1、DBUS的概念和基本原理
DBus是一种轻量级的进程间通信机制,可以用于进程间通信或进程与内核的通信。它由freedesktop.org项目提供,使用GPL许可证发行。D-Bus最主要的用途是在 Linux桌面环境为进程提供通信,同时能将Linux桌面环境和Linux内核事件作为消息传递到进程。D-Bus的主要概率为总线,注册后的进程可通 过总线接收或传递消息,进程也可注册后等待内核事件响应,例如等待网络状态的转变或者计算机发出关机指令。目前,D-Bus已被大多数Linux发行版所 采用,开发者可使用D-Bus实现各种复杂的进程间通信任务。关于dbus的详细内容也可以参考[dbus (www.freedesktop.org)]
下面介绍一下DBus中的一些基本概念:
会话总线(Session Buses)普通进程创建,可同时存在多条。会话总线属于某个进程私有,它用于进程间传递消息。
系统总线(System Bus)在引导时就会启动,它由操作系统和后台进程使用,安全性非常好,以使得任意的应用程序不能欺骗系统事件。当然,如果一个应用程序需要接受来自系统总线的消息,他也可以直接连接到系统总线中,但是他能发送的消息是受限的。
Bus Name按字面理解为总线名称貌似不是很贴切,应该是一个连接名称,主要是用来标识一个应用和消息总线的连接。从上图可以看出来,总线名称主要分为两类"org.kde.StatusNotifierWatcher"这种形式的称为公共名(well-knownname)。":1.3"这种形式的称为唯一名(Unique Name)
公共名提供众所周知的服务。其他应用通过这个名称来使用名称对应的服务。可能有多个连接要求提供同个公共名的服 务,即多个应用连接到消息总线,要求提供同个公共名的服务。消息总线会把这些连接排在链表中,并选择一个连接提供公共名代表的服务。可以说这个提供服务的 连接拥有了这个公共名。如果这个连接退出了,消息总线会从链表中选择下一个连接提供服务。
唯一名以“:”开头,“:”后面通常是圆点分隔的两个数字,例如“:1.0”。每个连接都有一个唯一名。在一个 消息总线的生命期内,不会有两个连接有相同的唯一名。拥有公众名的连接同样有唯一名,例如在前面的图 中,“org.kde.StatusNotifierWatcher”的唯一名是“:1.51”。
每个连接都有一个唯一名,但不一定有公共名。
只有唯一名而没有公共名叫做私有连接,因为它们没有提供可以通过公共名访问的服务。
Object Paths**:**“org.kde.StatusNotifierWatcher”这个连接中有三个Object Paths,标识这个连接中提供了三个不同的服务,每个Object Paths表示一个服务。这个路径在连接中是唯一的。
Interfaces:在每个Object Paths下都包含有多个接口(Interfaces),举例如下接口:
org.freedesktop.DBus.Introspectable
org.freedesktop.DBus.Properties
org.kde.StatusNotifierWatcher
红色的两个是消息总线提供的标准接口,而剩下的一个是需要具体的应用去实现的。
Methods和Signals**:**
Methods表示可以被具体调用的方法
Signals则表示的是信号,此信号可以被广播,而连接了这个信号的对象在接收到信号时就可以进行相应的处理。和Qt中的信号应该是一个意思。下图是DBUS通信机制的总体架构:
接下来通过一个小例子来演示dbus之间通信的过程:
server端:
use std::{error::Error, future::pending};
use zbus::{connection, interface};
struct Greeter {
count: u64
}
#[interface(name = "org zbus MyGreeter1")]
impl Greeter {
fn say_hello(&mut self, name: &str) -> String {
self count += 1;
format!("Hello {}! I have been called {} times", name, self.count)
}
}
#[async_std::main]
async fn main() -> Result<(), Box<dyn Error>> {
let greeter = Greeter { count: 0 };
print!("I am a server test");
let _conn = connection::Builder::session()?
name("org zbus MyGreeter")?
serve_at("/org/zbus/MyGreeter", greeter)?
build()
await?;
pending::<()>().await;
Ok(())
}
Client端:
use zbus::{Connection, Result, proxy};
#[proxy(
interface = "org.zbus.MyGreeter1",
default_service = "org.zbus.MyGreeter",
default_path = "/org/zbus/MyGreeter"
)]
trait MyGreeter {
async fn say_hello(&self, name: &str) -> Result<String>;
}
// Although we use `async-std` here, you can use any async runtime of choice
#[async_std::main]
async fn main() -> Result<()> {
let connection = Connection::session().await?;
// `proxy` macro creates `MyGreeterProxy` based on `Notifications` trait
let proxy = MyGreeterProxy::new(&connection).await?;
let reply = proxy.say_hello("Maria").await?;
println!("{reply}");
Ok(())
}
效果展示:

通信过程展示(以守护进程dbus-daemon为例):
- socket(AF_NETLINK, SOCK_RAW, NETLINK_AUDIT) = 5
- ......
- epoll_ctl(3, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, 6, {events=EPOLLIN, data={u32=6, u64=6}}) = 0
- ......
- socketpair(AF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM|SOCK_CLOEXEC, 0, [7, 8]) = 0
- epoll_ctl(3, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, 7, {events=EPOLLIN, data={u32=7, u64=7}}) = 0
- ......
- epoll_wait(3,[{events=EPOLLIN, data={u32=4, u64=4}}], 64, -1) = 1
- accept4(4, {sa_family=AF_UNIX}, [16 => 2], SOCK_CLOEXEC) = 9
- ......
- getsockname(9, {sa_family=AF_UNIX, sun_path=@"/tmp/dbus-wDGbb9EnNy"}, [128 => 23]) = 0
- getsockopt(9, SOL_SOCKET, SO_PEERSEC, "unconfined_u:unconfined_r:unconf"..., [256 => 54]) = 0
- epoll_ctl(3, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, 9, {events=EPOLLET, data={u32=9, u64=9}}) = 0
- epoll_ctl(3, EPOLL_CTL_MOD, 9, {events=EPOLLIN, data={u32=9, u64=9}}) = 0
- epoll_wait(3, [{events=EPOLLIN, data={u32=9, u64=9}}], 64, 239999) = 1
- recvmsg(9, {msg_name=NULL, msg_namelen=0, msg_iov=[{iov_base="\0", iov_len=1}], msg_iovlen=1, msg_controllen=0, msg_flags=0}, 0) = 1
- getsockopt(9, SOL_SOCKET, SO_PEERCRED, {pid=2569, uid=0, gid=0}, [12]) = 0
- getsockopt(9, SOL_SOCKET, SO_PEERSEC, "unconfined_u:unconfined_r:unconf"..., [1024 => 54]) = 0
- read(9, 0x56165597ac60, 2048) = -1 EAGAIN (Resource temporarily unavailable)
- epoll_wait(3, [{events=EPOLLIN, data={u32=9, u64=9}}], 64, 239999) = 1
- read(9, "AUTH EXTERNAL 30\r\n", 2048) = 18
- epoll_ctl(3, EPOLL_CTL_MOD, 9, {events=EPOLLET, data={u32=9, u64=9}}) = 0
- epoll_ctl(3, EPOLL_CTL_MOD, 9, {events=EPOLLOUT, data={u32=9, u64=9}}) = 0
- epoll_wait(3, [{events=EPOLLOUT, data={u32=9, u64=9}}], 64, 239998) = 1
- sendto(9, "OK c9903731c29e5c96c5510d8c6604d"..., 37, MSG_NOSIGNAL, NULL, 0) = 37
- epoll_ctl(3, EPOLL_CTL_MOD, 9, {events=EPOLLIN|EPOLLOUT, data={u32=9, u64=9}}) = 0
- epoll_ctl(3, EPOLL_CTL_MOD, 9, {events=EPOLLIN, data={u32=9, u64=9}}) = 0
- epoll_wait(3, [{events=EPOLLIN, data={u32=9, u64=9}}], 64, 239997) = 1
- read(9, "NEGOTIATE_UNIX_FD\r\n", 2048) = 19
- epoll_ctl(3, EPOLL_CTL_MOD, 9, {events=EPOLLET, data={u32=9, u64=9}}) = 0
- epoll_ctl(3, EPOLL_CTL_MOD, 9, {events=EPOLLOUT, data={u32=9, u64=9}}) = 0
- epoll_wait(3, [{events=EPOLLOUT, data={u32=9, u64=9}}], 64, 239997) = 1
- sendto(9, "AGREE_UNIX_FD\r\n", 15, MSG_NOSIGNAL, NULL, 0) = 15
- epoll_ctl(3, EPOLL_CTL_MOD, 9, {events=EPOLLIN|EPOLLOUT, data={u32=9, u64=9}}) = 0
- epoll_ctl(3, EPOLL_CTL_MOD, 9, {events=EPOLLIN, data={u32=9, u64=9}}) = 0
- epoll_wait(3, [{events=EPOLLIN, data={u32=9, u64=9}}], 64, 239997) = 1
- read(9, "BEGIN\r\n", 2048) = 7
- geteuid() = 0
- epoll_wait(3, [{events=EPOLLIN, data={u32=9, u64=9}}], 64, 239996) = 1
- recvmsg(9, {msg_name=NULL, msg_namelen=0, msg_iov=[{iov_base="l\1\0\1\0\0\0\0\1\0\0\0m\0\0\0\1\1o\0\25\0\0\0/org/fre"..., iov_len=2048}], msg_iovlen=1, msg_controllen=0, msg_flags=MSG_CMSG_CLOEXEC}, MSG_CMSG_CLOEXEC) = 128
- recvmsg(9, {msg_namelen=0}, MSG_CMSG_CLOEXEC) = -1 EAGAIN (Resource temporarily unavailable)
3、ctyunos自研组件ctsinstaller中的dbus
ctsinstaller中使用的是开源组件dasbus作为dbus协议的实现,为ctsinstaller提供了进程间通信的功能
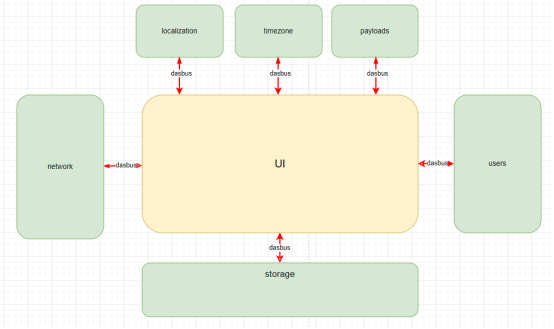
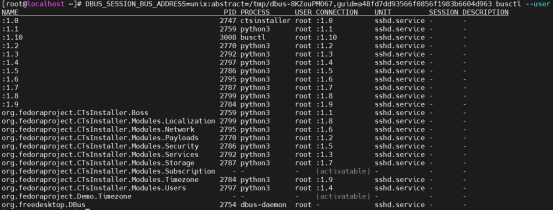
使用busctl工具可以看到各个模块在守护进程中注册的总线名,如下所示:
4、zbus介绍和相关工具介绍
zbus 是一个用于在 Rust 中进行 D-Bus 通信的库。zbus 库提供了一个简单而强大的方式来实现与 D-Bus 服务的交互,使得 Rust 程序可以方便地与其他通过 D-Bus 提供的服务进行通信。 zbus提供了对 D-Bus 基本概念(如对象、接口、方法调用等)的抽象,使得 Rust 开发者可以专注于业务逻辑而不必过多关注底层的通信细节。zbus 支持异步/同步操作,可以与 tokio 或 async-std 这样的异步运行时库集成,以实现非阻塞的 D-Bus 通信。此外,zbus 还提供了代码生成工具,可以根据 D-Bus 接口定义语言(xml)文件自动生成 Rust 的类型安全的接口代码,简化了开发过程并提高了代码的可维护性。仓库地址:[GitHub - dbus2/zbus: Rust D-Bus crate.]
4.1 接口转换
1)dasbus中通过XMLGenerator将接口文件生成xml文件
from dasbus.xml import XMLGenerator
@dbus_interface(xxx.interface_name)
class xxxInterface:
xxx
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Print the generated XML specification.
print(XMLGenerator.prettify_xml(xxxInterface.__dbus_xml__))
2)在zbus中使用
- cd /zbus/zbus_xmlgen/
- cargo build
- cd ../target/debug
- ./zbus-xmlgen file xxx.xml
例如将如下python接口文件转换rust接口crate:
@dbus_interface(TIMEZONE.interface_name)
class TimezoneInterface(KickstartModuleInterface):
def connect_signals(self):
super().connect_signals()
self.watch_property("Timezone", self.implementation.timezone_changed)
self.watch_property("IsUTC", self.implementation.is_utc_changed)
self.watch_property("NTPEnabled", self.implementation.ntp_enabled_changed)
self.watch_property("TimeSources", self.implementation.time_sources_changed)
@property
def Timezone(self) -> Str:
return self.implementation.timezone
@emits_properties_changed
def SetTimezone(self, timezone: Str):
self.implementation.set_timezone(timezone)
@property
def IsUTC(self) -> Bool:
return self.implementation.is_utc
@emits_properties_changed
def SetIsUTC(self, is_utc: Bool):
self.implementation.set_is_utc(is_utc)
@property
def NTPEnabled(self) -> Bool:
return self.implementation.ntp_enabled
@emits_properties_changed
def SetNTPEnabled(self, ntp_enabled: Bool):
self.implementation.set_ntp_enabled(ntp_enabled)
@property
def TimeSources(self) -> List[Structure]:
return CtsTimeSourceData.to_structure_list(
self.implementation.time_sources
)
@emits_properties_changed
def SetTimeSources(self, sources: List[Structure]):
self.implementation.set_time_sources(
CtsTimeSourceData.from_structure_list(sources)
)
def ConfigureNTPServiceEnablementWithTask(self, ntp_excluded: Bool) -> ObjPath:
return TaskContainer.to_object_path(
self.implementation.configure_ntp_service_enablement_with_task(ntp_excluded)
)
}
生成的xml文件:
<node>
<!--Specifies TimezoneInterface-->
<interface name="org.fedoraproject.CTsInstaller.Modules">
<method name="CollectRequirements">
<arg direction="out" name="return" type="aa{sv}"></arg>
</method>
<method name="ConfigureBootloaderWithTasks">
<arg direction="in" name="kernel_versions" type="as"></arg>
<arg direction="out" name="return" type="ao"></arg>
</method>
<method name="ConfigureWithTasks">
<arg direction="out" name="return" type="ao"></arg>
</method>
<method name="GenerateKickstart">
<arg direction="out" name="return" type="s"></arg>
</method>
<method name="InstallWithTasks">
<arg direction="out" name="return" type="ao"></arg>
</method>
<property access="read" name="KickstartAddons" type="as"></property>
<property access="read" name="KickstartCommands" type="as"></property>
<property access="read" name="KickstartSections" type="as"></property>
<property access="read" name="Kickstarted" type="b"></property>
<method name="Quit"></method>
<method name="ReadKickstart">
<arg direction="in" name="kickstart" type="s"></arg>
<arg direction="out" name="return" type="a{sv}"></arg>
</method>
<method name="SetKickstarted">
<arg direction="in" name="kickstarted" type="b"></arg>
</method>
<method name="SetLocale">
<arg direction="in" name="locale" type="s"></arg>
</method>
<method name="TeardownWithTasks">
<arg direction="out" name="return" type="ao"></arg>
</method>
</interface>
<interface name="org.fedoraproject.CTsInstaller.Modules.Timezone">
<property access="read" name="IsUTC" type="b"></property>
<property access="read" name="NTPEnabled" type="b"></property>
<method name="SetIsUTC">
<arg direction="in" name="is_utc" type="b"></arg>
</method>
<method name="SetNTPEnabled">
<arg direction="in" name="ntp_enabled" type="b"></arg>
</method>
<method name="SetTimeSources">
<arg direction="in" name="sources" type="aa{sv}"></arg>
</method>
<method name="SetTimezone">
<arg direction="in" name="timezone" type="s"></arg>
</method>
<property access="read" name="TimeSources" type="aa{sv}"></property>
<property access="read" name="Timezone" type="s"></property>
</interface>
</node>
最后通过zbusxmlgen产生的接口crate如下所示:
use zbus::proxy;
#[proxy(
interface = "org.fedoraproject.CTsInstaller.Modules.Timezone",
assume_defaults = true
)]
trait Timezone {
/// SetIsUTC method
#[zbus(name = "SetIsUTC")]
fn set_is_utc(&self, is_utc: bool) -> zbus::Result<()>;
/// SetNTPEnabled method
#[zbus(name = "SetNTPEnabled")]
fn set_ntpenabled(&self, ntp_enabled: bool) -> zbus::Result<()>;
/// SetTimeSources method
fn set_time_sources(
&self,
sources: &[std::collections::HashMap<&str, zbus::zvariant::Value<'_>>],
) -> zbus::Result<()>;
/// SetTimezone method
fn set_timezone(&self, timezone: &str) -> zbus::Result<()>;
/// IsUTC property
#[zbus(property, name = "IsUTC")]
fn is_utc(&self) -> zbus::Result<bool>;
/// NTPEnabled property
#[zbus(property, name = "NTPEnabled")]
fn ntpenabled(&self) -> zbus::Result<bool>;
/// TimeSources property
#[zbus(property)]
fn time_sources(
&self,
) -> zbus::Result<Vec<std::collections::HashMap<String, zbus::zvariant::OwnedValue>>>;
/// Timezone property
#[zbus(property)]
fn timezone(&self) -> zbus::Result<String>;
}
4.2 busctl
busctl 是一个用于在 Linux 系统上进行 D-Bus 调试和管理的命令行工具。它提供了一种方便的方式来查看系统中正在运行的 D-Bus 服务、对象和接口,以及与这些服务进行交互和调试。使用 busctl,你可以执行诸如以下操作:
列出系统上当前运行的 D-Bus 服务,并查看其状态
显示特定服务的对象和接口
查看服务提供的方法和信号
进行方法调用和接收信号
监视 D-Bus 总线上的消息流
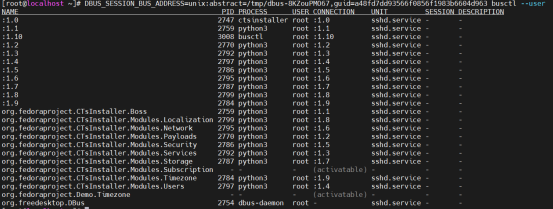
通过 busctl,开发人员可以方便地检查和调试他们的 D-Bus 服务,观察各个服务之间的通信,以及验证 D-Bus 接口的正确性。此外,busctl 还可以用于管理系统上的 D-Bus 服务,例如启动、停止或重新加载服务。例如使用busctl列出系统上当前运行的 D-Bus 服务,并查看其状态:
使用busctl模拟向服务端发送消息:
- [root@localhost ~]# DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS=unix:abstract=/tmp/dbus-8KZouPMO67,guid=a48fd7dd93566f0856f1983b6604d963 busctl --user call org.fedoraproject.CTsInstaller.Modules.Timezone /org/fedoraproject/CTsInstaller/Modules/Timezone org.freedesktop.DBus.Properties Get ss "org.fedoraproject.CTsInstaller.Modules.Timezone" "Timezone"
- v s "Asia/Shanghai"
4.3 dbus-send
dbus-send支持向指定的 D-Bus 地址发送消息,从而与其他应用程序或服务进行通信。
该功能的作用和busctl call有些类似,如下所示:
- [root@localhost ~]# DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS=unix:abstract=/tmp/dbus-8KZouPMO67,guid=a48fd7dd93566f0856f1983b6604d963 dbus-send --session --print-reply --dest=org.fedoraproject.CTsInstaller.Modules.Timezone /org/fedoraproject/CTsInstaller/Modules/Timezone org.freedesktop.DBus.Properties.Get string:"org.fedoraproject.CTsInstaller.Modules.Timezone" string:"Timezone"
- method return time=1711595697.877459 sender=:1.9 -> destination=:1.12 serial=29 reply_serial=2
- variant string "Asia/Shanghai"
4.4 dbus-monitor
dbus-monitor 是一个用于在 Linux 系统上监听和显示 D-Bus 消息的命令行工具。通过 dbus-monitor,你可以实时查看系统中正在传输的 D-Bus 消息,包括方法调用、信号发送等,有助于开发人员了解各个应用程序之间的通信过程。使用如下指令启动dbus-monitor:
- DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS=DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS=unix:abstract=/tmp/dbus-8KZouPMO67,guid=a48fd7dd93566f0856f1983b6604d963 dbus-monitor
以点击timezone为例,dbus-monitor捕获到的通信过程如下:
- method call time=1711595929.609401 sender=:1.0 -> destination=org.fedoraproject.CTsInstaller.Modules.Timezone serial=309 path=/org/fedoraproject/CTsInstaller/Modules/Timezone; interface=org.freedesktop.DBus.Properties; member=Get
- string "org.fedoraproject.CTsInstaller.Modules.Timezone"
- string "Timezone"
- method return time=1711595929.609584 sender=:1.9 -> destination=:1.0 serial=34 reply_serial=309
- variant string "Asia/Shanghai"
- method call time=1711595929.610841 sender=:1.0 -> destination=org.fedoraproject.CTsInstaller.Modules.Timezone serial=310 path=/org/fedoraproject/CTsInstaller/Modules/Timezone; interface=org.freedesktop.DBus.Properties; member=Get
- string "org.fedoraproject.CTsInstaller.Modules.Timezone"
- string "Timezone"
- method return time=1711595929.611543 sender=:1.9 -> destination=:1.0 serial=35 reply_serial=310
- variant string "Asia/Shanghai"
- DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS=unix:abstract=/tmp/dbus-8KZouPMO67,guid=a48fd7dd93566f0856f1983b6604d963
5、基于zbus,tui-rs的tui方案demo演示
5.1、最终效果

5.1、基于zbus,tui-rs的客户端代码:
use crossterm::{
event::{self, DisableMouseCapture, EnableMouseCapture, Event, KeyCode},
execute,
terminal::{disable_raw_mode, enable_raw_mode, EnterAlternateScreen, LeaveAlternateScreen},
};
use std::{io, time::Duration};
use tui::{
backend::{Backend, CrosstermBackend},
layout::{Constraint, Direction, Layout,Rect},
style::{Color, Modifier, Style},
text::{Span, Spans},
widgets::{Block, Borders, Paragraph},
Frame, Terminal,
};
use zbus::{Connection, Result, proxy};
#[proxy(
interface = "org.fedoraproject.CTsInstaller.Modules.Timezone",
default_service = "org.fedoraproject.CTsInstaller.Modules.Timezone",
default_path = "/org/fedoraproject/CTsInstaller/Modules/Timezone",
assume_defaults = true
)]
trait Timezone {
/// SetIsUTC method
#[zbus(name = "SetIsUTC")]
fn set_is_utc(&self, is_utc: bool) -> zbus::Result<()>;
/// SetNTPEnabled method
#[zbus(name = "SetNTPEnabled")]
fn set_ntpenabled(&self, ntp_enabled: bool) -> zbus::Result<()>;
/// SetTimeSources method
fn set_time_sources(
&self,
sources: &[std::collections::HashMap<&str, zbus::zvariant::Value<'_>>],
) -> zbus::Result<()>;
/// SetTimezone method
fn set_timezone(&self, timezone: &str) -> zbus::Result<()>;
/// IsUTC property
#[zbus(property, name = "IsUTC")]
fn is_utc(&self) -> zbus::Result<bool>;
/// NTPEnabled property
#[zbus(property, name = "NTPEnabled")]
fn ntpenabled(&self) -> zbus::Result<bool>;
/// TimeSources property
#[zbus(property)]
fn time_sources(
&self,
) -> zbus::Result<Vec<std::collections::HashMap<String, zbus::zvariant::OwnedValue>>>;
/// Timezone property
#[zbus(property)]
fn timezone(&self) -> zbus::Result<String>;
}
#[proxy(
interface = "org.fedoraproject.CTsInstaller.Modules.Storage.DiskSelection",
default_service = "org.fedoraproject.CTsInstaller.Modules.Storage",
default_path = "/org/fedoraproject/CTsInstaller/Modules/Storage/DiskSelection",
assume_defaults = true
)]
trait DiskSelection {
/// GetUsableDisks method
fn get_usable_disks(&self) -> zbus::Result<Vec<String>>;
/// SetDiskImages method
fn set_disk_images(
&self,
disk_images: std::collections::HashMap<&str, &str>,
) -> zbus::Result<()>;
/// SetExclusiveDisks method
fn set_exclusive_disks(&self, drives: &[&str]) -> zbus::Result<()>;
/// SetIgnoredDisks method
fn set_ignored_disks(&self, drives: &[&str]) -> zbus::Result<()>;
/// SetProtectedDevices method
fn set_protected_devices(&self, devices: &[&str]) -> zbus::Result<()>;
/// SetSelectedDisks method
fn set_selected_disks(&self, drives: &[&str]) -> zbus::Result<()>;
/// ValidateSelectedDisks method
fn validate_selected_disks(
&self,
drives: &[&str],
) -> zbus::Result<std::collections::HashMap<String, zbus::zvariant::OwnedValue>>;
/// DiskImages property
#[zbus(property)]
fn disk_images(&self) -> zbus::Result<std::collections::HashMap<String, String>>;
/// ExclusiveDisks property
#[zbus(property)]
fn exclusive_disks(&self) -> zbus::Result<Vec<String>>;
/// IgnoredDisks property
#[zbus(property)]
fn ignored_disks(&self) -> zbus::Result<Vec<String>>;
/// ProtectedDevices property
#[zbus(property)]
fn protected_devices(&self) -> zbus::Result<Vec<String>>;
/// SelectedDisks property
#[zbus(property)]
fn selected_disks(&self) -> zbus::Result<Vec<String>>;
}
struct App {
reply_from_server: String, // 存放一些数据或者 UI 状态
}
#[async_std::main]
//async fn main() -> Result<()> {
async fn main() -> std::result::Result<(), io::Error> {
let connection_timezone = Connection::session().await.expect("连接失败");
let proxy_timezone = TimezoneProxy::new(&connection_timezone).await.expect("创建代理失败");
let reply_timezone = proxy_timezone.timezone().await.expect("获取数据失败");
let connection_diskselect = Connection::session().await.expect("连接失败");
let proxy_diskselect = DiskSelectionProxy::new(&connection_diskselect).await.expect("创建代理失败");
let reply_diskselect = proxy_diskselect.get_usable_disks().await.expect("获取数据失败");
let usabledisk = reply_diskselect.get(0);
let reply = usabledisk.unwrap();
// 初始化终端
enable_raw_mode()?;
let mut stdout = io::stdout();
execute!(stdout, EnterAlternateScreen, EnableMouseCapture)?;
let backend = CrosstermBackend::new(stdout);
let mut terminal = Terminal::new(backend)?;
let mut apps : [ App; 2] = [
App {reply_from_server: String::from(reply_timezone),},
App {reply_from_server: String::from(reply),}
];
// 渲染界面
run_app(&mut terminal, apps)?;
// 恢复终端
disable_raw_mode()?;
execute!(
terminal.backend_mut(),
LeaveAlternateScreen,
DisableMouseCapture
)?;
terminal.show_cursor()?;
Ok(())
}
fn run_app<B: Backend>(terminal: &mut Terminal<B>, mut apps: [App;2]) -> io::Result<()> {
loop {
terminal.draw(|f| ui(f, &mut apps))?;
if crossterm::event::poll(Duration::from_secs(1))? {
if let Event::Key(key) = event::read()? {
match key.code {
KeyCode::Char(ch) => {
if 'q' == ch {
break;
}
}
_ => {}
}
}
}
}
Ok(())
}
fn ui<B: Backend>(f: &mut Frame<B>, apps: &mut [App; 2]) {
let total_height = f.size().height;
let first_paragraph_height = total_height / 2;
let first_chunk = Rect::new(0, 0, f.size().width, first_paragraph_height);
let second_chunk = Rect::new(0, first_paragraph_height, f.size().width, total_height - first_paragraph_height);
let paragraph1 = Paragraph::new(Spans::from(vec![
Span::styled(
apps[0].reply_from_server.as_str(),
Style::default().add_modifier(Modifier::BOLD).fg(Color::Green), // 设置文字颜色为绿色
)
]))
.block(Block::default().borders(Borders::ALL).title("Current time zone").title_style(Style::default().fg(Color::Red)))
.alignment(tui::layout::Alignment::Left);
f.render_widget(paragraph1, first_chunk);
let paragraph2 = Paragraph::new(Spans::from(vec![
Span::styled(
apps[1].reply_from_server.as_str(),
Style::default().add_modifier(Modifier::BOLD).fg(Color::Green), // 设置文字颜色为绿色
)
]))
.block(Block::default().borders(Borders::ALL).title("Current disk").title_style(Style::default().fg(Color::Red)))
.alignment(tui::layout::Alignment::Left);
f.render_widget(paragraph2, second_chunk);
}