我们在使用linux过程中经常和文件系统打交道,深入刨析文件系统后可以了解文件系统的设计很巧妙,本文就以linux ext2文件系统类型为例,说明一下内核是如何根据用户提供的路径来获取对应的数据结构,并找到最终的文件内容的过程。
用户的程序运行在用户态,向内核提供需要查找的路径信息。
通过系统调用,内核获取了用的路径名称,首先在root节点获取当前目录下的目录内容,然后依次获取对应目录信息,找到最终的目标文件。
在磁盘的管理数据结构中,磁盘的排列结果如下所示
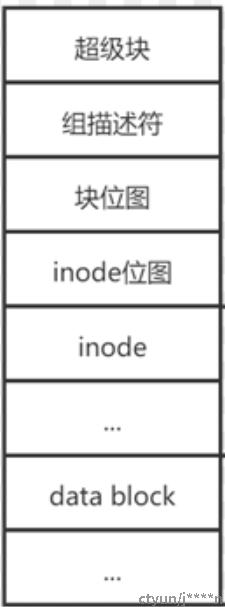
通过内核中的数据结构信息获取:
Ext2文件系统超级块数据结构如下:
struct ext2_super_block {
__le32 s_inodes_count; /* Inodes count */
__le32 s_blocks_count; /* Blocks count */
__le32 s_r_blocks_count; /* Reserved blocks count */
__le32 s_free_blocks_count; /* Free blocks count */
__le32 s_free_inodes_count; /* Free inodes count */
__le32 s_first_data_block; /* First Data Block */
__le32 s_log_block_size; /* Block size */
__le32 s_log_frag_size; /* Fragment size */
__le32 s_blocks_per_group; /* # Blocks per group */
__le32 s_frags_per_group; /* # Fragments per group */
__le32 s_inodes_per_group; /* # Inodes per group */
__le32 s_mtime; /* Mount time */
__le32 s_wtime; /* Write time */
__le16 s_mnt_count; /* Mount count */
__le16 s_max_mnt_count; /* Maximal mount count */
__le16 s_magic; /* Magic signature */
__le16 s_state; /* File system state */
__le16 s_errors; /* Behaviour when detecting errors */
__le16 s_minor_rev_level; /* minor revision level */
__le32 s_lastcheck; /* time of last check */
__le32 s_checkinterval; /* max. time between checks */
__le32 s_creator_os; /* OS */
__le32 s_rev_level; /* Revision level */
__le16 s_def_resuid; /* Default uid for reserved blocks */
__le16 s_def_resgid; /* Default gid for reserved blocks */
/*
* These fields are for EXT2_DYNAMIC_REV superblocks only.
*
* Note: the difference between the compatible feature set and
* the incompatible feature set is that if there is a bit set
* in the incompatible feature set that the kernel doesn't
* know about, it should refuse to mount the filesystem.
*
* e2fsck's requirements are more strict; if it doesn't know
* about a feature in either the compatible or incompatible
* feature set, it must abort and not try to meddle with
* things it doesn't understand...
*/
__le32 s_first_ino; /* First non-reserved inode */
__le16 s_inode_size; /* size of inode structure */
__le16 s_block_group_nr; /* block group # of this superblock */
__le32 s_feature_compat; /* compatible feature set */
__le32 s_feature_incompat; /* incompatible feature set */
__le32 s_feature_ro_compat; /* readonly-compatible feature set */
__u8 s_uuid[16]; /* 128-bit uuid for volume */
char s_volume_name[16]; /* volume name */
char s_last_mounted[64]; /* directory where last mounted */
__le32 s_algorithm_usage_bitmap; /* For compression */
/*
* Performance hints. Directory preallocation should only
* happen if the EXT2_COMPAT_PREALLOC flag is on.
*/
__u8 s_prealloc_blocks; /* Nr of blocks to try to preallocate*/
__u8 s_prealloc_dir_blocks; /* Nr to preallocate for dirs */
__u16 s_padding1;
/*
* Journaling support valid if EXT3_FEATURE_COMPAT_HAS_JOURNAL set.
*/
__u8 s_journal_uuid[16]; /* uuid of journal superblock */
__u32 s_journal_inum; /* inode number of journal file */
__u32 s_journal_dev; /* device number of journal file */
__u32 s_last_orphan; /* start of list of inodes to delete */
__u32 s_hash_seed[4]; /* HTREE hash seed */
__u8 s_def_hash_version; /* Default hash version to use */
__u8 s_reserved_char_pad;
__u16 s_reserved_word_pad;
__le32 s_default_mount_opts;
__le32 s_first_meta_bg; /* First metablock block group */
__u32 s_reserved[190]; /* Padding to the end of the block */
};
磁盘块组描述符数据结构:
struct ext2_group_desc
{
__le32 bg_block_bitmap; /* Blocks bitmap block */
__le32 bg_inode_bitmap; /* Inodes bitmap block */
__le32 bg_inode_table; /* Inodes table block */
__le16 bg_free_blocks_count; /* Free blocks count */
__le16 bg_free_inodes_count; /* Free inodes count */
__le16 bg_used_dirs_count; /* Directories count */
__le16 bg_pad;
__le32 bg_reserved[3];
};
两个数据结构对应磁盘管理结构的前两个数据块内容。数据位图和inode位图是通过bitmap的方式管理哪些block已经使用,用于快速找到空闲数据块。
Inode列表和数据块用于存储具体的inode数据内容和数据内容。
Inode内容使用ext2_inode数据结构表示,具体如下:
struct ext2_inode {
__le16 i_mode; /* File mode */
__le16 i_uid; /* Low 16 bits of Owner Uid */
__le32 i_size; /* Size in bytes */
__le32 i_atime; /* Access time */
__le32 i_ctime; /* Creation time */
__le32 i_mtime; /* Modification time */
__le32 i_dtime; /* Deletion Time */
__le16 i_gid; /* Low 16 bits of Group Id */
__le16 i_links_count; /* Links count */
__le32 i_blocks; /* Blocks count */
__le32 i_flags; /* File flags */
union {
struct {
__le32 l_i_reserved1;
} linux1;
struct {
__le32 h_i_translator;
} hurd1;
struct {
__le32 m_i_reserved1;
} masix1;
} osd1; /* OS dependent 1 */
__le32 i_block[EXT2_N_BLOCKS];/* Pointers to blocks */
__le32 i_generation; /* File version (for NFS) */
__le32 i_file_acl; /* File ACL */
__le32 i_dir_acl; /* Directory ACL */
__le32 i_faddr; /* Fragment address */
union {
struct {
__u8 l_i_frag; /* Fragment number */
__u8 l_i_fsize; /* Fragment size */
__u16 i_pad1;
__le16 l_i_uid_high; /* these 2 fields */
__le16 l_i_gid_high; /* were reserved2[0] */
__u32 l_i_reserved2;
} linux2;
struct {
__u8 h_i_frag; /* Fragment number */
__u8 h_i_fsize; /* Fragment size */
__le16 h_i_mode_high;
__le16 h_i_uid_high;
__le16 h_i_gid_high;
__le32 h_i_author;
} hurd2;
struct {
__u8 m_i_frag; /* Fragment number */
__u8 m_i_fsize; /* Fragment size */
__u16 m_pad1;
__u32 m_i_reserved2[2];
} masix2;
} osd2; /* OS dependent 2 */
};
Inode可以表示为具体的文件或者具体的目录,使用数据结构ext2_dir_entry_2来表示
struct ext2_dir_entry_2 {
__le32 inode; /* Inode number */
__le16 rec_len; /* Directory entry length */
__u8 name_len; /* Name length */
__u8 file_type;
char name[]; /* File name, up to EXT2_NAME_LEN */
};
其中file_type表示具体的类型如下所示:
/*
* Ext2 directory file types. Only the low 3 bits are used. The
* other bits are reserved for now.
*/
enum {
EXT2_FT_UNKNOWN = 0,
EXT2_FT_REG_FILE = 1,
EXT2_FT_DIR = 2,
EXT2_FT_CHRDEV = 3,
EXT2_FT_BLKDEV = 4,
EXT2_FT_FIFO = 5,
EXT2_FT_SOCK = 6,
EXT2_FT_SYMLINK = 7,
EXT2_FT_MAX
};
下面通过具体例子来说明具体的查找过程:
首先我们创建一个ext2的磁盘
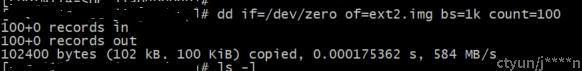
然后把磁盘格式化成ext2文件系统类型
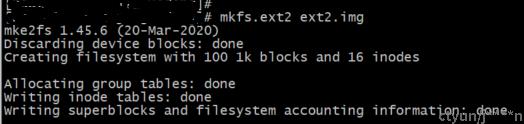
通过命令查看创建的ext2文件系统基本信息:
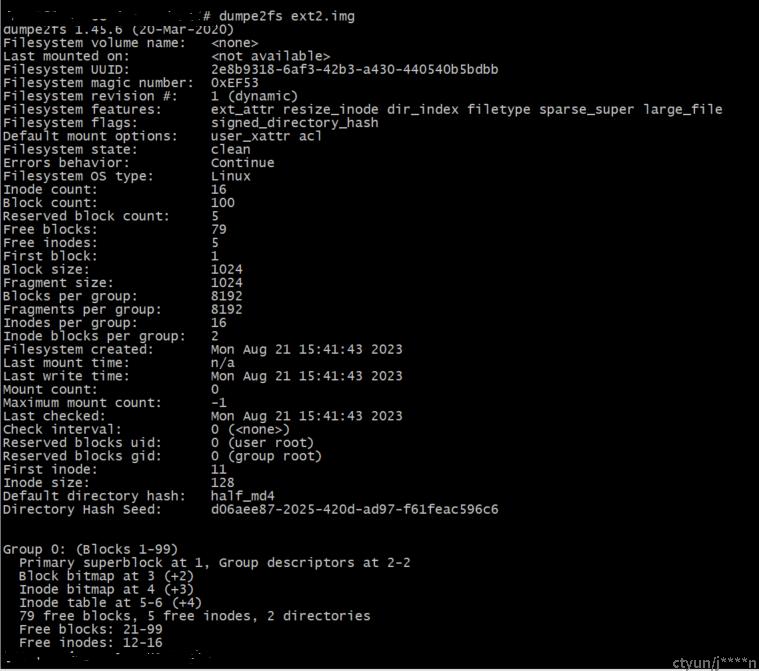
Filesystem magic number:
0xEF53 表示为ext2文件系统
Inode count: 16 表示文件系统inode个数为16
Block count: 100 表示文件系统块个数为100
Free blocks: 79 表示文件系统空闲块个数为79
Free inodes: 5 表示文件系统空闲inode个数为5
First block: 1 第一个数据块编号为1(编号0保留为引导块)
Block size: 1024 文件系统块大小为1k, 10bit
Blocks per group: 8192 每个块组8192个块
Inodes per group: 16 每个块组16个inode
Inode blocks per group: 2 每个块组2个inode块
First inode: 11 分配的第一个inode号为11(除根inode外,根inode号为2)
Inode size: 128 inode大小为128字节块组的信息
超级块块编号为 1
块组描述符块编号为 2
块位图块编号为 3
inode位图块编号为 4
inode表位于5和6块
79 个可用 块
5 个可用inode
通过命令查看具体的数据内容;

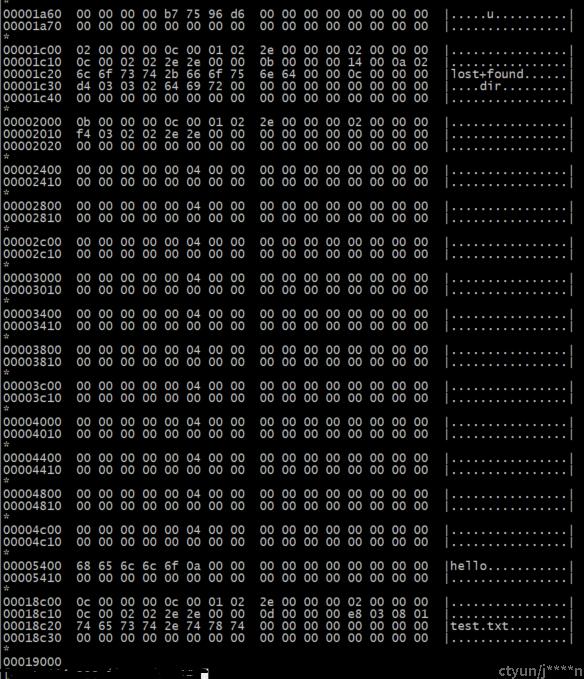
通过mount命令把镜像挂载到root_dir目录,
通过ls命令查看使用的inode编号
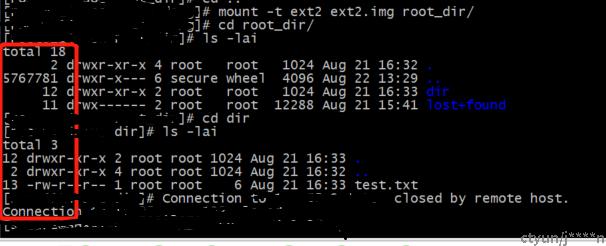
. 表示的是当前目录,inode编号为2表示根inode
..表示挂载的上一级目录在上一级文件系统中的inode编号
当前目录ext2文件系统中dir目录使用的inode编号为12
lost+found:系统发生错误时, 将一些遗失的片段放置到这个目录下
系统有一些保留的inode编号:
#define EXT2_BAD_INO 1 /* Bad blocks inode */
#define EXT2_ROOT_INO 2 /* Root inode */
#define EXT2_BOOT_LOADER_INO 5 /* Boot loader inode */
#define EXT2_UNDEL_DIR_INO 6 /* Undelete directory inode */
下面我们具体的解析一下根据路径名称查找具体文件/dir/test.txt的过程:
首先我们查找当前文件系统的根目录信息:
查看根目录内容过程:
因为根目录的inode编号是固定的,所以我们使用ino=2 根inode:
首先计算保存根inode的块组编号: block_group = (ino - 1) / EXT2_INODES_PER_GROUP(sb) = (2 - 1) / 16 = 0
然后计算保存inode表中的根inode偏移 : offset = ((ino - 1) % EXT2_INODES_PER_GROUP(sb)) * EXT2_INODE_SIZE(sb)= ( 1 % 16 ) * 128 = 128 =0x80
文件系统中的根inode所在块号 : block = le32_to_cpu(gdp->bg_inode_table) + (offset >>EXT2_BLOCK_SIZE_BITS(sb)) = 5 + (128 >> 10) = 5
根inode所在块中偏移:offset &= (EXT2_BLOCK_SIZE(sb) - 1) = 128 = 0x80
inode中位置 = bh->b_data + offset = 所在块 + 0x80
所以根inode所在镜像文件中第5个数据块,偏移为80的位置,一个数据块size为1k(0x400)
偏移为:5 * 0x400 + 0x80 = 0x1400 + 0x80 = 0x1480
Ext2文件系统中i_block字段保存了具体目录项内容:
对照ext2文件系统磁盘inode结构,i_block为inode结构的偏移40B(0x28) 0x14a8处
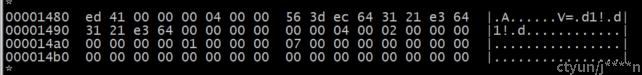
所以根目录使用的数据块的块号为0x7(偏移为0x7 * 0x400 = 0x1c00)
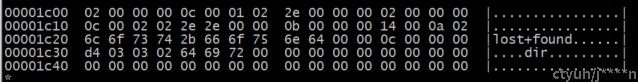
数据块中保存的是具体的磁盘目录项,使用数据结构ext2_dir_entry_2来解析:
所以具体的内容如下:
磁盘目录项 (.)
struct ext2_dir_entry_2 {
__le32 inode; 0x00 00 00 02
__le16 rec_len; 0x00 0c
__u8 name_len; 0x01
__u8 file_type; 0x02
char name[];
}; endaddr: 0x1c0c
磁盘目录项(..)
struct ext2_dir_entry_2 {
__le32 inode; 0x00 00 00 02
__le16 rec_len; 0x00 0c
__u8 name_len; 0x02
__u8 file_type; 0x02
char name[];
}; endaddr: 0x1c18
磁盘目录项(lost+found)
struct ext2_dir_entry_2 {
__le32 inode; 0x00 00 00 0b
__le16 rec_len; 0x00 14
__u8 name_len; 0x0a
__u8 file_type; 0x02
char name[];
}; endaddr: 0x1c2c
磁盘目录项(dir)
struct ext2_dir_entry_2 {
__le32 inode; 0x00 00 00 0c
__le16 rec_len; 0x03 d4
__u8 name_len; 0x03
__u8 file_type; 0x02 (EXT2_FT_DIR )
char name[];
};
获取到dir是一个目录类型, 使用的inode编号为12
计算dir的目录项具体内容:
查看dir目录内容过程:
dir目录所在块组编号: block_group = (ino - 1) / EXT2_INODES_PER_GROUP(sb) = (12 - 1) / 16 = 0
dir目录所在inode表中的inode偏移 : offset = ((ino - 1) % EXT2_INODES_PER_GROUP(sb))
* EXT2_INODE_SIZE(sb) = ( 11 % 16 ) * 128 = 1408(0x580)
文件系统中的dir目录的inode所在块号 : block = le32_to_cpu(gdp->bg_inode_table) +
(offset >> EXT2_BLOCK_SIZE_BITS(sb)) = 5 + (1408 >> 10) = 5 +1 =6
dir目录的inode所在块号中偏移:offset &= (EXT2_BLOCK_SIZE(sb) - 1)
= 1408(0x580)& (0x400 -1) = 0x180
inode中位置 = bh->b_data + offset = 所在块 + 0x180
所以最终得到:
dir目录inode所在的镜像文件中偏移为:= 6 * 0x400 + 0x180 = 0x1800 + 0x180 = 0x1980
对照ext2文件系统磁盘inode结构,可知i_block为磁盘inode结构的偏移40B(0x28)
获取dir目录的数据块号为0x63.
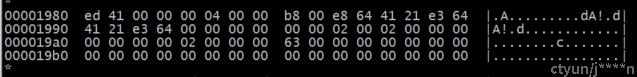
计算dir目录数据块的块号 为0x63(偏移为0x63 * 0x400 = 18c00)
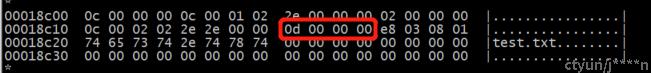
获取0x18c0对应的数据同样方式解析ext2_dir_entry_2数据结构,获取到test.txt文件使用的inode编号为0xd
再次根据inode编号来获取test.txt的inode数据结构内容:
查看test.txt内容过程:
test.txt文件inode所在块组 编号: block_group = (ino - 1) / EXT2_INODES_PER_GROUP(sb) = (13 - 1) / 16 = 0
test.txt文件inode在 inode表中的inode偏移 : offset = ((ino - 1) % EXT2_INODES_PER_GROUP(sb)) * EXT2_INODE_SIZE(sb)= ( 12 % 16 ) * 128 = 1536(0x600)
文件系统中的test.txt文件inode所在块号 : block = le32_to_cpu(gdp->bg_inode_table) + (offset >> EXT2_BLOCK_SIZE_BITS(sb)) = 5 + (1536 >> 10) = 5 +1 =6
test.txt文件inode所在块号中偏移:offset &= (EXT2_BLOCK_SIZE(sb) - 1) = 1408(0x600)& (0x400 -1) = 0x200
inode中位置 = bh->b_data + offset = 所在块 + 0x200
最终计算得到:
test.txt文件inode所在的镜像文件中偏移为:= 6 * 0x400 + 0x200 = 0x1800 + 0x200 = 0x1a00
对照ext2文件系统磁盘inode结构,可知i_block为磁盘inode结构的偏移40B(0x28)
查找地址为0x1a28出的数据,得到了test.txt的具体数据块号为0x15.
通过test.txt文件数据块的块号 为0x15获取保存数据的最终偏移地址为(偏移为0x15 * 0x400 = 0x5400)
最终获取到test.txt文件中保存的内容为hello。