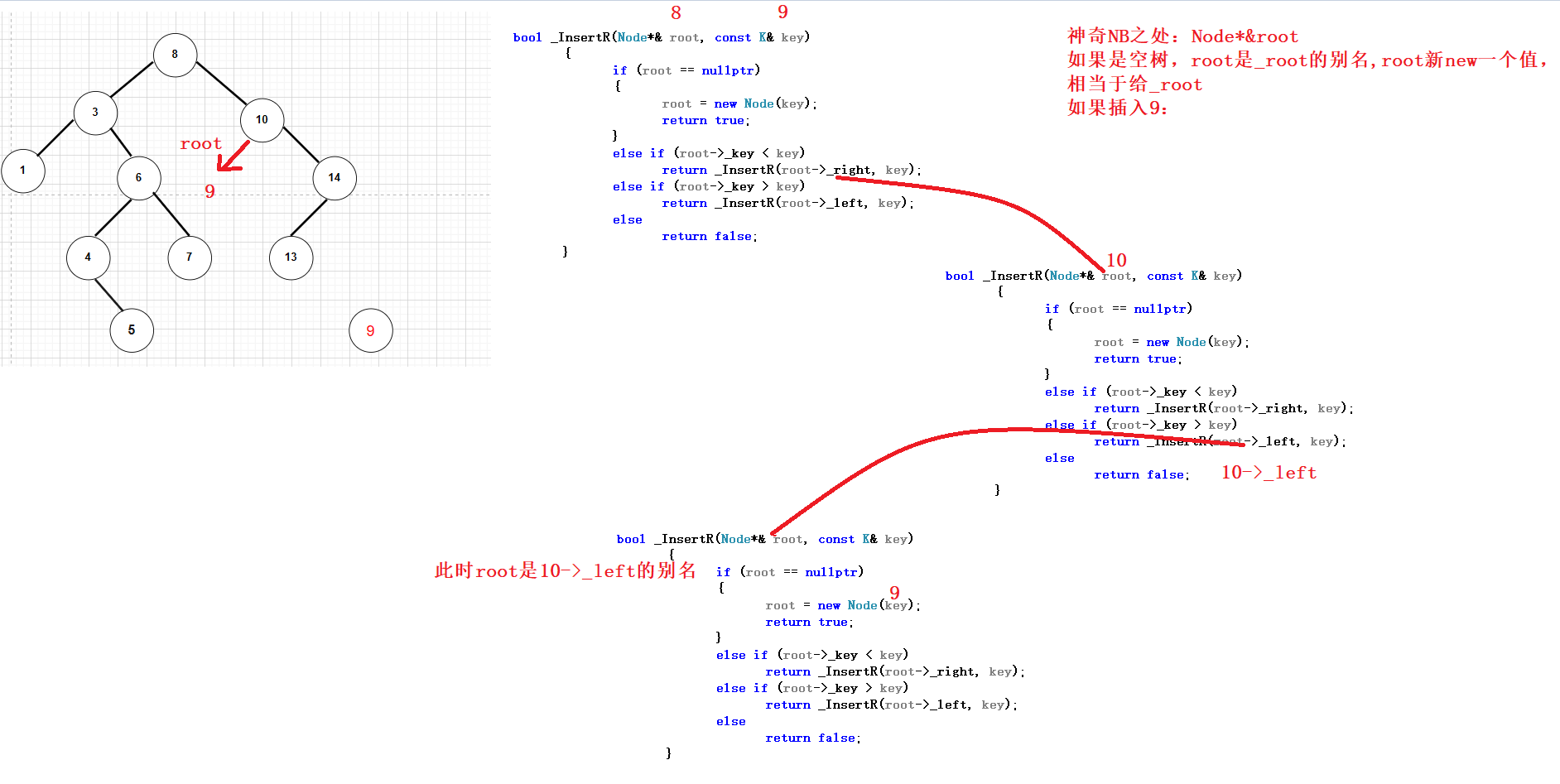
3.递归删除
递归删除怎么找到父节点?root = root->_left/ root = root->_right;

bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return false;
}
if (root->_key < key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
else if (root->_key > key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_left, key);
}
else
{
Node* del = root;
if (root->_right == nullptr)
{
root = root->_left;
}
else if (root->_left == nullptr)
{
root = root->_right;
}
else
{
Node* minRight = root->_right;
while (minRight->_left)
{
minRight = minRight->_left;
}
swap(root->_key, minRight->_key);
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
delete del;
return true;
}
}
四、应用
最优情况下,二叉搜索树为完全二叉树,其平均比较次数为:log2N
最差情况下,二叉搜索树退化为单支树,其平均比较次数为: N/2

1.K模型:K模型即只有key作为关键码,结构中只需要存储Key即可,关键码即为需要搜索到的值,判断关键字是否存在。
比如:给一个单词word,判断该单词是否拼写正确,具体方式如下:
以单词集合中的每个单词作为key,构建一棵二叉搜索树,在二叉搜索树中检索该单词是否存在,存在则拼写正确,不存在则拼写错误。
2.KV模型:每一个关键码key,都有与之对应的值Value,即**<Key, Value>**的键值对。
比如英汉词典就是英文与中文的对应关系,通过英文可以快速找到与其对应的中文,英文单词与其对应的中文<word, chinese>就构成一种键值对;再比如统计单词次数,统计成功后,给定单词就可快速找到其出现的次数,单词与其出现次数就是**<word, count>**就构成一种键值对。
namespace KV
{
template <class K,class V>
struct BSTreeNode
{
BSTreeNode<K,V>* _left;
BSTreeNode<K,V>* _right;
K _key;
V _value;
BSTreeNode(const K& key,const V&value)
:_key(key),
_value(value),
_left(nullptr),
_right(nullptr)
{}
};
template <class K,class V>
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K, V> Node;
public:
bool Insert(const K& key, const V& value)
Node* find(const K& key)
void InOrder()
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};
}
void TestBSTree()
{
//key/Value的搜索模型;通过key查找或修改Value
KV::BSTree<string, string> dict;
dict.Insert("sort", "排序");
dict.Insert("string", "字符串");
dict.Insert("left", "左");
dict.Insert("right", "右");
string str;
while (cin >> str)
{
KV::BSTreeNode<string, string>* ret = dict.find(str);
if (ret)
{
cout << ret->_value << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找不到" << endl;
}
}
}
源代码:
BSTree.h
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
namespace K
{
template <class K>
struct BSTreeNode
{
BSTreeNode<K>* _left;
BSTreeNode<K>* _right;
K _key;
BSTreeNode(const K& key)
:_key(key),
_left(nullptr),
_right(nullptr)
{}
};
template <class K>
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node;
public:
BSTree()
:_root(nullptr)
{}
BSTree(const BSTree<K>& t)
{
_root = Copy(t._root);
}
BSTree<K>& operator = (BSTree<K> t)
{
swap(_root, t._root);
return *this;
}
~BSTree()
{
Destroy(_root);
_root = nullptr;
}
bool Insert(const K& key)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(key);
if (parent->_key < key)
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
return true;
}
bool find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
//左为空
if (cur->_left == nullptr)
{
//删除根结点
//if(parent==nullptr)
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_right;
}
else
{
if (parent->_left == cur)
{
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
}
delete cur;
}
//右为空
else if (cur->_right == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_left;
}
else
{
if (parent->_left == cur)
{
parent->_left = cur->_left;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
}
delete cur;
}
//左右都不为空,找替换节点
else
{
//不能初始化为nullptr
Node* parent = cur;
//右子树最小节点
Node* minRight = cur->_right;
while (minRight->_left)
{
parent = minRight;
minRight = minRight->_left;
}
cur->_key = minRight->_key;
//判断minRight是父亲的左还是右
if (minRight == parent->_left)
{
parent->_left = minRight->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_right = minRight->_right;
}
delete minRight;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
//递归
bool InsertR(const K& key)
{
return _InsertR(_root, key);
}
bool FindR(const K& key)
{
return _FindR(_root, key);
}
bool EraseR(const K& key)
{
return _EraseR(_root, key);
}
private:
void Destroy(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
Destroy(root->_left);
Destroy(root->_right);
delete root;
}
Node* Copy(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return nullptr;
Node* newRoot = new Node(root->_key);
newRoot->_left = Copy(root->_left);
newRoot->_right = Copy(root->_right);
return newRoot;
}
bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return false;
}
if (root->_key < key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
else if (root->_key > key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_left, key);
}
else
{
Node* del = root;
if (root->_right == nullptr)
{
root = root->_left;
}
else if (root->_left == nullptr)
{
root = root->_right;
}
else
{
Node* minRight = root->_right;
while (minRight->_left)
{
minRight = minRight->_left;
}
swap(root->_key, minRight->_key);
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
delete del;
return true;
}
}
bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
else if (root->_key < key)
return _InsertR(root->_right, key);
else if (root->_key > key)
return _InsertR(root->_left, key);
else
return false;
}
bool _FindR(Node* root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr) return false;
else if (root->_key < key) return _FindR(root->_right, key);
else if (root->_key > key) return _FindR(root->_left, key);
else return true;
}
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << " ";
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
Node* _root = nullptr;
};
}
namespace KV
{
template <class K,class V>
struct BSTreeNode
{
BSTreeNode<K,V>* _left;
BSTreeNode<K,V>* _right;
K _key;
V _value;
BSTreeNode(const K& key,const V&value)
:_key(key),
_value(value),
_left(nullptr),
_right(nullptr)
{}
};
template <class K,class V>
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K, V> Node;
public:
bool Insert(const K& key, const V& value)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key, value);
return true;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(key, value);
if (parent->_key < key)
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
return true;
}
Node* find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return cur;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
}
private:
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr) return;
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << ":"<<root->_value<<endl;
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
Node* _root = nullptr;
};
}
void TestBSTree1()
{
int a[] = { 8, 3, 1, 10, 6, 4, 7, 14, 13 };
K::BSTree<int> t;
for (auto e : a)
{
t.Insert(e);
}
t.InOrder();
K::BSTree<int> copyt(t);
copyt.InOrder();
t.InsertR(9);
t.InOrder();
t.EraseR(9);
t.InOrder();
t.EraseR(3);
t.InOrder();
for (auto e : a)
{
t.EraseR(e);
t.InOrder();
}
}
void TestBSTree2()
{
KV::BSTree<string, string> dict;
dict.Insert("sort", "排序");
dict.Insert("string", "字符串");
dict.Insert("left", "左");
dict.Insert("right", "右");
string str;
while (cin >> str)
{
KV::BSTreeNode<string, string>* ret = dict.find(str);
if (ret)
{
cout << ret->_value << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找不到" << endl;
}
}
}
void TestBSTree3()
{
string arr[] = { "苹果","西瓜","苹果" };
KV::BSTree<string, int> countTree;
for (auto e : arr)
{
auto* ret = countTree.find(e);
if (ret == nullptr)
{
countTree.Insert(e, 1);
}
else
{
ret->_value++;
}
}
countTree.InOrder();
}
#include "BSTree.h"
int main()
{
//TestBSTree1();
TestBSTree2();
//TestBSTree3();
return 0;
}
五、题目练习
根据二叉树创建字符串

前序遍历,左为空,右不为空的括号不可以省略,右为空的括号可以省略
class Solution {
public:
string tree2str(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return string();
string ret;
ret += to_string(root->val);
if(root->left)
{
ret+='(';
ret+= tree2str(root->left);
ret+=')';
}
else if(root->right)
{
ret+="()";
}
if(root->right)
{
ret+='(';
ret+=tree2str(root->right);
ret+=')';
}
return ret;
}
};
二叉树的层序遍历
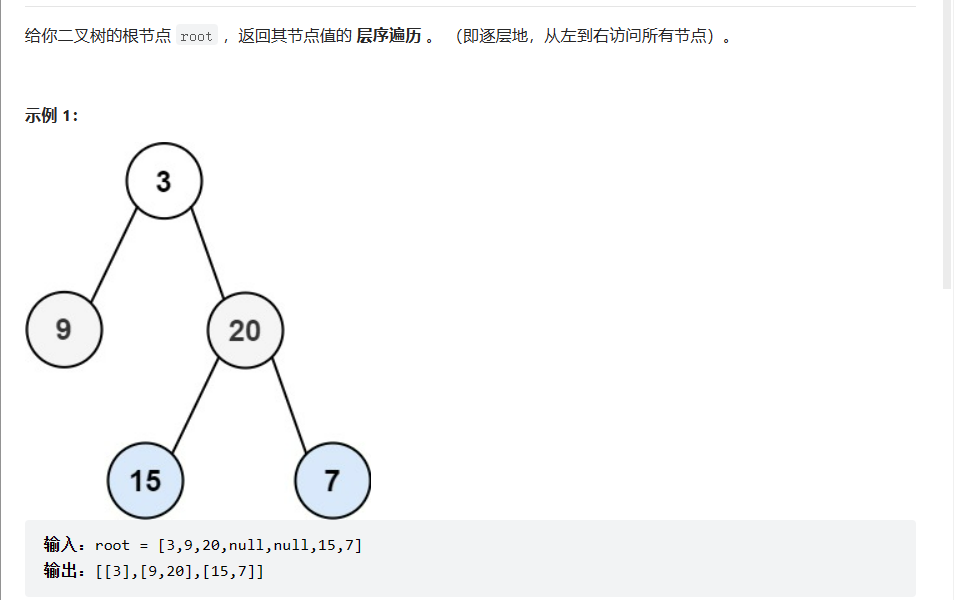
层序遍历,可以通过一个队列来实现,同时定义每次队列的大小
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> q;
vector<vector<int>> vv;
size_t levelSize = 0;
if(root)
{
q.push(root);
levelSize=1;
}
while(!q.empty())
{
vector<int> v;
while(levelSize--)
{
TreeNode* front = q.front();
q.pop();
v.push_back(front->val);
if(front->left)
{
q.push(front->left);
}
if(front->right)
{
q.push(front->right);
}
}
vv.push_back(v);
levelSize = q.size();
}
return vv;
}
};
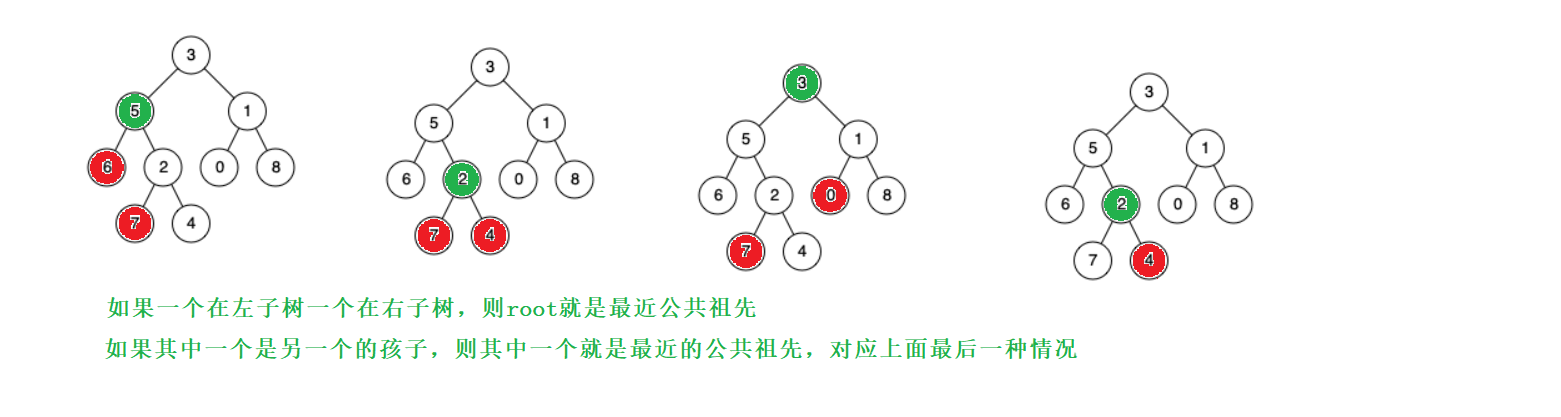
二叉树的最近公共祖先

class Solution {
bool isInTree(TreeNode*root,TreeNode*x)
{
if(root == nullptr) return false;
if(root == x) return true;
else
return isInTree(root->left,x)
|| isInTree(root->right,x);
}
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(root==nullptr)
return nullptr;
if(root == p||root==q) return root;
bool pLeft = isInTree(root->left,p);
bool pRight = !pLeft;
bool qLeft = isInTree(root->left,q);
bool qRight = !qLeft;
//一个在左一个在右
if((pLeft&&qRight)||(pRight&&qLeft))
return root;
//同左
if(pLeft&&qLeft)
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->left,p,q);
//同右
else
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->right,p,q);
}
};
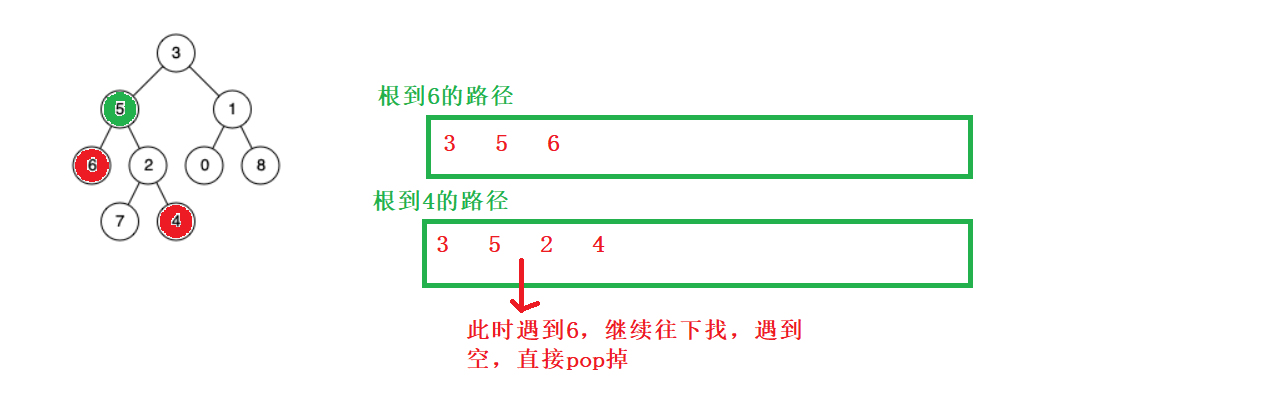
把根到对应节点的路径存储起来,在找出相交的结点即是最近的公共结点:
class Solution {
bool GetPath(TreeNode*root,TreeNode*x,stack<TreeNode*>& stack)
{
if(root == nullptr) return false;
stack.push(root);
if(root == x)
{
return true;
}
if(GetPath(root->left,x,stack))
return true;
if(GetPath(root->right,x,stack))
return true;
stack.pop();
return false;
}
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(root==nullptr)
return nullptr;
stack<TreeNode*> pPath;
stack<TreeNode*> qPath;
GetPath(root,p,pPath);
GetPath(root,q,qPath);
//长的先pop
while(pPath.size()!=qPath.size())
{
if(pPath.size()>qPath.size())
{
pPath.pop();
}
else
qPath.pop();
}
//同时pop,找出交点
while(()!=())
{
pPath.pop();
qPath.pop();
}
return ();
}
};
二叉搜索树与双向链表
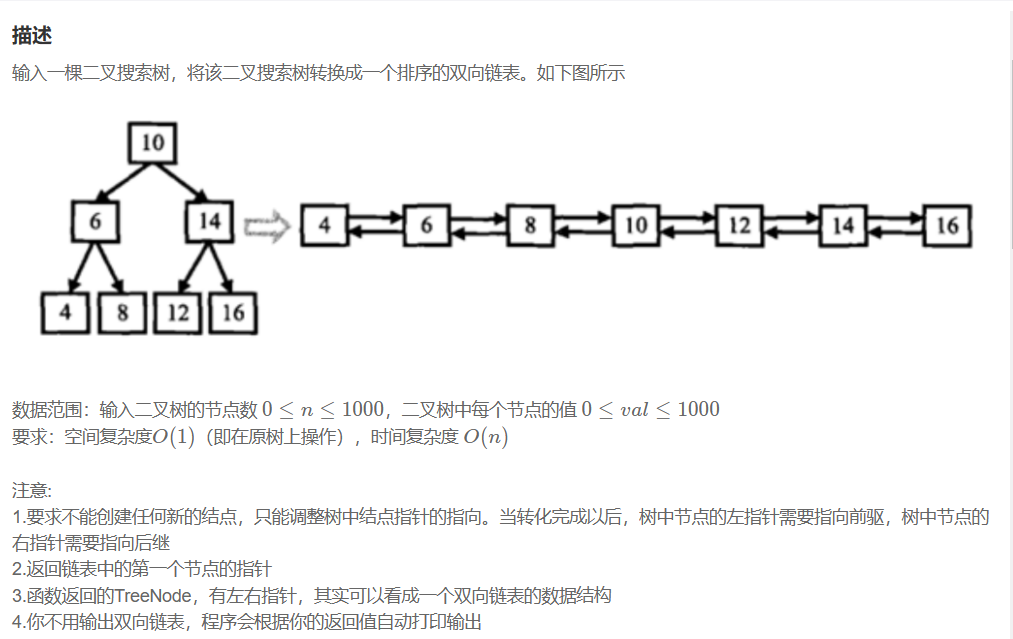
思路一:中序遍历,将节点放到一个vector中,在链接节点,但是空间复杂度不符合题目要求:
class Solution {
void InOrder(TreeNode*root,vector<TreeNode*>& v)
{
if(root==nullptr) return;
InOrder(root->left,v);
v.push_back(root);
InOrder(root->right,v);
}
public:
TreeNode* Convert(TreeNode* pRootOfTree) {
if(pRootOfTree==nullptr) return nullptr;
vector<TreeNode*> v;
InOrder(pRootOfTree,v);
if(v.size()<=1) return v[0];
v[0]->left =nullptr;
v[0]->right = v[1];
for(int i =1;i<v.size()-1;i++)
{
v[i]->left = v[i-1];
v[i]->right = v[i+1];
}
v[v.size()-1]->left = v[v.size()-2];
v[v.size()-1]->right = nullptr;
return v[0];
}
};
思路二:递归直接进行转换
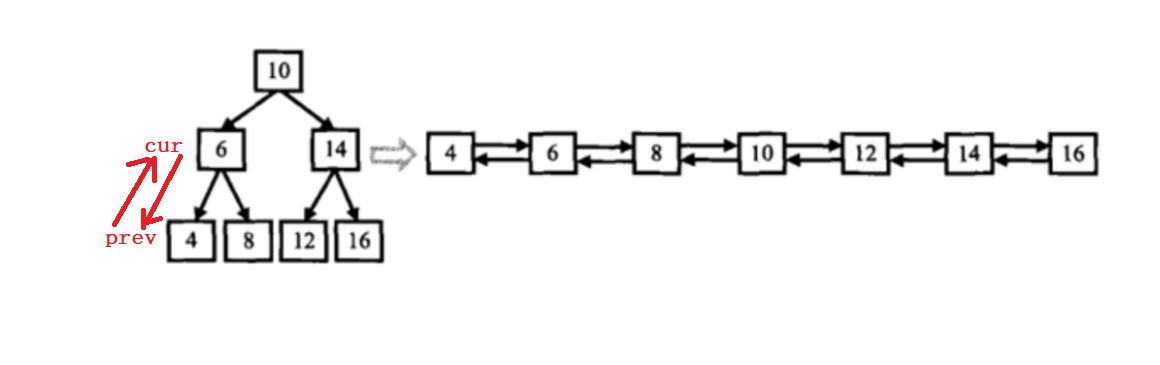
class Solution {
void InOrder(TreeNode*cur,TreeNode*&prev)
{
if(cur==nullptr)
{
return;
}
InOrder(cur->left,prev);
cur->left = prev;
if(prev)
{
prev->right = cur;
}
prev = cur;
InOrder(cur->right,prev);
}
public:
TreeNode* Convert(TreeNode* pRootOfTree) {
TreeNode*prev = nullptr;
InOrder(pRootOfTree,prev);
//找头
TreeNode*head = pRootOfTree;
while(head&&head->left)
{
head = head->left;
}
return head;
}
};
从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树

根据前序结果去创建树,前序是根左右,前序第一个元素就是根,在通过中序去进行分割左右子树。子树区间确认是否继续递归创建子树,区间不存在则是空树。所以根据前序先构造根,在通过中序构造左子树、在构造右子树即可。
class Solution {
TreeNode* _buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder,int&prei,int inbegin,int inend)
{
if(inbegin>inend)
{
return nullptr;
}
TreeNode*root = new TreeNode(preorder[prei]);
int rooti = inbegin;
while(inbegin<=inend)
{
if(preorder[prei] == inorder[rooti])
{
break;
}
else rooti++;
}
prei++;
//[inbegin,rooti-1]rooti[rooti+1,inend]
root->left= _buildTree(preorder,inorder,prei,inbegin,rooti-1);
root->right = _buildTree(preorder,inorder,prei,rooti+1,inend);
return root;
}
public:
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {
int prei = 0;
return _buildTree(preorder,inorder,prei,0,inorder.size()-1);
}
};
传引用问题:因为prei是遍历前序数组开始的下标,整个递归遍历中都要使用,所以我们需要传引用。如果不是传引用而是传值的话,左子树构建好返回,如果此时prei不是传引用,只是形参,无法将上一次递归的结果保留下来,那么也就无构建右子树了。
从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
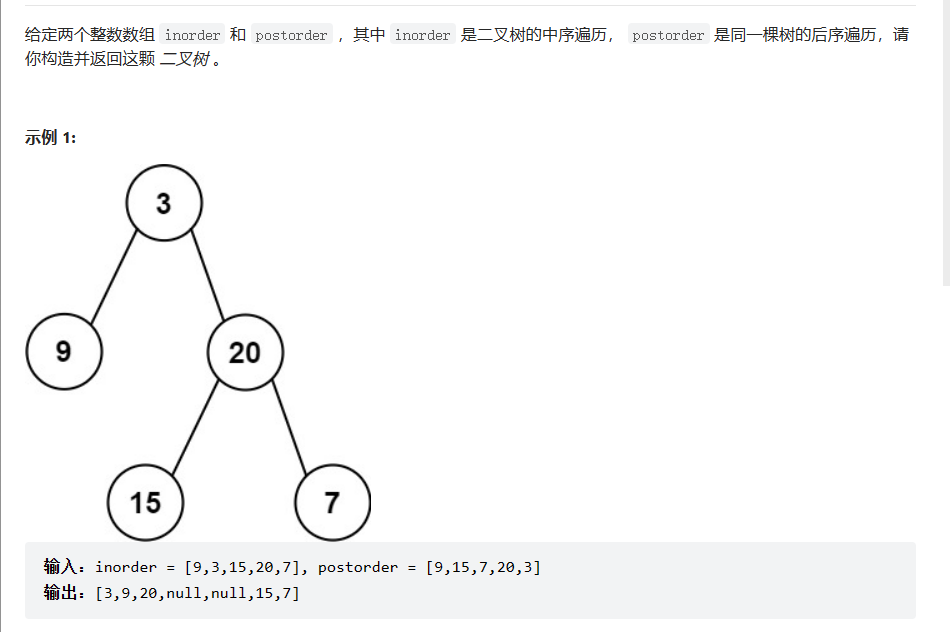
根据后序遍历的最后一个元素可以确定根结点,有了根结点做为切割点然后再去根据中序遍历划分左右区间,在继续下去,构造成二叉树,区间不存在就是空树了。同时,后序遍历是左右根,所以最后一个是根节点。所以当我们构造根结点后,由于前面是右子树,所以先构造右子树,在构造左子数。
class Solution {
TreeNode* _buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder,int &posi,int inbegin,int inend)
{
if(inbegin>inend)
{
return nullptr;
}
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(postorder[posi]);
int rooti = inbegin;
while(inbegin<=inend)
{
if(postorder[posi] == inorder[rooti])
{
break;
}
else rooti++;
}
posi--;
//[inbegin,rooti-1]rooti[rooti+1,inend];
root->right = _buildTree(inorder,postorder,posi,rooti+1,inend);
root->left = _buildTree(inorder,postorder,posi,inbegin,rooti-1);
return root;
}
public:
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {
int posi = postorder.size()-1;
return _buildTree(inorder,postorder,posi,0,inorder.size()-1);
}
};


