一、哈希表的模拟实现(开散列)
1. 开散列的概念
开散列又叫链地址法(开链法),首先对关键码集合用散列函数计算散列地址,即 key 映射的下标位置,具有相同地址的关键码 (哈希冲突) 归于同一子集合,每一个子集合称为一个桶 (哈希桶),各个桶中的元素通过一个单链表链接起来,各链表的头结点存储在哈希表中;也就是说,当发生哈希冲突时,把 key 作为一个节点直接链接到下标位置的哈希桶中。
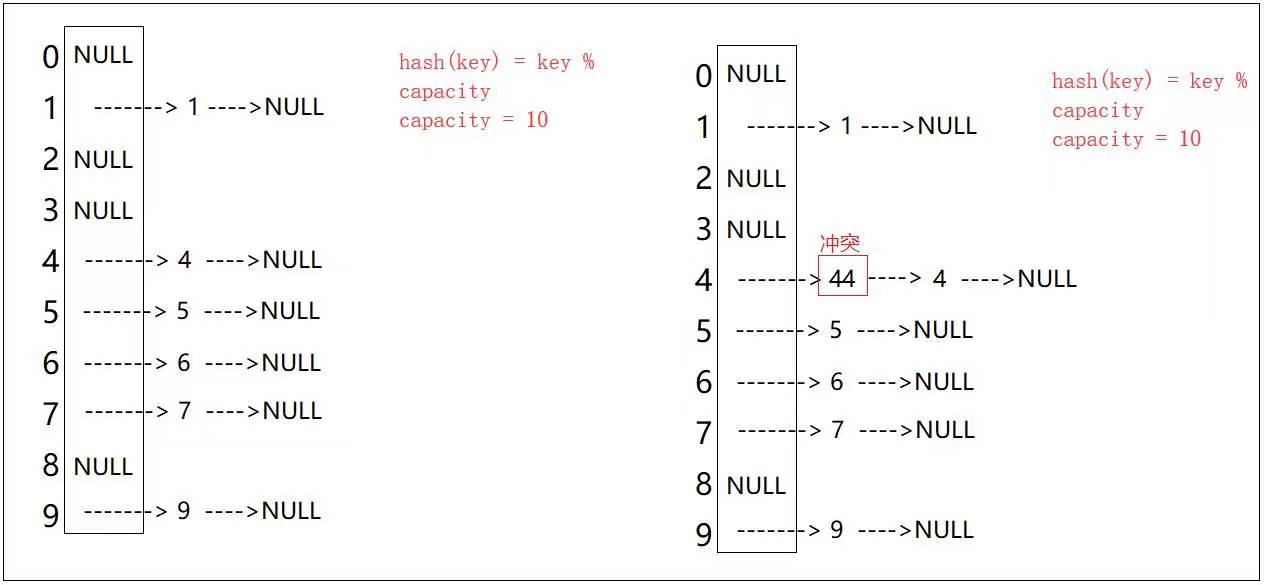
在这里我们可以看到,开散列中每个桶中放的都是发生哈希冲突的元素;由于开散列的不同冲突之间不会互相影响——同一冲突都链接在自己下标位置的哈希桶中,并不会去占用别人的下标位置;所以不管是在插入还是在查找方面,开散列都比闭散列要高效,所以C++STL中的unordered_map和unordered_set容器以及Java中的HashMap和HashSet容器的底层哈希表都是使用开散列来实现的,只是某些细节方面有些不同罢了,所以开散列也是我们学习哈希表的重点。
2. 开散列的节点结构
由于开散列的不同冲突之间不会互相影响,所以开散列不再需要 state 变量来记录每个下表位置的状态;同时,因为开散列每个下标位置链接的都是一个哈希桶,所以 vector 中的每个元素都是一个节点的指针,指向单链表的第一个元素,所以 _tables 是一个指针数组;最后,为了是不同类型的 key 都能够计算出映射的下标位置,所以我们这里也需要传递仿函数;如下:
template<class K,class V>
struct HashNode
{
pair<K, V> _kv;
HashNode<K, V>* _next;
HashNode(const pair<K,V>& kv)
:_kv(kv)
,_next(nullptr)
{}
};
//哈希表的仿函数
template<class K>
struct HashFunc
{
size_t operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
//类模板的特化
template<>
struct HashFunc<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string& key)
{
size_t sum = 0;
for (auto ch : key)
sum = sum * 131 + ch;
return sum;
}
};
template<class K,class V,class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class HashTable
{
typedef HashNode<K, V> Node;
private:
vector<Node*> _tables; //指针数组
size_t _n = 0; //有效存储的数据个数
};
3. 开散列的插入删除与查找
💕 开散列的插入
开散列的插入的前半部分和闭散列一样,根据key与哈希表大小得到映射的下标位置,与闭散列不同的是,由于哈希表中每个下标位置都是一个哈希桶,即一个单链表,所以对于发现哈希冲突的元素我们只需要将其链接到哈希桶中即可,这里一共有两种链接方式:
- 将发生冲突的元素链接到单链表的末尾,即尾插
- 将发生冲突的元素链接到单链表的开头,即头插
在这里我们还需要考虑一下开散列的扩容问题。
由于开散列桶的个数是一定的,即哈希表的长度,所以随着元素的不断插入,每个桶中元素的个数会不断增多;那么在极端情况下,可能会导致一个桶中链表的节点非常多,这样会影响哈希表的性能 – 查找与删除效率变低,因此在一定条件下需要对哈希表进行增容;
那么增容条件该怎么确认呢?开散列最好的情况是每个哈希桶中刚好挂一个节点,再继续插入元素时,每一次都会发生哈希冲突;因此,在元素个数刚好等于桶的个数时,可以给考虑哈希表增容,即载荷因子为1时。
这里我们给出了两种扩容的办法:
一种是闭散列的方法 – 通过复用 insert 函数接口来进行扩容,但是这种扩容方法的效率很低,因为我们将旧表节点插入到新表时需要重新开辟节点,在插入并交换完毕后,我们又需要释放掉旧表中的节点,而 new 和 delete 的代价是很大的,特别是当 KV 是自定义类型时;
所以这里我们选择第二组方法进行扩容 – 取出旧表中的每个节点链接到新表中,然后再交换旧表与新表;这样做就减少了 new 和 delete 的过程,大大提高了扩容的效率。(注:这里不能将原表中的整个哈希桶链接到新表中,因为新表的大小改变后原表中的元素可能会映射到新表的其他位置)
同时,开散列的析构函数是需要我们自己实现的,因为默认生成的析构函数并不会释放掉哈希桶。
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
if (Find(kv.first))
return false;
Hash hash;
//负载因子 == 1时扩容
if (_n == _tables.size())
{
//这种方法不太好,一个一个的插入,会导致效率及其低下,而且还需要释放掉原来的节点
/*size_t newsize = _tables.size() == 0 ? 10 : _tables.size() * 2;
HashTable<K,V> newht;
newht._tables.resize(newsize);
for (auto cur : _tables)
{
while (cur)
{
newht.Insert(cur->_kv);
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
_tables.swap(newht._tables);*/
size_t newsize = _tables.size() == 0 ? 10 : _tables.size() * 2;
vector<Node*>newtables(newsize, nullptr);
for (auto& cur : _tables)
{
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
size_t hashi = hash(cur->_kv.first) % newtables.size();
//头插到新表
cur->_next = newtables[hashi];
newtables[hashi] = cur;
cur = next;
}
}
_tables.swap(newtables);
}
size_t hashi = hash(kv.first) % _tables.size();
//头插
Node* newnode = new Node(kv);
newnode->_next = _tables[hashi];
_tables[hashi] = newnode;
++_n;
return true;
}
💕 开散列的查找
先根据余数找到下标,由于下标位置存储的是首元素的地址,所以我们只需要取出首元素的地址,然后遍历单链表查找即可。
//查询
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
if (_tables.size() == 0)
return nullptr;
Hash hash;
size_t hashi = hash(key) % _tables.size();
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first == key)
return cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
return nullptr;
}
💕 开散列的删除
开散列的删除不能直接通过查找函数的返回值来进行删除,因为单链表在删除结点的时候还需要改变父节点的指向,让其指向目标节点的下一个节点,所以我们通过遍历单链表的方式来进行删除。
//删除
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Hash hash;
size_t hashi = hash(key) % _tables.size();
Node* prev = nullptr;
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first == key)
{
if (prev == nullptr)
_tables[hashi] = cur->_next;
else
prev->_next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
return true;
}
else
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
return false;
}
4. 开散列整体代码实现
//开散列实现哈希表——拉链法
namespace HashBucket
{
template<class K,class V>
struct HashNode
{
pair<K, V> _kv;
HashNode<K, V>* _next;
HashNode(const pair<K,V>& kv)
:_kv(kv)
,_next(nullptr)
{}
};
//哈希表的仿函数
template<class K>
struct HashFunc
{
size_t operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
//类模板的特化
template<>
struct HashFunc<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string& key)
{
size_t sum = 0;
for (auto ch : key)
sum = sum * 131 + ch;
return sum;
}
};
template<class K,class V,class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class HashTable
{
typedef HashNode<K, V> Node;
public:
//插入
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
if (Find(kv.first))
return false;
Hash hash;
//负载因子 == 1时扩容
if (_n == _tables.size())
{
//这种方法不太好,一个一个的插入,会导致效率及其低下,而且还需要释放掉原来的节点
/*size_t newsize = _tables.size() == 0 ? 10 : _tables.size() * 2;
HashTable<K,V> newht;
newht._tables.resize(newsize);
for (auto cur : _tables)
{
while (cur)
{
newht.Insert(cur->_kv);
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
_tables.swap(newht._tables);*/
size_t newsize = _tables.size() == 0 ? 10 : _tables.size() * 2;
vector<Node*>newtables(newsize, nullptr);
for (auto& cur : _tables)
{
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
size_t hashi = hash(cur->_kv.first) % newtables.size();
//头插到新表
cur->_next = newtables[hashi];
newtables[hashi] = cur;
cur = next;
}
}
_tables.swap(newtables);
}
size_t hashi = hash(kv.first) % _tables.size();
//头插
Node* newnode = new Node(kv);
newnode->_next = _tables[hashi];
_tables[hashi] = newnode;
++_n;
return true;
}
//查询
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
if (_tables.size() == 0)
return nullptr;
Hash hash;
size_t hashi = hash(key) % _tables.size();
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first == key)
return cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
return nullptr;
}
//删除
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Hash hash;
size_t hashi = hash(key) % _tables.size();
Node* prev = nullptr;
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first == key)
{
if (prev == nullptr)
_tables[hashi] = cur->_next;
else
prev->_next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
return true;
}
else
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
return false;
}
private:
vector<Node*> _tables; //指针数组
size_t _n = 0; //有效存储的数据个数
};
void TestHashTable1()
{
int a[] = { 3, 33, 2, 13, 5, 12, 1002 };
HashTable<int, int> ht;
for (auto e : a)
{
ht.Insert(make_pair(e, e));
}
ht.Insert(make_pair(15, 15));
ht.Insert(make_pair(25, 25));
ht.Insert(make_pair(35, 35));
ht.Insert(make_pair(45, 45));
}
void TestHashTable2()
{
int a[] = { 3, 33, 2, 13, 5, 12, 1002 };
HashTable<int, int> ht;
for (auto e : a)
{
ht.Insert(make_pair(e, e));
}
ht.Erase(12);
ht.Erase(3);
ht.Erase(33);
}
}
这里还存在一个问题,在我们上面的实现中,哈希桶是一个单链表,并且当哈希表的载荷因子等于1时,我们就进行扩容,这样在大多数情况下,每个哈希桶中的节点数都在1~2个,最坏情况下应该也不会超过 3~5 节点;这样我们查找时每次经过常数次查找就能够找到,即查找效率为 O(1);
但是在某些极端情况下,或者面对某些碰撞攻击时 (对方如果知道了你哈希表的长度即除数,可能会专门向你传递属于同一冲突的数据,比如全部为哈希表长度的倍数),那么就会导致单链表过长,从而降低哈希表的查询与删除效率;
为了应对这种情况,在 Java 8 中,如果一个桶中元素的数量超过了阈值,就会将其转换为红黑树,红黑树可以保证查找、插入和删除操作的时间复杂度都是 O(log n),比链表快得多,而对于较小的桶,仍然使用链表来存储元素;即 Java 8 中的 HashMap 使用红黑树来优化哈希冲突的极端情况,从而提高了 HashMap 的性能和效率。
同样,C++11 也引入了一个新的数据结构 – 开放定址哈希表 (open addressing hash table),用于存储哈希冲突时的元素;开放定址哈希表是一种不使用链表来解决冲突的哈希表实现方式。在这种实现方式中,如果一个槽(slot)已经被占据了,就会尝试找到下一个可用的槽,直到找到一个空槽。因此,开放定址哈希表可以更好地利用缓存,从而提高查找性能。
也就是说,在 C++11 及以后的版本中,unordered_map 的哈希桶使用了两种不同的数据结构,包括单链表和开放定址哈希表 – 当桶中元素数量较少时,使用链表;当桶中元素数量超过一定阈值时,会自动转换为开放定址哈希表。
二、unordered系列容器的封装实现(开散列)
1. 迭代器
哈希表也需要单独定义一个类来实现迭代器,不过由于哈希表的迭代器是单向的,所以我们不用实现 operator–();其中,哈希表的 begin() 为第一个哈希桶中的第一个节点,即哈希表中第一个非空位置的数据,哈希表的 end() 这里我们定义为 nullptr;
哈希表迭代器实现的难点在于 operator++,哈希表的迭代器 ++ 分为两种情况:
- 当前哈希桶的下面还有节点,说明当前下标位置的哈希桶还没遍历完,此时迭代器++到当前哈希桶的下一个节点;
- 当前哈希桶的下面没有节点,即cur->next==nullptr,说明当前下标位置的哈希桶已经遍历完了,此时迭代器++到哈希表的下一个非空位置,即下一个哈希桶。
因为我们需要访问哈希表的_tables数组来确定下一个哈希桶的位置,所以要在迭代器类中定义一个HashTable类型的指针变量,同时,由于_tables是HashTable类的私有成员,所以我们还必须将HashTable类中将_HashTableIterator类声明为友元类,这样我们才能正确实现迭代器++的功能。
💕 注意
- 由于我们在迭代器类中增加了一个哈希表的指针变量_ht,所以我们在HashTable中定义 begin() 和 end() 时除了要传递节点的指针来初始化_node,还需要传递this指针来初始化 _ht。
- 由于迭代器类中要定义HashTable类型的指针变量,同时HashTable类中又要typedef迭代器类型作为迭代器,所以在这里就存在相互引用的问题,为了解决这个问题,我们需要在迭代器类前面声明一下HashTable类。
代码实现:
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class Hash>
class HashTable;
template<class K, class T, class Ref, class Ptr, class KeyOfT, class Hash>
struct __HashIterator
{
typedef HashNode<T> Node;
typedef __HashIterator<K, T, Ref, Ptr, KeyOfT, Hash> Self;
typedef HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, Hash> HT;
typedef __HashIterator<K, T, T&, T*, KeyOfT, Hash> Iterator;
__HashIterator(Node* node, const HT* ht)
:_node(node)
,_ht(ht)
{}
__HashIterator(const Iterator& it)
:_node(it._node)
, _ht(it._ht)
{}
//重载 *
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
//重载 ->
Ptr operator->()
{
return &(_node->_data);
}
//重载 !=
bool operator!=(const Self& s)
{
return _node != s._node;
}
//重载 ++it
Self& operator++()
{
//判断下一个节点是否为nullptr
if (_node->_next)
{
_node = _node->_next;
}
else
{
KeyOfT kot;
Hash hash;
//寻找下一个节点不为空的桶
size_t hashi = hash(kot(_node->_data)) % _ht->_tables.size();
hashi++;
while (hashi < _ht->_tables.size())
{
if (_ht->_tables[hashi]) {
_node = _ht->_tables[hashi];
break;
}
else
{
hashi++;
}
}
if (hashi == _ht->_tables.size())
_node = nullptr;
return *this;
}
}
Node* _node;
const HT* _ht;
};
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class Hash>
class HashTable
{
template<class K, class T, class Ref, class Ptr, class KeyOfT, class Hash>
friend struct __HashIterator;
typedef HashNode<T> Node;
public:
//迭代器的实现
typedef __HashIterator<K, T, T&, T*, KeyOfT, Hash> iterator;
typedef __HashIterator<K, T, const T&, const T*, KeyOfT, Hash> const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
Node* cur = nullptr;
for (auto& node : _tables)
{
cur = node;
if (cur)
break;
}
return iterator(cur, this);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(nullptr, this);
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
Node* cur = nullptr;
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)
{
cur = _tables[i];
if (cur)
{
break;
}
}
return const_iterator(cur, this);
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return const_iterator(nullptr, this);
}
private:
vector<Node*> _tables; //指针数组
size_t _n = 0; //有效存储的数据个数
}
在哈希表中,我们继续使用增加模板参数Ref和Ptr来解决const迭代器问题。这里我们和前面的红黑树一样,使用哈希表迭代器类中构造函数来实现用普通迭代器来构造 const迭代器。
typedef __HashIterator<K, T, T&, T*, KeyOfT, Hash> Iterator;
__HashIterator(const Iterator& it)
:_node(it._node)
, _ht(it._ht)
{}
2. unordered_set和unordered_map的封装实现
-
为了使哈希表能够同时封装 KV模型的 unordered_map 和 K模型的 unordered_set,哈希表不能将节点的数据类型直接定义为 pair< K, V >,而是需要通过参数 T 来确定;同时,由于 insert 函数在求余数时需要取出 T 中的 key 转化为整形,所以上层的 unordered_map 和 unordered_set 需要定义一个仿函数 MapKeyOfT 和 SetKeyOfT 来获取 key (主要是为了 unordered_map 而设计);
-
为了保证 unordered_set 的 key 值不被修改,我们需要使用 哈希表 的 const 迭代器来封装 unordered_set 的普通迭代器,但是这样会导致哈希表的普通迭代器赋值给 const 迭代器的问题,所以我们需要将 unordered_set 的 begin() 和 end() 函数都定义为 const 成员函数;
-
因为 unordered_map 的 operator 函数兼具插入、查找、和修改功能,所以如果我们要在模拟实现的 unordered_map 中重载 [] 运算符,就需要将 find 函数的返回值改为 iterator,将 insert 函数的返回值改为 pair\u003Citerator, bool>,并且要改的话 哈希表、unordered_map、unordered_set 这三个地方都要改。
同时,unordered_set insert 函数的返回值变为 pair<iterator, bool> 后又会引发普通迭代器赋值给 const 迭代器的问题,所以对于 unordered_set 的 insert 函数,我们要先使用哈希表的普通迭代器构造的键值对去完成插入操作,然后再利用 普通迭代器来构造 const 迭代器进行返回;
而要用普通迭代器构造 const 迭代器,我们又需要在哈希表的 const 迭代器类中增加一个类似于拷贝构造的函数,来将普通迭代器构造为 const 迭代器进行返回;
💕 UnorderedSet
//UnorderedSet
#pragma once
#include"HashTable.h"
namespace cjl
{
template<class K,class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class unordered_set
{
public:
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
typedef typename HashBucket::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT, Hash>::const_iterator iterator;
typedef typename HashBucket::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT, Hash>::const_iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _ht.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _ht.end();
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _ht.begin();
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _ht.end();
}
pair<iterator,bool> insert(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Insert(key);
}
iterator find(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Find(key);
}
bool erase(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Erase(key);
}
private:
HashBucket::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT, Hash> _ht;
};
void test_unordered_set1()
{
int a[] = { 3, 33, 2, 13, 5, 12, 1002 };
unordered_set<int> s;
for (auto e : a)
{
s.insert(e);
}
unordered_set<int>::iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
//*it = 2;
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_unordered_set2()
{
int a[] = { 3, 33, 2, 13, 5, 12, 1002 };
unordered_set<int> s;
for (auto e : a)
{
s.insert(e);
}
s.insert(54);
s.insert(107);
unordered_set<int>::iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
s.erase(54);
s.erase(107);
for (auto e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
auto it2 = s.find(1002);
if (it2 != s.end())
cout << "找到了" << endl;
else
cout << "没找到" << endl;
}
}
💕 UnorderedMap
#pragma once
#include"HashTable.h"
namespace cjl
{
template<class K, class V, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class unordered_map
{
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
typedef typename HashBucket::HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT, Hash>::iterator iterator;
typedef typename HashBucket::HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT, Hash>::const_iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _ht.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _ht.end();
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _ht.begin();
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _ht.end();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return _ht.Insert(kv);
}
iterator find(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Find(key);
}
bool erase(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Erase(key);
}
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert({ key,V() });
return ret.first->second;
}
private:
HashBucket::HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT, Hash> _ht;
};
}
UnorderedMap测试代码
namespace cjl
{
void test_unordered_map1()
{
int a[] = { 3, 33, 2, 13, 5, 12, 1002 };
unordered_map<int,int> s;
for (auto e : a)
{
s.insert({ e, e });
}
unordered_map<int, int>::iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_unordered_map2()
{
string arr[] = { "西瓜", "西瓜", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "香蕉", "苹果", "香蕉", "梨" };
unordered_map<string, int> countMap;
for (auto& e : arr)
{
countMap[e]++;
}
for (auto& kv : countMap)
{
cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
auto it = countMap.find("西瓜");
if (it != countMap.end())
cout << "找到了:" << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;
else
cout << "没找到" << endl;
countMap.erase("西瓜");
it = countMap.find("西瓜");
if (it != countMap.end())
cout << "找到了:" << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;
else
cout << "没找到" << endl;
}
class Date
{
friend struct HashDate;
public:
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
: _year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{}
bool operator<(const Date& d)const
{
return (_year < d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month < d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day);
}
bool operator>(const Date& d)const
{
return (_year > d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month > d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day);
}
bool operator==(const Date& d) const
{
return _year == d._year
&& _month == d._month
&& _day == d._day;
}
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const Date& d);
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const Date& d)
{
_cout << d._year << "-" << d._month << "-" << d._day;
return _cout;
}
struct HashDate
{
size_t operator()(const Date& d)
{
size_t hash = 0;
hash += d._year;
hash *= 31;
hash += d._month;
hash *= 31;
hash += d._day;
hash *= 31;
return hash;
}
};
void test_unordered_map3()
{
Date d1(2023, 3, 13);
Date d2(2023, 3, 13);
Date d3(2023, 3, 12);
Date d4(2023, 3, 11);
Date d5(2023, 3, 12);
Date d6(2023, 3, 13);
Date a[] = { d1, d2, d3, d4, d5, d6 };
unordered_map<Date, int, HashDate> countMap;
for (auto e : a)
{
countMap[e]++;
}
for (auto& kv : countMap)
{
cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
countMap.erase(d4);
for (auto& kv : countMap)
{
cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;
}
}
}
3. 哈希表整体源码
#pragma once
template<class K>
struct HashFunc
{
size_t operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
//模板的特化
template<>
struct HashFunc<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string& str)
{
size_t hash = 0;
for (auto e : str)
{
hash += e;
hash *= 31;
}
return hash;
}
};
namespace HashBucket
{
template<class T>
struct HashNode
{
T _data;
HashNode<T>* _next;
HashNode(const T& data)
:_data(data)
,_next(nullptr)
{}
};
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class Hash>
class HashTable;
template<class K, class T, class Ref, class Ptr, class KeyOfT, class Hash>
struct __HashIterator
{
typedef HashNode<T> Node;
typedef __HashIterator<K, T, Ref, Ptr, KeyOfT, Hash> Self;
typedef HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, Hash> HT;
typedef __HashIterator<K, T, T&, T*, KeyOfT, Hash> Iterator;
__HashIterator(Node* node, const HT* ht)
:_node(node)
,_ht(ht)
{}
__HashIterator(const Iterator& it)
:_node(it._node)
, _ht(it._ht)
{}
//重载 *
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
//重载 ->
Ptr operator->()
{
return &(_node->_data);
}
//重载 !=
bool operator!=(const Self& s)
{
return _node != s._node;
}
//重载 ++it
Self& operator++()
{
//判断下一个节点是否为nullptr
if (_node->_next)
{
_node = _node->_next;
}
else
{
KeyOfT kot;
Hash hash;
//寻找下一个节点不为空的桶
size_t hashi = hash(kot(_node->_data)) % _ht->_tables.size();
hashi++;
while (hashi < _ht->_tables.size())
{
if (_ht->_tables[hashi]) {
_node = _ht->_tables[hashi];
break;
}
else
{
hashi++;
}
}
if (hashi == _ht->_tables.size())
_node = nullptr;
return *this;
}
}
Node* _node;
const HT* _ht;
};
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class Hash>
class HashTable
{
template<class K, class T, class Ref, class Ptr, class KeyOfT, class Hash>
friend struct __HashIterator;
typedef HashNode<T> Node;
public:
//迭代器的实现
typedef __HashIterator<K, T, T&, T*, KeyOfT, Hash> iterator;
typedef __HashIterator<K, T, const T&, const T*, KeyOfT, Hash> const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
Node* cur = nullptr;
for (auto& node : _tables)
{
cur = node;
if (cur)
break;
}
return iterator(cur, this);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(nullptr, this);
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
Node* cur = nullptr;
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)
{
cur = _tables[i];
if (cur)
{
break;
}
}
return const_iterator(cur, this);
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return const_iterator(nullptr, this);
}
~HashTable()
{
for (auto& node : _tables)
{
while (node)
{
Node* next = node->_next;
delete node;
node = next;
}
node = nullptr;
}
}
//插入
pair<iterator,bool> Insert(const T& data)
{
KeyOfT kot;
Hash hash;
iterator it = Find(kot(data));
if (it != end())
return { it, false };
//负载因子 == 1时扩容
if (_n == _tables.size())
{
size_t newsize = _tables.size() == 0 ? 10 : _tables.size() * 2;
vector<Node*>newtables(newsize, nullptr);
for (auto& cur : _tables)
{
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
size_t hashi = hash(kot(cur->_data)) % newtables.size();
//头插到新表
cur->_next = newtables[hashi];
newtables[hashi] = cur;
cur = next;
}
}
_tables.swap(newtables);
}
size_t hashi = hash(kot(data)) % _tables.size();
//头插
Node* newnode = new Node(data);
newnode->_next = _tables[hashi];
_tables[hashi] = newnode;
++_n;
return { iterator(newnode,this), true };
}
//查询
iterator Find(const K& key)
{
if (_tables.size() == 0)
return end();
KeyOfT kot;
Hash hash;
size_t hashi = hash(key) % _tables.size();
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) == key)
return iterator(cur, this);
cur = cur->_next;
}
return end();
}
//删除
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
KeyOfT kot;
Hash hash;
size_t hashi = hash(key) % _tables.size();
Node* prev = nullptr;
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) == key)
{
if (prev == nullptr)
_tables[hashi] = cur->_next;
else
prev->_next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
_n--;
return true;
}
else
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
return false;
}
private:
vector<Node*> _tables; //指针数组
size_t _n = 0; //有效存储的数据个数
};
}

