一、黑客攻击就像半夜的小偷
你以为服务器很安全?防火墙开着、密码复杂、IP隐藏…但某天深夜,服务器突然卡死,CPU直接拉满——黑客早就进来转了一圈,而你却毫不知情!
“不是没防护,是压根没发现!”
入侵检测(IDS)就是你的"24小时保安",能在黑客搞破坏前及时拉响警报。今天我们就用国产CTyunOS,教你搭建简单又高效的防护系统。
二、CTyunOS:国产系统的安全王牌
CTyunOS是中国电信推出的企业级操作系统,政府、银行、大厂都在用。它自带"铜墙铁壁":
- 内核级防护
- 智能权限管理
- 自动安全加固
但再好的锁也怕"钥匙"出问题(比如员工手滑输错命令,或者有人故意使坏)。
别担心!CTyunOS内置三大安全法宝:
✔️ 全流程监控:记录所有可疑操作
✔️ 文件保镖:核心文件被改立即告警
✔️ 日志审计:记录所有正常和异常行为
三、CTyunOS上的入侵检测手段有哪些?
要想在 CTyunOS上做好入侵检测,我们可以从以下二层入手:
1️⃣ 系统日志审计:用 auditd 抓行为日志
Linux 内核的审计子系统 auditd,可以记录文件访问、系统调用、用户行为等详细操作日志,是判断是否被“入侵”的关键证据源。
2️⃣ 实时行为监控:用 aide 监控文件被篡改
AIDE(Advanced Intrusion Detection Environment)可定期对系统关键文件、配置、权限等进行“快照”,并进行对比,一旦发现篡改,立马报警。
四、实战演练:在 CTyunOS上部署文件完整性检测
这里我们以 aide 为例,看看如何在 CTyunOS上实现最基础的入侵检测——文件完整性检测。
安装命令:
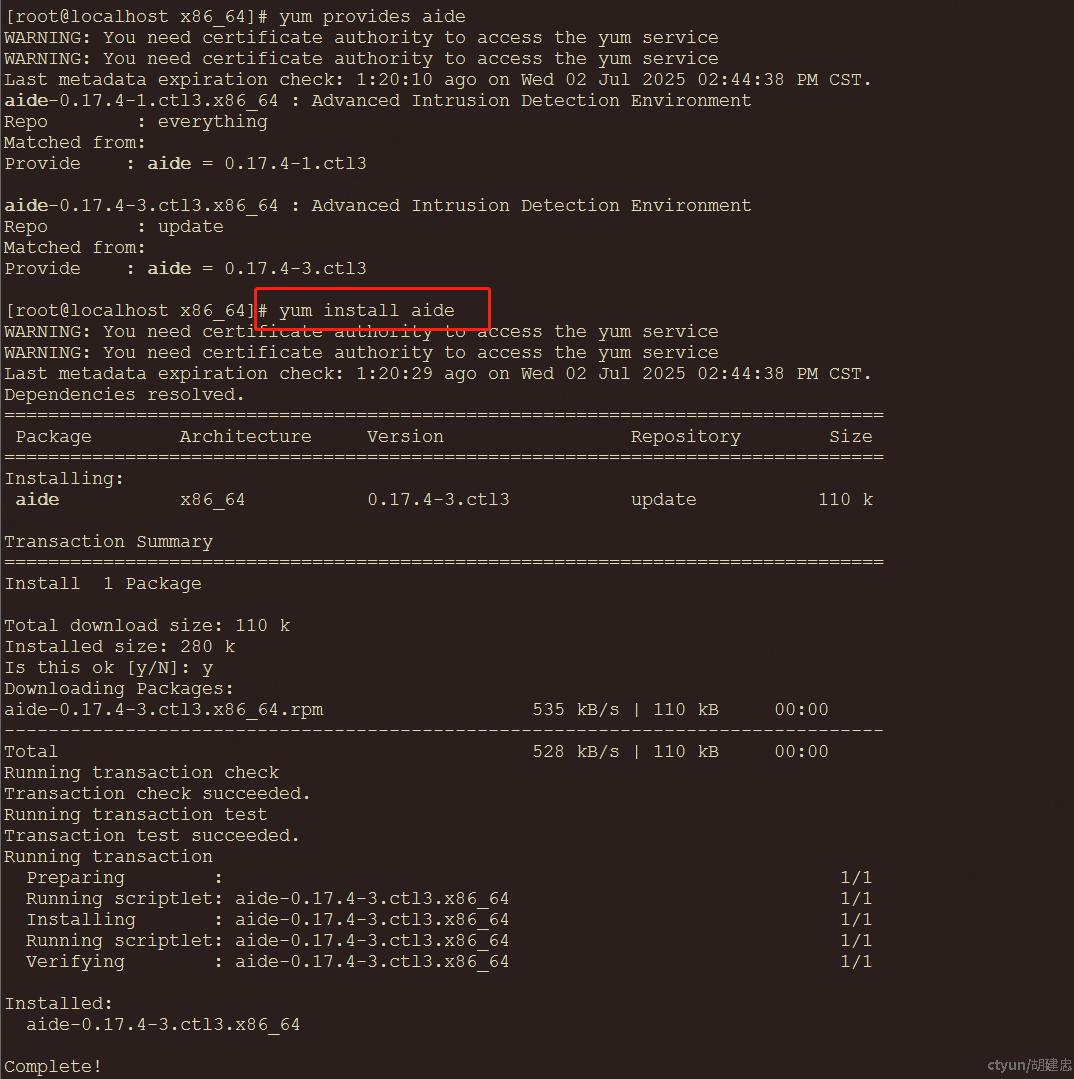
初始化数据库(生成基准快照):
aide --init
mv /var/lib/aide/aide.db.new.gz /var/lib/aide/aide.db.gz
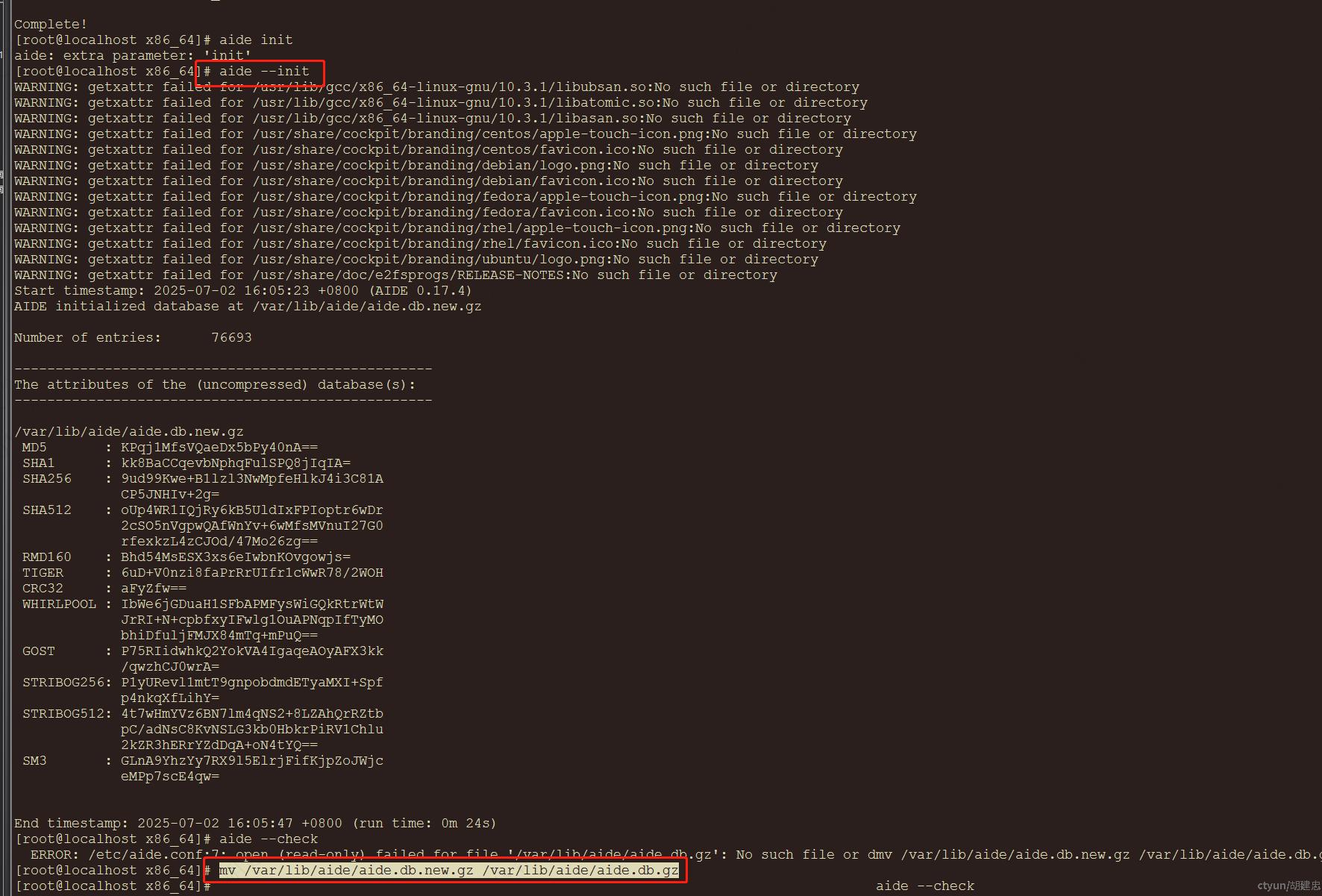
配置规则(默认配置为/etc/aide.conf,可自定义监控路径):
/etc/aide.conf
# 示例规则
/etc FIPSR
/bin FIPSR
/usr/sbin FIPSR
/boot NORMAL
/bin NORMAL规则解释:
NORMAL是AIDE默认提供的检测规则组合,通常包含以下文件属性的检查:
- 基础属性:权限(p)、索引节点(i)、链接数(n)、用户(u)、用户组(g)、文件大小(s)
- 时间戳:修改时间(m)、创建时间(c)
- 安全上下文:SELinux上下文(selinux)
- 校验值:使用MD5(md5)或SHA1(sha1)等算法生成的文件哈希值
- F:文件类型
- I:inode变化
- P:权限
- S:文件大小
- R:修改时间
DATA:仅检查文件内容(如哈希值),忽略属性变化,适用于日志等频繁变动的文件。
DIR:专用于目录的规则,侧重权限和结构。
LSPP:更严格的规则,包含ACL和扩展属性(xattrs)
定期执行检测(建议写入crontab):
aide --check输出报告样式:
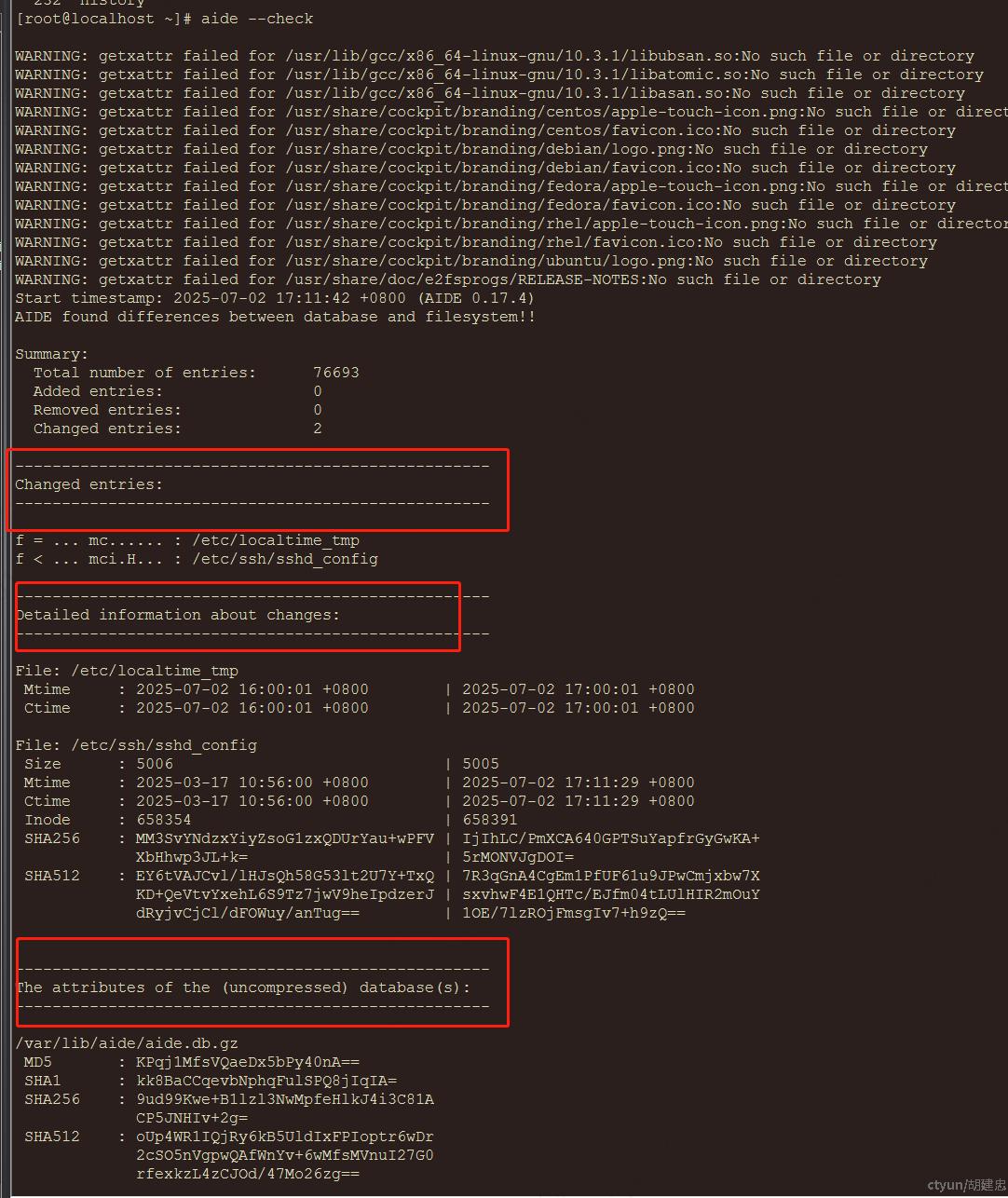
从这份清单你可以看出:哪怕你没被黑,这份清单也能提醒你哪些配置被误删、文件被改动。
附件:
/etc/aide.conf详细配置
/etc/aide.conf
[root@localhost x86_64]# cat /etc/aide.conf
# Example configuration file for AIDE.
@@define DBDIR /var/lib/aide
@@define LOGDIR /var/log/aide
# The location of the database to be read.
database_in=file:@@{DBDIR}/aide.db.gz
# The location of the database to be written.
database_out=file:@@{DBDIR}/aide.db.new.gz
# Whether to gzip the output to database
gzip_dbout=yes
# Default.
log_level=warning
report_url=file:@@{LOGDIR}/aide.log
report_url=stdout
FIPSR = p+i+n+u+g+s+m+c+acl+selinux+xattrs+sha256
# You can create custom rules like this.
ALLXTRAHASHES = sha1+rmd160+sha256+sha512+tiger
# Everything but access time (Ie. all changes)
EVERYTHING = R+ALLXTRAHASHES
# Sane, with multiple hashes
NORMAL = FIPSR+sha512
# For directories, don't bother doing hashes
DIR = p+i+n+u+g+acl+selinux+xattrs
# Access control only
PERMS = p+i+u+g+acl+selinux
# Logfile are special, in that they often change
LOG = >
# Just do sha256 and sha512 hashes
LSPP = FIPSR+sha512
# Some files get updated automatically, so the inode/ctime/mtime change
# but we want to know when the data inside them changes
DATAONLY = p+n+u+g+s+acl+selinux+xattrs+sha256
# Next decide what directories/files you want in the database.
/boot NORMAL
/bin NORMAL
/sbin NORMAL
/lib NORMAL
/lib64 NORMAL
/opt NORMAL
/usr NORMAL
/root NORMAL
# These are too volatile
!/usr/src
!/usr/tmp
# Check only permissions, inode, user and group for /etc, but
# cover some important files closely.
/etc PERMS
!/etc/mtab
# Ignore backup files
!/etc/.*~
/etc/exports NORMAL
/etc/fstab NORMAL
/etc/passwd NORMAL
/etc/group NORMAL
/etc/gshadow NORMAL
/etc/shadow NORMAL
/etc/security/opasswd NORMAL
/etc/hosts.allow NORMAL
/etc/hosts.deny NORMAL
/etc/sudoers NORMAL
/etc/skel NORMAL
/etc/logrotate.d NORMAL
/etc/resolv.conf DATAONLY
/etc/nscd.conf NORMAL
/etc/securetty NORMAL
# Shell/X starting files
/etc/profile NORMAL
/etc/bashrc NORMAL
/etc/bash_completion.d/ NORMAL
/etc/login.defs NORMAL
/etc/zprofile NORMAL
/etc/zshrc NORMAL
/etc/zlogin NORMAL
/etc/zlogout NORMAL
/etc/profile.d/ NORMAL
/etc/X11/ NORMAL
# Pkg manager
/etc/yum.conf NORMAL
/etc/yumex.conf NORMAL
/etc/yumex.profiles.conf NORMAL
/etc/yum/ NORMAL
/etc/yum.repos.d/ NORMAL
/var/log LOG
/var/run/utmp LOG
# This gets new/removes-old filenames daily
!/var/log/sa
# As we are checking it, we've truncated yesterdays size to zero.
!/var/log/aide.log
# LSPP rules...
# AIDE produces an audit record, so this becomes perpetual motion.
/etc/audit/ LSPP
/etc/libaudit.conf LSPP
/usr/sbin/stunnel LSPP
/var/spool/at LSPP
/etc/at.allow LSPP
/etc/at.deny LSPP
/etc/cron.allow LSPP
/etc/cron.deny LSPP
/etc/cron.d/ LSPP
/etc/cron.daily/ LSPP
/etc/cron.hourly/ LSPP
/etc/cron.monthly/ LSPP
/etc/cron.weekly/ LSPP
/etc/crontab LSPP
/var/spool/cron/root LSPP
/etc/login.defs LSPP
/etc/securetty LSPP
/var/log/faillog LSPP
/var/log/lastlog LSPP
/etc/hosts LSPP
/etc/sysconfig LSPP
/etc/inittab LSPP
/etc/grub/ LSPP
/etc/rc.d LSPP
/etc/ld.so.conf LSPP
/etc/localtime LSPP
/etc/sysctl.conf LSPP
/etc/modprobe.conf LSPP
/etc/pam.d LSPP
/etc/security LSPP
/etc/aliases LSPP
/etc/postfix LSPP
/etc/ssh/sshd_config LSPP
/etc/ssh/ssh_config LSPP
/etc/stunnel LSPP
/etc/vsftpd.ftpusers LSPP
/etc/vsftpd LSPP
/etc/issue LSPP
/etc/issue.net LSPP
/etc/cups LSPP
# Ditto /var/log/sa reason...
!/var/log/and-httpd
# Admins dot files constantly change, just check perms
/root/\..* PERMS