Kernel Thread ksmd Running on PMD Isolated Cores Causes High Latency in OVS Packet Processing
内核线程ksmd跑到PMD核心,导致OVS报文延时大
perf sched
在物理机上查看隔离核心cpu 43 的时间片使用情况:
perf sched record -C 43
perf sched timehist
通过下图可以看到内核线程ksmd被周期性调度,每次运行时长12ms左右。
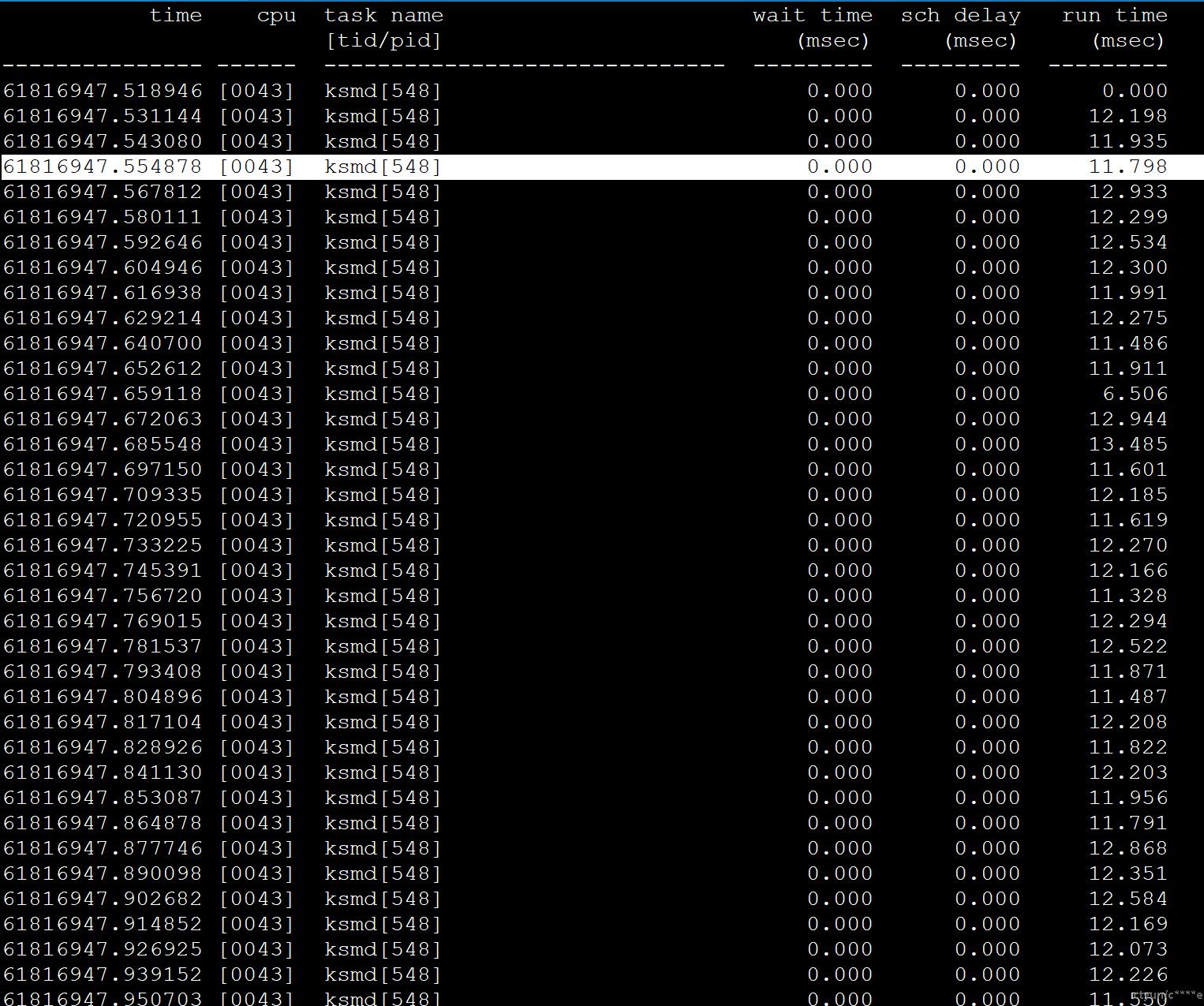
ksmd
内核中的Kernel Samepage Merging (KSM)机制被设计用于合并相同的内存页,以节省物理内存。
合并相同的内存页是Kernel Samepage Merging (KSM) 的核心功能,其目的是通过检测并合并相同的内存页来减少物理内存的使用。这一机制特别适用于虚拟化环境,在这些环境中,多个虚拟机可能会运行相同的操作系统和应用程序,从而拥有大量相同的内存页。
ksmd内核参数
ksmd是内核KSM机制的守护进程,它的相关信息可以在/sys/kernel/mm/ksm目录中找到。
在/sys/kernel/mm/ksm目录中,您会找到以下文件,每个文件都有特定的功能和用途:
- full_scans:显示自KSM启动以来完成的完整 scan 次数。
- max_page_sharing:控制一个共享页面的最大引用次数。
- merge_across_nodes:控制是否允许在不同NUMA节点之间合并页面。值为1表示允许,0表示不允许。
- pages_shared:显示当前被共享的内存页数。
- pages_sharing:显示当前有多少页在共享同一页。
- pages_to_scan:控制每个 scan 周期中KSM scan 的页数。
- pages_unshared:显示当前未被共享的页数。
- pages_volatile:显示当前不稳定的页数,这些页可能会被KSM合并。
- run:控制KSM的运行状态。写入
0停止KSM,写入1启动KSM。 - sleep_millisecs:控制KSM scan 周期的时间间隔,以毫秒为单位。
- stable_node_chains:显示稳定节点链的数量。
- stable_node_chains_prune_millisecs:控制修剪稳定节点链的时间间隔,以毫秒为单位。
- stable_node_dups:显示稳定节点的副本数量。
- use_zero_pages:控制是否使用零页来合并空闲页。值为1表示使用,0表示不使用。
动态调整ksmd参数
ksmd 线程在以下情况下会被调度运行:
启动KSM后
KSM通过将/sys/kernel/mm/ksm/run文件的值设置为1来启动。一旦启动,ksmd线程会按照配置开始周期性地 scan 和合并内存页。
配置的 scan 周期
ksmd线程的调度频率由/sys/kernel/mm/ksm/sleep_millisecs文件中配置的 scan 周期决定。该文件的值是一个以毫秒为单位的时间间隔,表示ksmd线程在每次 scan 之间的睡眠时间。例如:
# 设置 scan 周期为100毫秒
echo 100 | sudo tee /sys/kernel/mm/ksm/sleep_millisecs
在这种配置下,ksmd线程会每隔100毫秒被调度运行一次,以 scan 和合并内存页。
每次 scan 的页数
ksmd线程在每次被调度运行时,会根据/sys/kernel/mm/ksm/pages_to_scan文件中配置的值来决定每次 scan 的页数。例如:
# 设置每次 scan 的页数为256页
echo 256 | sudo tee /sys/kernel/mm/ksm/pages_to_scan
这意味着每次ksmd线程被调度运行时,它将 scan 256个内存页。
housekeeping_isolcpus_setup
在grub中传入isolcpus=参数时,kernel/sched/isolation.c文件中的housekeeping_isolcpus_setup函数会被调用。
// vim kernel/sched/isolation.c +126
126 static int __init housekeeping_isolcpus_setup(char *str) // 定义一个静态的初始化函数 housekeeping_isolcpus_setup ,接收一个字符指针参数
127 {
128 unsigned int flags = 0; // 定义一个无符号整型变量 flags 并初始化为 0
129
130 while (isalpha(*str)) { // 当字符串指针所指字符为字母时进行循环
131 if (!strncmp(str, "nohz,", 5)) { // 如果字符串开头为 "nohz,"
132 str += 5; // 字符串指针向后移动 5 个位置
133 flags |= HK_FLAG_TICK; // 对 flags 进行位或操作,设置相应标志位
134 continue; // 继续下一次循环
135 }
136
137 if (!strncmp(str, "domain,", 7)) { // 如果字符串开头为 "domain,"
138 str += 7; // 字符串指针向后移动 7 个位置
139 flags |= HK_FLAG_DOMAIN; // 对 flags 进行位或操作,设置相应标志位
140 continue; // 继续下一次循环
141 }
142
143 pr_warn("isolcpus: Error, unknown flag\n"); // 打印警告信息
144 return 0; // 返回 0
145 }
146
147 /* Default behaviour for isolcpus without flags */ // 对于没有标志的 isolcpus 的默认行为
148 if (!flags) // 如果 flags 为 0
149 flags |= HK_FLAG_DOMAIN; // 对 flags 进行位或操作,设置相应标志位
150
151 return housekeeping_setup(str, flags); // 返回 housekeeping_setup 函数的执行结果
152 }
153 __setup("isolcpus=", housekeeping_isolcpus_setup); // 定义一个设置项 "isolcpus=" ,关联处理函数 housekeeping_isolcpus_setup
内核调度器
ksmd线程作为内核线程,由内核调度器进行调度。内核调度器会根据系统的整体 load和ksmd线程的优先级来决定何时运行ksmd线程。尽管ksmd线程的优先级通常较低,但在配置的 scan 周期到达时,调度器会尝试调度它运行。
start_kernel // 0号线程
-> sched_init // 调度器初始化
-> init_sched_fair_class // cfs_class初始化
-> reset_init
-> kernel_init // 1号线程, sched_normal
-> kernel_init_freeable
-> wait_for_completion(&kthreadd_done) // Wait until kthreadd is all set-up.
-> smp_init // 多核初始化
-> sched_init_smp // 多核调度器初始化
-> sched_init_domains
-> cpumask_and // 排除isolated cpus
-> init_sched_rt_class
-> init_sched_vms_class
-> init_sched_dl_class
-> do_basic_setup
-> do_initcalls
-> subsys_initcall(ksm_init) // ksmd, sched_normal
-> kthreadd // 2号线程,sched_normal
-> complete(&kthreadd_done)
taskset -pc 2
pid 2's current affinity list: 0-95
taskset -pc 510
pid 510's current affinity list: 0-95
rest_init
// vim init/main.c +397
397 static noinline void __ref rest_init(void) // 定义静态内联函数 rest_init
398 {
399 struct task_struct *tsk; // 定义任务结构体指针 tsk
400 int pid; // 定义进程 ID 变量 pid
401
402 rcu_scheduler_starting(); // 启动 RCU 调度器
403 /*
404 * We need to spawn init first so that it obtains pid 1, however // 我们首先需要生成 init 进程,以便它获得 PID 1,然而
405 * the init task will end up wanting to create kthreads, which, if // init 任务最终会想要创建内核线程,如果
406 * we schedule it before we create kthreadd, will OOPS. // 我们在创建 kthreadd 之前对其进行调度,将会出错
407 */
408 pid = kernel_thread(kernel_init, NULL, CLONE_FS); // 创建内核线程 kernel_init,并获取其进程 ID
409 /*
410 * Pin init on the boot CPU. Task migration is not properly working // 将 init 固定在启动 CPU 上。任务迁移尚未正常工作
411 * until sched_init_smp() has been run. It will set the allowed // 直到 sched_init_smp() 运行。将设置
412 * CPUs for init to the non isolated CPUs. // init 到非隔离的 CPU 上
413 */
414 rcu_read_lock(); // 读取锁
415 tsk = find_task_by_pid_ns(pid, &init_pid_ns); // 通过 PID 和命名空间查找任务
416 set_cpus_allowed_ptr(tsk, cpumask_of(smp_processor_id())); // 设置允许的 CPU 掩码
417 rcu_read_unlock(); // 读取解锁
418
419 numa_default_policy(); // 设置 NUMA 默认策略
420 pid = kernel_thread(kthreadd, NULL, CLONE_FS | CLONE_FILES); // 创建 kthreadd 内核线程,并获取其进程 ID
421 rcu_read_lock(); // 读取锁
422 kthreadd_task = find_task_by_pid_ns(pid, &init_pid_ns); // 通过 PID 和命名空间查找 kthreadd 任务
423 rcu_read_unlock(); // 读取解锁
424
425 /*
426 * Enable might_sleep() and smp_processor_id() checks. // 启用 might_sleep() 和 smp_processor_id() 检查
427 * They cannot be enabled earlier because with CONFIG_PREEMPT=y // 它们不能更早启用,因为在 CONFIG_PREEMPT=y 时
428 * kernel_thread() would trigger might_sleep() splats. With // kernel_thread() 会触发 might_sleep() 问题。在
429 * CONFIG_PREEMPT_VOLUNTARY=y the init task might have scheduled // CONFIG_PREEMPT_VOLUNTARY=y 时,init 任务可能已经调度
430 * already, but it's stuck on the kthreadd_done completion. // 但它会卡在 kthreadd_done 完成处
431 */
432 system_state = SYSTEM_SCHEDULING; // 设置系统状态为 SYSTEM_SCHEDULING
433
434 complete(&kthreadd_done); // 完成 kthreadd_done 操作
435
436 /*
437 * The boot idle thread must execute schedule() // 启动空闲线程必须执行 schedule()
438 * at least once to get things moving: // 至少一次以启动进程
439 */
440 schedule_preempt_disabled(); // 执行调度,禁用抢占
441 /* Call into cpu_idle with preempt disabled */ // 以禁用抢占的方式调用 cpu_idle
442 cpu_startup_entry(CPUHP_ONLINE); // CPU 启动入口
443 }
sched_init_numa
1385 void sched_init_numa(void) // 定义一个名为 sched_init_numa 的无返回值函数
1386 {
1387 int next_distance, curr_distance = node_distance(0, 0); // 定义两个整型变量,curr_distance 并初始化为 node_distance(0, 0) 的返回值
1388 struct sched_domain_topology_level *tl; // 定义一个指向结构体 sched_domain_topology_level 的指针
1389 int level = 0; // 定义并初始化整型变量 level 为 0
1390 int i, j, k; // 定义三个整型变量 i, j, k
1391
1392 sched_domains_numa_distance = kzalloc(sizeof(int) * (nr_node_ids + 1), GFP_KERNEL); // 动态分配内存
1393 if (!sched_domains_numa_distance) // 如果分配失败
1394 return; // 直接返回
1395
1396 /* Includes NUMA identity node at level 0. */ // 包含在 0 级的 NUMA 标识节点
1397 sched_domains_numa_distance[level++] = curr_distance; // 为数组元素赋值并递增 level
1398 sched_domains_numa_levels = level; // 更新 sched_domains_numa_levels 的值
1399
1400 /*
1401 * O(nr_nodes^2) deduplicating selection sort -- in order to find the
1402 * unique distances in the node_distance() table.
1403 *
1404 * Assumes node_distance(0,j) includes all distances in
1405 * node_distance(i,j) in order to avoid cubic time.
1406 */
1407 next_distance = curr_distance; // 初始化 next_distance
1408 for (i = 0; i < nr_node_ids; i++) { // 开始一个循环
1409 for (j = 0; j < nr_node_ids; j++) { // 嵌套循环
1410 for (k = 0; k < nr_node_ids; k++) { // 嵌套循环
1411 int distance = node_distance(i, k); // 获取距离值
1412
1413 if (distance > curr_distance && // 条件判断
1414 (distance < next_distance || // 条件判断
1415 next_distance == curr_distance))
1416 next_distance = distance; // 更新 next_distance
1417
1418 /*
1419 * While not a strong assumption it would be nice to know
1420 * about cases where if node A is connected to B, B is not
1421 * equally connected to A.
1422 */
1423 if (sched_debug() && node_distance(k, i)!= distance) // 条件判断
1424 sched_numa_warn("Node-distance not symmetric"); // 调用警告函数
1425
1426 if (sched_debug() && i &&!find_numa_distance(distance)) // 条件判断
1427 sched_numa_warn("Node-0 not representative"); // 调用警告函数
1428 }
1429 if (next_distance!= curr_distance) { // 条件判断
1430 sched_domains_numa_distance[level++] = next_distance; // 赋值并递增 level
1431 sched_domains_numa_levels = level; // 更新值
1432 curr_distance = next_distance; // 更新 curr_distance
1433 } else break; // 否则退出循环
1434 }
1435
1436 /*
1437 * In case of sched_debug() we verify the above assumption.
1438 */
1439 if (!sched_debug()) // 条件判断
1440 break; // 退出循环
1441 }
1442
1443 /*
1444 * 'level' contains the number of unique distances
1445 *
1446 * The sched_domains_numa_distance[] array includes the actual distance
1447 * numbers.
1448 */
1449
1450 /*
1451 * Here, we should temporarily reset sched_domains_numa_levels to 0.
1452 * If it fails to allocate memory for array sched_domains_numa_masks[][],
1453 * the array will contain less then 'level' members. This could be
1454 * dangerous when we use it to iterate array sched_domains_numa_masks[][]
1455 * in other functions.
1456 *
1457 * We reset it to 'level' at the end of this function.
1458 */
1459 sched_domains_numa_levels = 0; // 暂时重置值
1460
1461 sched_domains_numa_masks = kzalloc(sizeof(void *) * level, GFP_KERNEL); // 动态分配内存
1462 if (!sched_domains_numa_masks) // 如果分配失败
1463 return; // 直接返回
1464
1465 /*
1466 * Now for each level, construct a mask per node which contains all
1467 * CPUs of nodes that are that many hops away from us.
1468 */
1469 for (i = 0; i < level; i++) { // 开始一个循环
1470 sched_domains_numa_masks[i] = // 为数组元素赋值
1471 kzalloc(nr_node_ids * sizeof(void *), GFP_KERNEL); // 动态分配内存
1472 if (!sched_domains_numa_masks[i]) // 如果分配失败
1473 return; // 直接返回
1474
1475 for (j = 0; j < nr_node_ids; j++) { // 嵌套循环
1476 struct cpumask *mask = kzalloc(cpumask_size(), GFP_KERNEL); // 动态分配内存
1477 if (!mask) // 如果分配失败
1478 return; // 直接返回
1479
1480 sched_domains_numa_masks[i][j] = mask; // 赋值
1481
1482 for_each_node(k) { // 循环
1483 if (node_distance(j, k) > sched_domains_numa_distance[i]) // 条件判断
1484 continue; // 继续下一次循环
1485
1486 cpumask_or(mask, mask, cpumask_of_node(k)); // 进行位或操作
1487 }
1488 }
1489 }
1490
1491 /* Compute default topology size */ // 计算默认拓扑大小
1492 for (i = 0; sched_domain_topology[i].mask; i++); // 循环
1493
1494 tl = kzalloc((i + level + 1) * // 动态分配内存
1495 sizeof(struct sched_domain_topology_level), GFP_KERNEL); // 动态分配内存
1496 if (!tl) // 如果分配失败
1497 return; // 直接返回
1498
1499 /*
1500 * Copy the default topology bits..
1501 */
1502 for (i = 0; sched_domain_topology[i].mask; i++) // 循环
1503 tl[i] = sched_domain_topology[i]; // 赋值
1504
1505 /*
1506 * Add the NUMA identity distance, aka single NODE.
1507 */
1508 tl[i++] = (struct sched_domain_topology_level){ // 赋值
1509 .mask = sd_numa_mask,
1510 .numa_level = 0,
1511 SD_INIT_NAME(NODE)
1512 };
1513
1514 /*
1515 *.. and append 'j' levels of NUMA goodness.
1516 */
1517 for (j = 1; j < level; i++, j++) { // 循环
1518 tl[i] = (struct sched_domain_topology_level){ // 赋值
1519 .mask = sd_numa_mask,
1520 .sd_flags = cpu_numa_flags,
1521 .flags = SDTL_OVERLAP,
1522 .numa_level = j,
1523 SD_INIT_NAME(NUMA)
1524 };
1525 }
1526
1527 sched_domain_topology = tl; // 赋值
1528
1529 sched_domains_numa_levels = level; // 更新值
1530 sched_max_numa_distance = sched_domains_numa_distance[level - 1]; // 赋值
1531
1532 init_numa_topology_type(); // 调用函数
1533 }
init_numa_topology_type
1333 /*
1334 * A system can have three types of NUMA topology: // 一个系统可以有三种 NUMA 拓扑类型:
1335 * NUMA_DIRECT: all nodes are directly connected, or not a NUMA system // NUMA_DIRECT:所有节点直接相连,或者不是 NUMA 系统
1336 * NUMA_GLUELESS_MESH: some nodes reachable through intermediary nodes // NUMA_GLUELESS_MESH:一些节点通过中间节点可达
1337 * NUMA_BACKPLANE: nodes can reach other nodes through a backplane // NUMA_BACKPLANE:节点可以通过背板到达其他节点
1338 *
1339 * The difference between a glueless mesh topology and a backplane // 无胶网格拓扑和背板之间的区别
1340 * topology lies in whether communication between not directly // 在于不直接
1341 * connected nodes goes through intermediary nodes (where programs // 连接的节点之间的通信是否通过中间节点(程序
1342 * could run), or through backplane controllers. This affects // 可以运行),还是通过背板控制器。这会影响
1343 * placement of programs. // 程序的放置
1344 *
1345 * The type of topology can be discerned with the following tests: // 拓扑类型可以通过以下测试来辨别
1346 * - If the maximum distance between any nodes is 1 hop, the system // - 如果任意节点之间的最大距离为 1 跳,系统
1347 * is directly connected. // 是直接连接的
1348 * - If for two nodes A and B, located N > 1 hops away from each other, // - 如果对于两个节点 A 和 B,彼此距离 N > 1 跳
1349 * there is an intermediary node C, which is < N hops away from both // 存在一个中间节点 C,它距离 A 和 B 都小于 N 跳
1350 * nodes A and B, the system is a glueless mesh. // 系统是无胶网格
1351 */
1352 static void init_numa_topology_type(void) // 定义一个静态的无返回值函数 init_numa_topology_type
1353 {
1354 int a, b, c, n; // 定义四个整型变量 a, b, c, n
1355
1356 n = sched_max_numa_distance; // 为 n 赋值
1357
1358 if (sched_domains_numa_levels <= 2) { // 如果条件成立
1359 sched_numa_topology_type = NUMA_DIRECT; // 赋值
1360 return; // 返回
1361 }
1362
1363 for_each_online_node(a) { // 开始循环
1364 for_each_online_node(b) { // 嵌套循环
1365 /* Find two nodes furthest removed from each other. */ // 找到彼此距离最远的两个节点
1366 if (node_distance(a, b) < n) // 如果条件成立
1367 continue; // 继续下一次循环
1368
1369 /* Is there an intermediary node between a and b? */ // a 和 b 之间是否存在中间节点?
1370 for_each_online_node(c) { // 嵌套循环
1371 if (node_distance(a, c) < n && // 如果条件成立
1372 node_distance(b, c) < n) { // 如果条件成立
1373 sched_numa_topology_type = // 赋值
1374 NUMA_GLUELESS_MESH;
1375 return; // 返回
1376 }
1377 }
1378
1379 sched_numa_topology_type = NUMA_BACKPLANE; // 赋值
1380 return; // 返回
1381 }
1382 }
1383 }
kernel_thread
// vim kernel/fork.c +2348
2348 /*
2349 * Create a kernel thread.
2350 */
2351 pid_t kernel_thread(int (*fn)(void *), void *arg, unsigned long flags)
2352 {
2353 return _do_fork(flags|CLONE_VM|CLONE_UNTRACED, (unsigned long)fn,
2354 (unsigned long)arg, NULL, NULL, 0);
2355 }
_do_fork
// vim kernel/fork.c +2257
2257 /*
2258 * Ok, this is the main fork-routine.
2259 *
2260 * It copies the process, and if successful kick-starts
2261 * it and waits for it to finish using the VM if required.
2262 */
2263 long _do_fork(unsigned long clone_flags,
2264 unsigned long stack_start,
2265 unsigned long stack_size,
2266 int __user *parent_tidptr,
2267 int __user *child_tidptr,
2268 unsigned long tls)
2269 {
2270 struct completion vfork;
2271 struct pid *pid;
2272 struct task_struct *p;
2273 int trace = 0;
2274 long nr;
2275
2276 /*
2277 * Determine whether and which event to report to ptracer. When
2278 * called from kernel_thread or CLONE_UNTRACED is explicitly
2279 * requested, no event is reported; otherwise, report if the event
2280 * for the type of forking is enabled.
2281 */
2282 if (!(clone_flags & CLONE_UNTRACED)) {
2283 if (clone_flags & CLONE_VFORK)
2284 trace = PTRACE_EVENT_VFORK;
2285 else if ((clone_flags & CSIGNAL) != SIGCHLD)
2286 trace = PTRACE_EVENT_CLONE;
2287 else
2288 trace = PTRACE_EVENT_FORK;
2289
2290 if (likely(!ptrace_event_enabled(current, trace)))
2291 trace = 0;
2292 }
2293
2294 p = copy_process(clone_flags, stack_start, stack_size,
2295 child_tidptr, NULL, trace, tls, NUMA_NO_NODE);
2296 add_latent_entropy();
2297
2298 if (IS_ERR(p))
2299 return PTR_ERR(p);
2300
2301 /*
2302 * Do this prior waking up the new thread - the thread pointer
2303 * might get invalid after that point, if the thread exits quickly.
2304 */
2305 trace_sched_process_fork(current, p);
2306
2307 pid = get_task_pid(p, PIDTYPE_PID);
2308 nr = pid_vnr(pid);
2309
2310 if (clone_flags & CLONE_PARENT_SETTID)
2311 put_user(nr, parent_tidptr);
2312
2313 if (clone_flags & CLONE_VFORK) {
2314 p->vfork_done = &vfork;
2315 init_completion(&vfork);
2316 get_task_struct(p);
2317 }
2318
2319 wake_up_new_task(p);
2320
2321 /* forking complete and child started to run, tell ptracer */
2322 if (unlikely(trace))
2323 ptrace_event_pid(trace, pid);
2324
2325 if (clone_flags & CLONE_VFORK) {
2326 if (!wait_for_vfork_done(p, &vfork))
2327 ptrace_event_pid(PTRACE_EVENT_VFORK_DONE, pid);
2328 }
2329
2330 put_pid(pid);
2331 return nr;
2332 }
wake_up_new_task
// vim kernel/sched/core.c +2420
2420 * wake_up_new_task - wake up a newly created task for the first time. // wake_up_new_task - 首次唤醒新创建的任务
2421 *
2422 * This function will do some initial scheduler statistics housekeeping // 此函数将进行一些初始的调度器统计维护工作
2423 * that must be done for every newly created context, then puts the task // 这些工作必须为每个新创建的上下文完成,然后将任务
2424 * on the runqueue and wakes it. // 放入运行队列并唤醒它
2425 */
2426 void wake_up_new_task(struct task_struct *p) // 定义 wake_up_new_task 函数,参数为任务结构体指针 p
2427 { // 函数体开始
2428 struct rq_flags rf; // 定义 rq_flags 结构体变量 rf
2429 struct rq *rq; // 定义 rq 结构体指针 rq
2430
2431 raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&p->pi_lock, rf.flags); // 上锁并保存中断状态
2432 p->state = TASK_RUNNING; // 设置任务状态为运行
2433 #ifdef CONFIG_SMP // 如果定义了 CONFIG_SMP
2434 /*
2435 * Fork balancing, do it here and not earlier because: // 分叉平衡,在此处进行而不是更早,因为:
2436 * - cpus_allowed can change in the fork path // 在分叉路径中 cpus_allowed 可能会改变
2437 * - any previously selected CPU might disappear through hotplug // 任何先前选择的 CPU 可能因热插拔而消失
2438 *
2439 * Use __set_task_cpu() to avoid calling sched_class::migrate_task_rq, // 使用 __set_task_cpu() 避mian调用 sched_class::migrate_task_rq
2440 * as we're not fully set-up yet. // 因为我们还没有完全设置好
2441 */
2442 p->recent_used_cpu = task_cpu(p); // 设置最近使用的 CPU
2443 rseq_migrate(p); // 进行 rseq 迁移
2444 __set_task_cpu(p, select_task_rq(p, task_cpu(p), SD_BALANCE_FORK, 0)); // 设置任务的 CPU
2445 #endif // 结束 CONFIG_SMP 条件编译
2446 rq = __task_rq_lock(p, &rf); // 锁定任务的运行队列
2447 update_rq_clock(rq); // 更新运行队列的时钟
2448 post_init_entity_util_avg(&p->se); // 初始化实体的平均利用率
2449
2450 activate_task(rq, p, ENQUEUE_NOCLOCK); // 激活任务
2451 p->on_rq = TASK_ON_RQ_QUEUED; // 设置任务在运行队列的状态
2452 trace_sched_wakeup_new(p); // 跟踪调度器的唤醒新任务
2453 check_preempt_curr(rq, p, WF_FORK); // 检查抢占当前任务
2454 #ifdef CONFIG_SMP // 如果定义了 CONFIG_SMP
2455 if (p->sched_class->task_woken) { // 如果任务的调度类有 task_woken 函数
2456 /*
2457 * Nothing relies on rq->lock after this, so its fine to // 在此之后没有依赖 rq->lock,所以可以
2458 * drop it. // 释放它
2459 */
2460 rq_unpin_lock(rq, &rf); // 解锁运行队列
2461 p->sched_class->task_woken(rq, p); // 调用调度类的 task_woken 函数
2462 rq_repin_lock(rq, &rf); // 重新锁定运行队列
2463 }
2464 #endif // 结束 CONFIG_SMP 条件编译
2465 task_rq_unlock(rq, p, &rf); // 解锁任务的运行队列
2466 }
select_task_rq_fair
:cl
9 kernel/sched/core.c:2066: <<try_to_wake_up>> cpu = select_task_rq(p, p->wake_cpu, SD_BALANCE_WAKE, wake_flags);
10 kernel/sched/core.c:2444: <<wake_up_new_task>> __set_task_cpu(p, select_task_rq(p, task_cpu(p), SD_BALANCE_FORK, 0));
11 kernel/sched/core.c:2994: <<sched_exec>> dest_cpu = p->sched_class->select_task_rq(p, task_cpu(p), SD_BALANCE_EXEC, 0);
// vim CTKernel/kernel/sched/fair.c +6437
6424 /*
6425 * select_task_rq_fair: 为具有设置“sd_flag”标志的域中的唤醒任务选择目标运行队列
6426 * 在实践中,这是 SD_BALANCE_WAKE、SD_BALANCE_FORK 或 SD_BALANCE_EXEC
6427 *
6428 * 通过选择最空闲组中的最空闲 CPU 来平衡 load,或者在某些条件下,如果域设置了 SD_WAKE_AFFINE,则选择空闲的兄弟 CPU
6429 *
6430 * 返回目标 CPU 编号
6431 *
6432 * 必须禁用抢占
6433 */
6434 static int // 声明静态整型函数
6435 select_task_rq_fair(struct task_struct *p, int prev_cpu, int sd_flag, int wake_flags) // 函数定义,接收任务结构体指针、前一个 CPU 编号、标志和唤醒标志
6436 {
6437 struct sched_domain *tmp, *sd = NULL; // 定义调度域结构体指针 tmp 和 sd,并初始化为 NULL
6438 int cpu = smp_processor_id(); // 获取当前 CPU 编号
6439 int new_cpu = prev_cpu; // 新的 CPU 编号初始化为前一个 CPU 编号
6440 int want_affine = 0; // 初始化是否想要亲和性为 0
6441 int sync = (wake_flags & WF_SYNC) &&!(current->flags & PF_EXITING); // 根据条件计算同步标志
6442
6443 if (sd_flag & SD_BALANCE_WAKE) { // 如果标志包含 SD_BALANCE_WAKE
6444 record_wakee(p); // 记录唤醒的任务
6445 want_affine =!wake_wide(p) &&!wake_cap(p, cpu, prev_cpu) // 根据条件设置是否想要亲和性
6446 && cpumask_test_cpu(cpu, &p->cpus_allowed);
6447 }
6448
6449 rcu_read_lock(); // 读锁
6450 for_each_domain(cpu, tmp) { // 遍历调度域
6451 if (!(tmp->flags & SD_LOAD_BALANCE)) // 如果域没有 load均衡标志
6452 break; // 跳出循环
6453
6454 /*
6455 * 如果“cpu”和“prev_cpu”都是这个域的一部分,
6456 * “cpu”是有效的 SD_WAKE_AFFINE 目标。
6457 */
6458 if (want_affine && (tmp->flags & SD_WAKE_AFFINE) && // 如果想要亲和性且域有相应标志
6459 cpumask_test_cpu(prev_cpu, sched_domain_span(tmp))) { // 且前一个 CPU 在域范围内
6460 if (cpu!= prev_cpu) // 如果当前 CPU 与前一个 CPU 不同
6461 new_cpu = wake_affine(tmp, p, cpu, prev_cpu, sync); // 执行亲和性相关操作
6462
6463 sd = NULL; /* 优先选择 wake_affine 而不是平衡标志 */
6464 break; // 跳出循环
6465 }
6466
6467 if (tmp->flags & sd_flag) // 如果域具有指定标志
6468 sd = tmp; // 赋值给 sd
6469 else if (!want_affine) // 否则如果不想要亲和性
6470 break; // 跳出循环
6471 }
6472
6473 if (unlikely(sd)) { // 如果不太可能出现的情况:sd 不为空
6474 /* 慢路径 */
6475 new_cpu = find_idlest_cpu(sd, p, cpu, prev_cpu, sd_flag); // 查找最空闲的 CPU
6476 } else if (sd_flag & SD_BALANCE_WAKE) {
6477 /* 快路径 */
6478
6479 new_cpu = select_idle_sibling(p, prev_cpu, new_cpu); // 选择空闲的兄弟 CPU
6480
6481 if (want_affine) // 如果想要亲和性
6482 current->recent_used_cpu = cpu; // 更新最近使用的 CPU
6483 }
6484 rcu_read_unlock(); // 读解锁
6485
6486 return new_cpu; // 返回新的 CPU 编号
6487 }
// vim CTKernel/include/linux/sched/topology.h +20
20 #define SD_LOAD_BALANCE 0x0001 /* Do load balancing on this domain. */
21 #define SD_BALANCE_NEWIDLE 0x0002 /* Balance when about to become idle */
22 #define SD_BALANCE_EXEC 0x0004 /* Balance on exec */
23 #define SD_BALANCE_FORK 0x0008 /* Balance on fork, clone */
24 #define SD_BALANCE_WAKE 0x0010 /* Balance on wakeup */
25 #define SD_WAKE_AFFINE 0x0020 /* Wake task to waking CPU */
26 #define SD_ASYM_CPUCAPACITY 0x0040 /* Groups have different max cpu capacities */
27 #define SD_SHARE_CPUCAPACITY 0x0080 /* Domain members share cpu capacity */
28 #define SD_SHARE_POWERDOMAIN 0x0100 /* Domain members share power domain */
29 #define SD_SHARE_PKG_RESOURCES 0x0200 /* Domain members share cpu pkg resources */
30 #define SD_SERIALIZE 0x0400 /* Only a single load balancing instance */
31 #define SD_ASYM_PACKING 0x0800 /* Place busy groups earlier in the domain */
32 #define SD_PREFER_SIBLING 0x1000 /* Prefer to place tasks in a sibling domain */
33 #define SD_OVERLAP 0x2000 /* sched_domains of this level overlap */
34 #define SD_NUMA 0x4000 /* cross-node balancing */
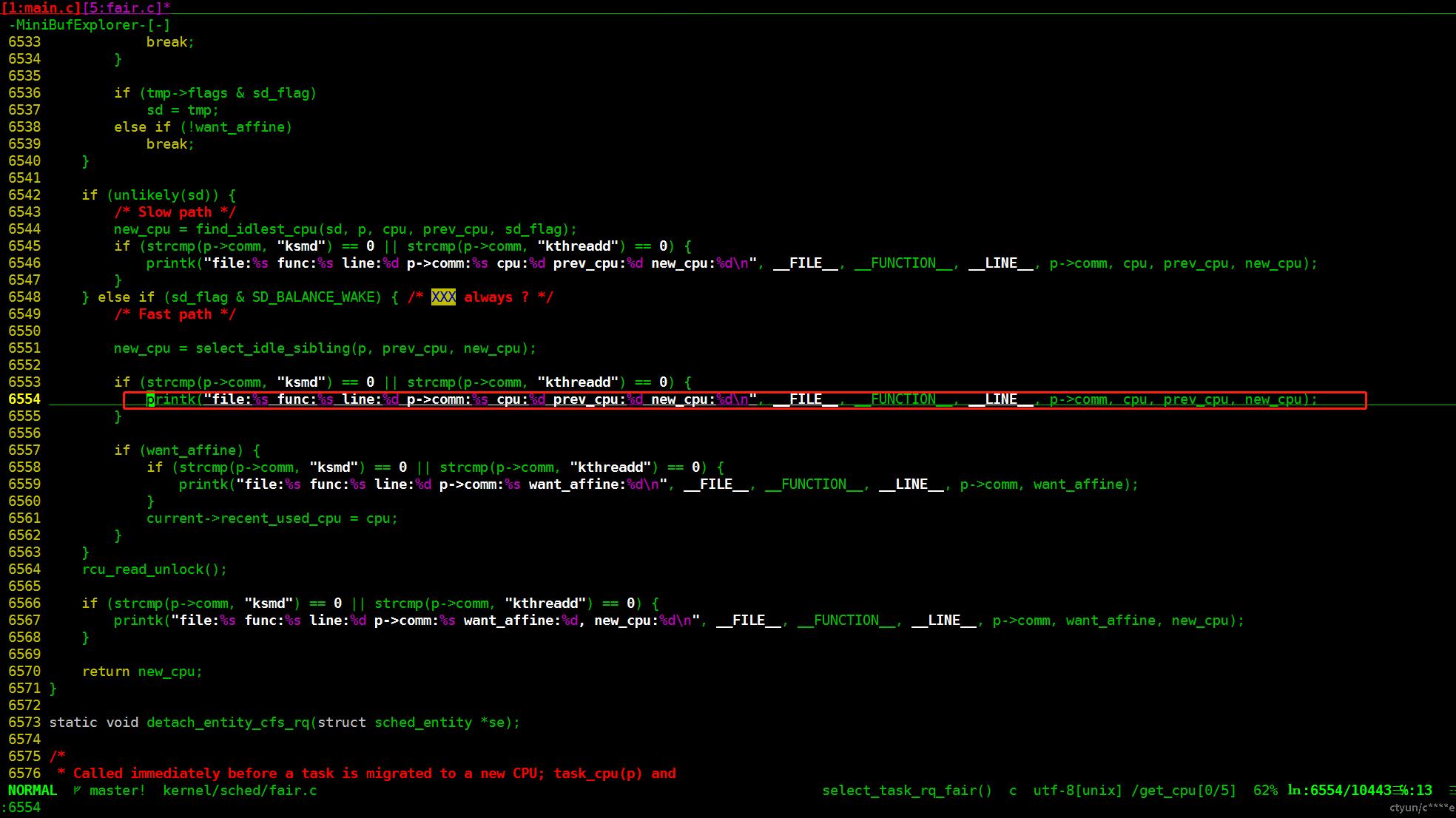
select_idle_sibling
6258 /*
6259 * Try and locate an idle core/thread in the LLC cache domain. // 尝试在 LLC 缓存域中定位一个空闲的核心/线程
6260 */
6261 static int select_idle_sibling(struct task_struct *p, int prev, int target) // 定义一个静态函数 select_idle_sibling ,接收任务结构体指针、两个整型参数
6262 {
6263 struct sched_domain *sd; // 定义一个调度域结构体指针
6264 int i, recent_used_cpu; // 定义两个整型变量
6265
6266 if (available_idle_cpu(target)) // 如果目标 CPU 可用且空闲
6267 return target; // 返回目标 CPU
6268
6269 /*
6270 * If the previous CPU is cache affine and idle, don't be stupid: // 如果前一个 CPU 与缓存相关且空闲,别犯傻
6271 */
6272 if (prev!= target && cpus_share_cache(prev, target) && available_idle_cpu(prev)) // 如果前一个 CPU 满足条件
6273 return prev; // 返回前一个 CPU
6274
6275 /* Check a recently used CPU as a potential idle candidate: */ // 检查最近使用的 CPU 作为潜在的空闲候选
6276 recent_used_cpu = p->recent_used_cpu; // 获取最近使用的 CPU
6277 if (recent_used_cpu!= prev && // 如果最近使用的 CPU 满足条件
6278 recent_used_cpu!= target &&
6279 cpus_share_cache(recent_used_cpu, target) &&
6280 available_idle_cpu(recent_used_cpu) &&
6281 cpumask_test_cpu(p->recent_used_cpu, &p->cpus_allowed)) {
6282 /*
6283 * Replace recent_used_cpu with prev as it is a potential
6284 * candidate for the next wake: // 因为前一个 CPU 是潜在的候选,所以替换最近使用的 CPU
6285 */
6286 p->recent_used_cpu = prev; // 进行替换
6287 return recent_used_cpu; // 返回最近使用的 CPU
6288 }
6289
6290 sd = rcu_dereference(per_cpu(sd_llc, target)); // 获取与目标 CPU 相关的调度域
6291 if (!sd) // 如果获取失败
6292 return target; // 返回目标 CPU
6293
6294 i = select_idle_core(p, sd, target); // 执行一个选择空闲核心的操作
6295 if ((unsigned)i < nr_cpumask_bits) // 如果结果满足条件
6296 return i; // 返回结果
6297
6298 i = select_idle_cpu(p, sd, target); // 执行一个选择空闲 CPU 的操作
6299 if ((unsigned)i < nr_cpumask_bits) // 如果结果满足条件
6300 return i; // 返回结果
6301
6302 i = select_idle_smt(p, sd, target); // 执行一个选择空闲 SMT 的操作
6303 if ((unsigned)i < nr_cpumask_bits) // 如果结果满足条件
6304 return i; // 返回结果
6305
6306 return target; // 否则返回目标 CPU
6307 }
kthreadd
// vim kernel/kthread.c +569
569 int kthreadd(void *unused) // 定义 kthreadd 函数,参数为 void 指针 unused
570 {
571 struct task_struct *tsk = current; // 获取当前任务结构体指针并赋值给 tsk
572
573 /* Setup a clean context for our children to inherit. */ // 为子进程设置一个干净的上下文以供继承
574 set_task_comm(tsk, "kthreadd"); // 设置任务的名称为 "kthreadd"
575 ignore_signals(tsk); // 忽略信号
576 set_cpus_allowed_ptr(tsk, cpu_all_mask); // 设置允许的 CPU
577 set_mems_allowed(node_states[N_MEMORY]); // 设置允许的内存
578
579 current->flags |= PF_NOFREEZE; // 设置当前进程的标志位 PF_NOFREEZE
580 cgroup_init_kthreadd(); // 初始化 cgroup 相关的 kthreadd
581
582 for (;;) { // 无限循环
583 set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE); // 设置当前状态为可中断等待
584 if (list_empty(&kthread_create_list)) // 如果 kthread_create_list 为空
585 schedule(); // 进行调度
586 __set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING); // 设置当前状态为运行
587
588 spin_lock(&kthread_create_lock); // 加自旋锁
589 while (!list_empty(&kthread_create_list)) { // 当 kthread_create_list 不为空时
590 struct kthread_create_info *create; // 定义 kthread_create_info 结构体指针 create
591
592 create = list_entry(kthread_create_list.next, // 获取列表中的元素
593 struct kthread_create_info, list); // 并将其赋值给 create
594 list_del_init(&create->list); // 从列表中删除并初始化
595 spin_unlock(&kthread_create_lock); // 释放自旋锁
596
597 create_kthread(create); // 创建线程
598
599 spin_lock(&kthread_create_lock); // 加自旋锁
600 } // 结束内层 while 循环
601 spin_unlock(&kthread_create_lock); // 释放自旋锁
602 } // 结束无限 for 循环
603
604 return 0; // 返回 0
605 }
create_kthread
271 static void create_kthread(struct kthread_create_info *create) // 定义静态函数 create_kthread,参数为 kthread_create_info 结构体指针
272 {
273 int pid; // 定义进程 ID 变量
274
275 #ifdef CONFIG_NUMA // 如果定义了 CONFIG_NUMA
276 current->pref_node_fork = create->node; // 设置当前进程的偏好节点为传入的节点
277 #endif // 结束 CONFIG_NUMA 条件编译
278 /* We want our own signal handler (we take no signals by default). */ // 我们想要自己的信号处理程序(默认不接收信号)
279 pid = kernel_thread(kthread, create, CLONE_FS | CLONE_FILES | SIGCHLD); // 创建内核线程,并获取进程 ID
280 if (pid < 0) { // 如果进程 ID 小于 0
281 /* If user was SIGKILLed, I release the structure. */ // 如果用户被 SIGKILL 信号终止,释放结构
282 struct completion *done = xchg(&create->done, NULL); // 交换并获取完成变量
283 __se tate(TASK_RUNNING); // 设置任务状态为运行
284 if (!done) { // 如果完成变量为空
285 kfree(create); // 释放创建信息结构体的内存
286 return; // 返回
287 }
288 create->result = ERR_PTR(pid); // 设置创建结果为错误指针
289 complete(done); // 完成操作
290 }
291 }
ksm_init
// vim mm/ksm.c +3172
3172 static int __init ksm_init(void)
3173 {
3174 struct task_struct *ksm_thread;
3175 int err;
3176
3177 /* The correct value depends on page size and endianness */
3178 zero_checksum = calc_checksum(ZERO_PAGE(0));
3179 /* Default to false for backwards compatibility */
3180 ksm_use_zero_pages = false;
3181
3182 err = ksm_slab_init();
3183 if (err)
3184 goto out;
3185
3186 ksm_thread = kthread_run(ksm_scan_thread, NULL, "ksmd");
3187 if (IS_ERR(ksm_thread)) {
3188 pr_err("ksm: creating kthread failed\n");
3189 err = PTR_ERR(ksm_thread);
3190 goto out_free;
3191 }
3192
3193 #ifdef CONFIG_SYSFS
3194 err = sysfs_create_group(mm_kobj, &ksm_attr_group);
3195 if (err) {
3196 pr_err("ksm: register sysfs failed\n");
3197 kthread_stop(ksm_thread);
3198 goto out_free;
3199 }
3200 #else
3201 ksm_run = KSM_RUN_MERGE; /* no way for user to start it */
3202
3203 #endif /* CONFIG_SYSFS */
3204
3205 #ifdef CONFIG_MEMORY_HOTREMOVE
3206 /* There is no significance to this priority 100 */
3207 hotplug_memory_notifier(ksm_memory_callback, 100);
3208 #endif
3209 return 0;
3210
3211 out_free:
3212 ksm_slab_free();
3213 out:
3214 return err;
3215 }
// vim include/linux/kthread.h +34
34 /**
35 * kthread_run - create and wake a thread.
36 * @threadfn: the function to run until signal_pending(current).
37 * @data: data ptr for @threadfn.
38 * @namefmt: printf-style name for the thread.
39 *
40 * Description: Convenient wrapper for kthread_create() followed by
41 * wake_up_process(). Returns the kthread or ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM).
42 */
43 #define kthread_run(threadfn, data, namefmt, ...) \
44 ({ \
45 struct task_struct *__k \
46 = kthread_create(threadfn, data, namefmt, ## __VA_ARGS__); \
47 if (!IS_ERR(__k)) \
48 wake_up_process(__k); \
49 __k; \
50 })
kthread_create
// vim include/linux/kthread.h +14
14 /**
15 * kthread_create - create a kthread on the current node
16 * @threadfn: the function to run in the thread
17 * @data: data pointer for @threadfn()
18 * @namefmt: printf-style format string for the thread name
19 * @arg...: arguments for @namefmt.
20 *
21 * This macro will create a kthread on the current node, leaving it in
22 * the stopped state. This is just a helper for kthread_create_on_node();
23 * see the documentation there for more details.
24 */
25 #define kthread_create(threadfn, data, namefmt, arg...) \
26 kthread_create_on_node(threadfn, data, NUMA_NO_NODE, namefmt, ##arg)
kthread_create_on_node
// kernel/kthread.c +357
357 /**
358 * kthread_create_on_node - create a kthread.
359 * @threadfn: the function to run until signal_pending(current).
360 * @data: data ptr for @threadfn.
361 * @node: task and thread structures for the thread are allocated on this node
362 * @namefmt: printf-style name for the thread.
363 *
364 * Description: This helper function creates and names a kernel
365 * thread. The thread will be stopped: use wake_up_process() to start
366 * it. See also kthread_run(). The new thread has SCHED_NORMAL policy and
368 *
369 * If thread is going to be bound on a particular cpu, give its node
370 * in @node, to get NUMA affinity for kthread stack, or else give NUMA_NO_NODE.
371 * When woken, the thread will run @threadfn() with @data as its
372 * argument. @threadfn() can either call do_exit() directly if it is a
373 * standalone thread for which no one will call kthread_stop(), or
374 * return when 'kthread_should_stop()' is true (which means
375 * kthread_stop() has been called). The return value should be zero
376 * or a negative error number; it will be passed to kthread_stop().
377 *
378 * Returns a task_struct or ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM) or ERR_PTR(-EINTR).
379 */
380 struct task_struct *kthread_create_on_node(int (*threadfn)(void *data),
381 void *data, int node,
382 const char namefmt[],
383 ...)
384 {
385 struct task_struct *task;
386 va_list args;
387
388 va_start(args, namefmt);
389 task = __kthread_create_on_node(threadfn, data, node, namefmt, args);
390 va_end(args);
391
392 return task;
393 }
394 EXPORT_SYMBOL(kthread_create_on_node);
__kthread_create_on_node
293 static __printf(4, 0)
294 struct task_struct *__kthread_create_on_node(int (*threadfn)(void *data),
295 void *data, int node,
296 const char namefmt[],
297 va_list args)
298 {
299 DECLARE_COMPLETION_ONSTACK(done);
300 struct task_struct *task;
301 struct kthread_create_info *create = kmalloc(sizeof(*create),
302 GFP_KERNEL);
303
304 if (!create)
305 return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
306 create->threadfn = threadfn;
307 create->data = data;
308 create->node = node;
309 create->done = &done;
310
311 spin_lock(&kthread_create_lock);
312 list_add_tail(&create->list, &kthread_create_list);
313 spin_unlock(&kthread_create_lock);
314
315 wake_up_process(kthreadd_task);
316 /*
317 * Wait for completion in killable state, for I might be chosen by
318 * the OOM killer while kthreadd is trying to allocate memory for
319 * new kernel thread.
320 */
321 if (unlikely(wait_for_completion_killable(&done))) {
322 /*
323 * If I was SIGKILLed before kthreadd (or new kernel thread)
324 * calls complete(), leave the cleanup of this structure to
325 * that thread.
326 */
327 if (xchg(&create->done, NULL))
328 return ERR_PTR(-EINTR);
329 /*
330 * kthreadd (or new kernel thread) will call complete()
331 * shortly.
332 */
333 wait_for_completion(&done);
334 }
335 task = create->result;
336 if (!IS_ERR(task)) {
337 static const struct sched_param param = { .sched_priority = 0 };
338 char name[TASK_COMM_LEN];
339
340 /*
341 * task is already visible to other tasks, so updating
342 * COMM must be protected.
343 */
344 vsnprintf(name, sizeof(name), namefmt, args);
345 set_task_comm(task, name);
346 /*
347 * root may have changed our (kthreadd's) priority or CPU mask.
348 * The kernel thread should not inherit these properties.
349 */
350 sched_setscheduler_nocheck(task, SCHED_NORMAL, ¶m);
351 set_cpus_allowed_ptr(task, cpu_all_mask);
352 }
353 kfree(create);
354 return task;
wake_up_process
2141 /**
2142 * wake_up_process - Wake up a specific process
2143 * @p: The process to be woken up.
2144 *
2145 * Attempt to wake up the nominated process and move it to the set of runnable
2146 * processes.
2147 *
2148 * Return: 1 if the process was woken up, 0 if it was already running.
2149 *
2150 * This function executes a full memory barrier before accessing the task state.
2151 */
2152 int wake_up_process(struct task_struct *p)
2153 {
2154 return try_to_wake_up(p, TASK_NORMAL, 0);
2155 }
2156 EXPORT_SYMBOL(wake_up_process);
try_to_wake_up
1959 /**
1960 * try_to_wake_up - wake up a thread
1961 * @p: the thread to be awakened
1962 * @state: the mask of task states that can be woken
1963 * @wake_flags: wake modifier flags (WF_*)
1964 *
1965 * If (@state & @p->state) @p->state = TASK_RUNNING.
1966 *
1967 * If the task was not queued/runnable, also place it back on a runqueue.
1968 *
1969 * Atomic against schedule() which would dequeue a task, also see
1970 * set_current_state().
1971 *
1972 * This function executes a full memory barrier before accessing the task
1973 * state; see set_current_state().
1974 *
1975 * Return: %true if @p->state changes (an actual wakeup was done),
1976 * %false otherwise.
1977 */
1978 static int
1979 try_to_wake_up(struct task_struct *p, unsigned int state, int wake_flags)
1980 {
1981 unsigned long flags;
1982 int cpu, success = 0;
1983
1984 /*
1985 * If we are going to wake up a thread waiting for CONDITION we
1986 * need to ensure that CONDITION=1 done by the caller can not be
1987 * reordered with p->state check below. This pairs with mb() in
1988 * set_current_state() the waiting thread does.
1989 */
1990 raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&p->pi_lock, flags);
1991 smp_mb__after_spinlock();
1992 if (!(p->state & state))
1993 goto out;
1994
1995 trace_sched_waking(p);
1996
1997 /* We're going to change ->state: */
1998 success = 1;
1999 cpu = task_cpu(p);
2000
2001 /*
2002 * Ensure we load p->on_rq _after_ p->state, otherwise it would
2003 * be possible to, falsely, observe p->on_rq == 0 and get stuck
2004 * in smp_cond_load_acquire() below.
2005 *
2006 * sched_ttwu_pending() try_to_wake_up()
2007 * STORE p->on_rq = 1 LOAD p->state
2008 * UNLOCK rq->lock
2009 *
2010 * __schedule() (switch to task 'p')
2011 * LOCK rq->lock smp_rmb();
2012 * smp_mb__after_spinlock();
2013 * UNLOCK rq->lock
2014 *
2015 * [task p]
2016 * STORE p->state = UNINTERRUPTIBLE LOAD p->on_rq
2017 *
2018 * Pairs with the LOCK+smp_mb__after_spinlock() on rq->lock in
2019 * __schedule(). See the comment for smp_mb__after_spinlock().
2020 */
2021 smp_rmb();
2022 if (p->on_rq && ttwu_remote(p, wake_flags))
2023 goto stat;
2024
2025 #ifdef CONFIG_SMP
2026 /*
2027 * Ensure we load p->on_cpu _after_ p->on_rq, otherwise it would be
2028 * possible to, falsely, observe p->on_cpu == 0.
2029 *
2030 * One must be running (->on_cpu == 1) in order to remove oneself
2031 * from the runqueue.
2032 *
2033 * __schedule() (switch to task 'p') try_to_wake_up()
2034 * STORE p->on_cpu = 1 LOAD p->on_rq
2035 * UNLOCK rq->lock
2036 *
2037 * __schedule() (put 'p' to sleep)
2038 * LOCK rq->lock smp_rmb();
2039 * smp_mb__after_spinlock();
2040 * STORE p->on_rq = 0 LOAD p->on_cpu
2041 *
2042 * Pairs with the LOCK+smp_mb__after_spinlock() on rq->lock in
2043 * __schedule(). See the comment for smp_mb__after_spinlock().
2044 */
2045 smp_rmb();
2046
2047 /*
2048 * If the owning (remote) CPU is still in the middle of schedule() with
2049 * this task as prev, wait until its done referencing the task.
2050 *
2051 * Pairs with the smp_store_release() in finish_task().
2052 *
2053 * This ensures that tasks getting woken will be fully ordered against
2054 * their previous state and preserve Program Order.
2055 */
2056 smp_cond_load_acquire(&p->on_cpu, !VAL);
2057
2058 p->sched_contributes_to_load = !!task_contributes_to_load(p);
2059 p->state = TASK_WAKING;
2060
2061 if (p->in_iowait) {
2062 delayacct_blkio_end(p);
2063 atomic_dec(&task_rq(p)->nr_iowait);
2064 }
2065
2066 cpu = select_task_rq(p, p->wake_cpu, SD_BALANCE_WAKE, wake_flags);
2067 if (task_cpu(p) != cpu) {
2068 wake_flags |= WF_MIGRATED;
2069 psi_ttwu_dequeue(p);
2070 set_task_cpu(p, cpu);
2071 }
2072
2073 #else /* CONFIG_SMP */
2074
2075 if (p->in_iowait) {
2076 delayacct_blkio_end(p);
2077 atomic_dec(&task_rq(p)->nr_iowait);
2078 }
2079
2080 #endif /* CONFIG_SMP */
2081
2082 ttwu_queue(p, cpu, wake_flags);
2083 stat:
2084 ttwu_stat(p, cpu, wake_flags);
2085 out:
2086 raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&p->pi_lock, flags);
2087
2088 return success;
2089 }
修复方案
bug复现
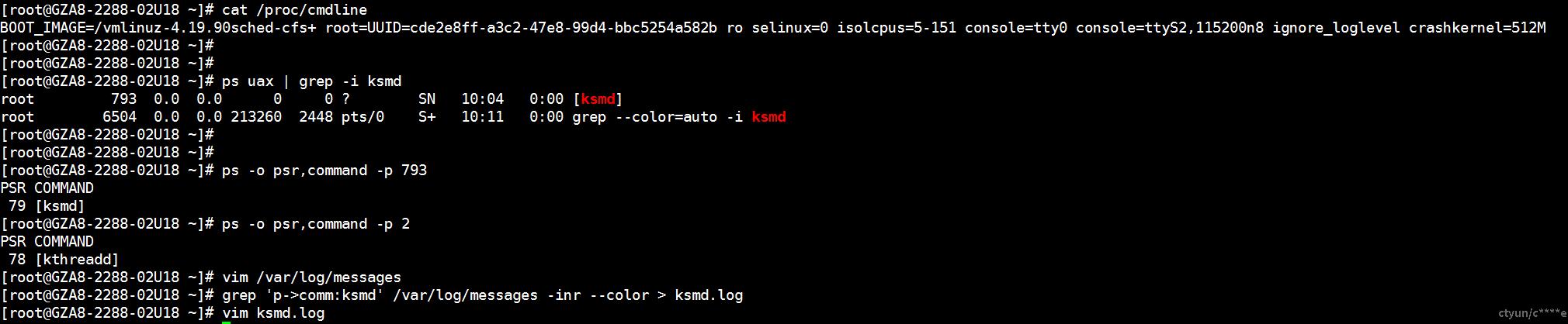
0号进程
查看系统初始化smp多核心前0号进程位于哪个cpu上:
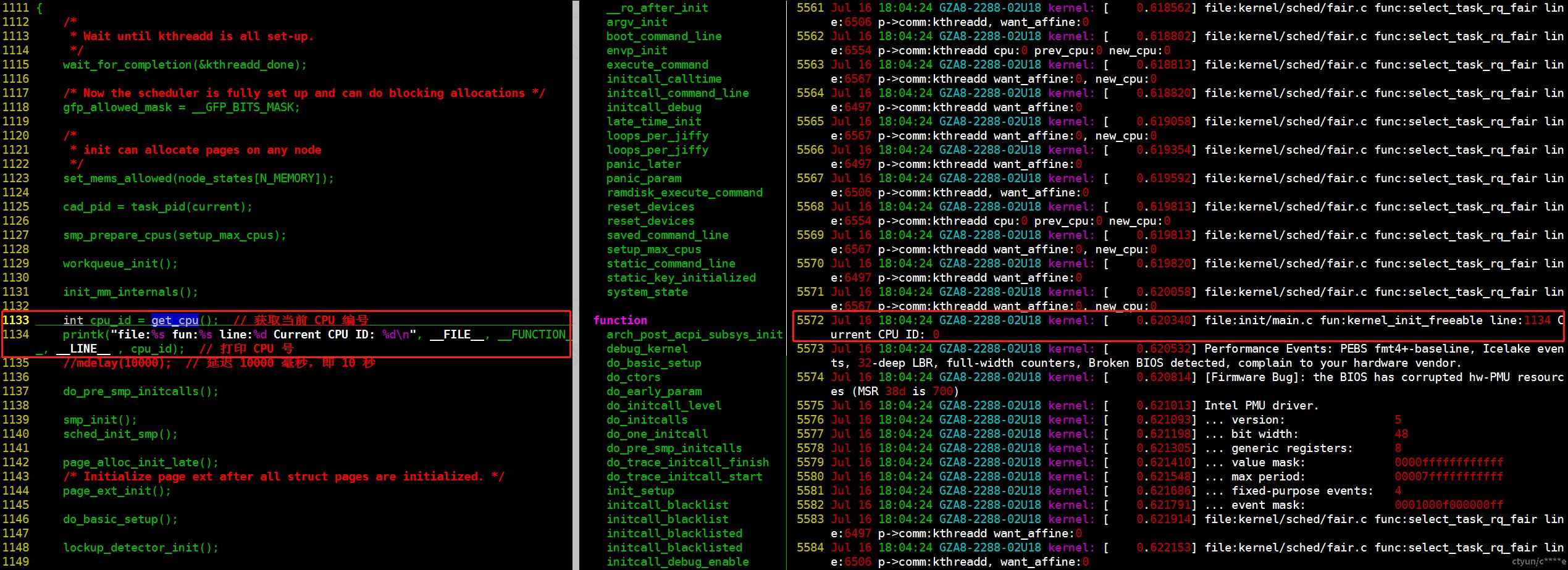
ksmd
从/var/log/messages中查看ksmd被调度到隔离核心上的日志:
grep 'p->comm:ksmd' /var/log/messages -inr --color > ksmd.log
vim ksmd.log
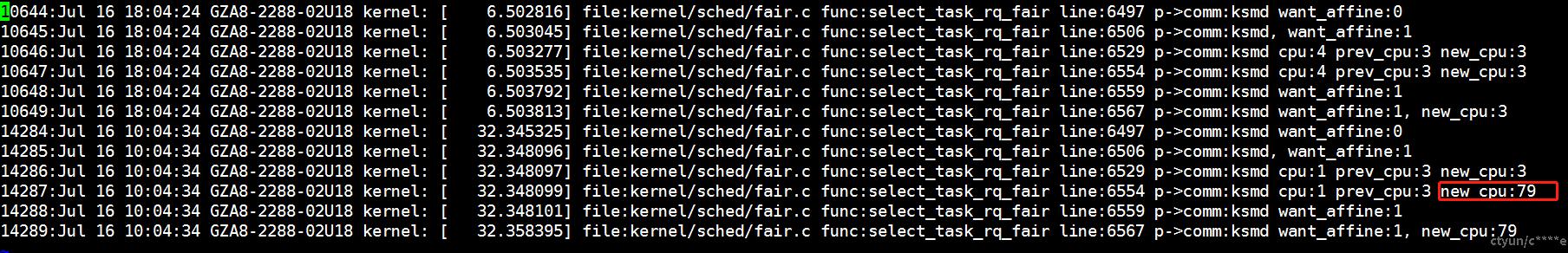
kthreadd
从/var/log/messages中查看kthreadd被调度到隔离核心上的日志:
grep 'p->comm:kthreadd' /var/log/messages -inr --color > kthreadd.log
vim kthreadd.log
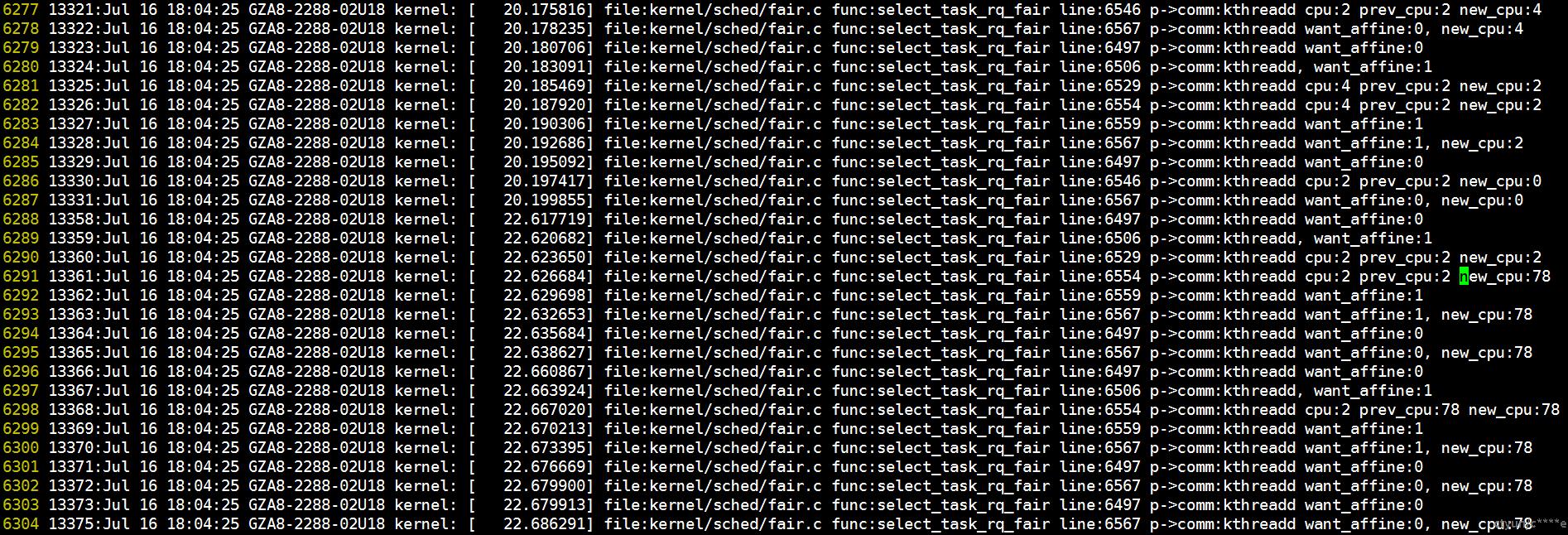
关键代码
上方日志代码位置参见下图。
select_task_rq_fair
vim kernel/sched/fair.c +6554
vim -t select_idle_sibling
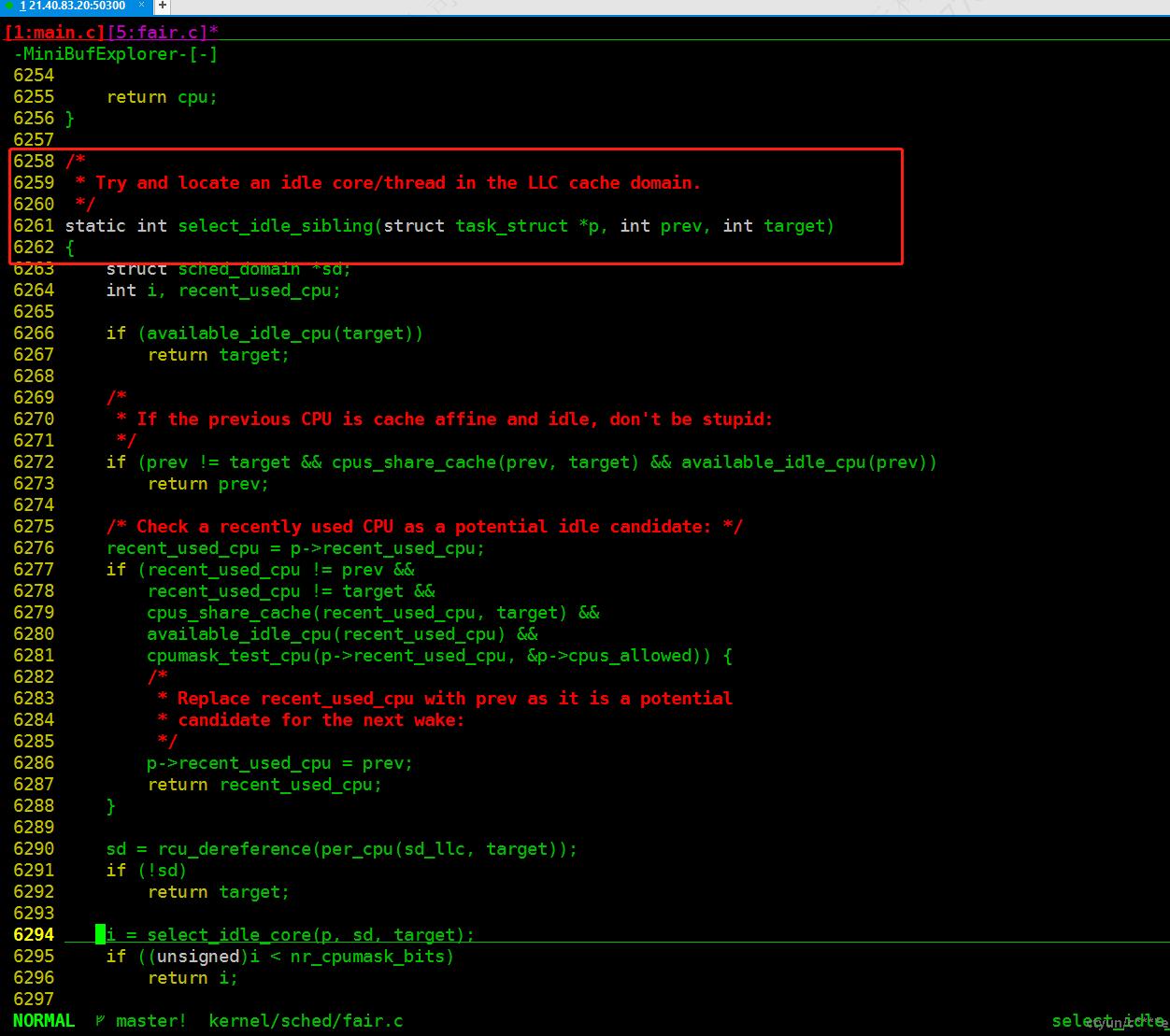
select_idle_smt
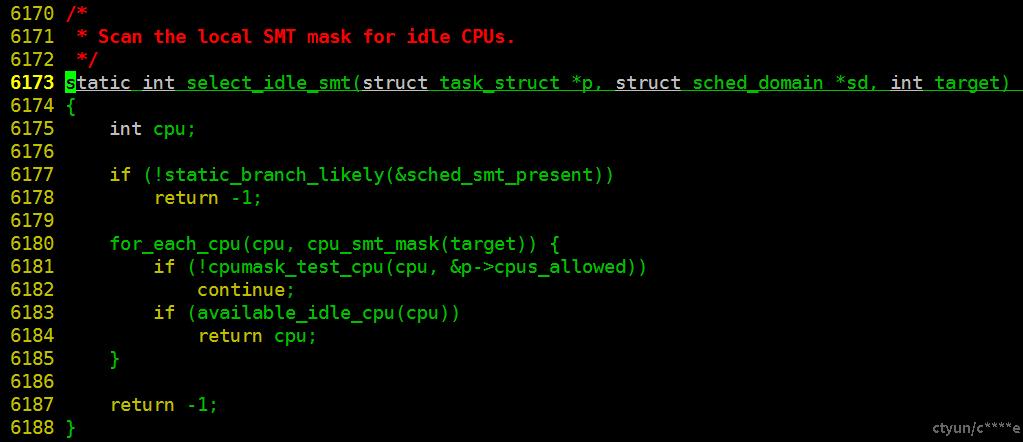
// vim -t select_idle_smt
6170 /*
6171 * Scan the local SMT mask for idle CPUs.
6172 */
6173 static int select_idle_smt(struct task_struct *p, struct sched_domain *sd, int target)
6174 {
6175 int cpu;
6176
6177 if (!static_branch_likely(&sched_smt_present))
6178 return -1;
6179
6180 for_each_cpu(cpu, cpu_smt_mask(target)) {
6181 if (!cpumask_test_cpu(cpu, &p->cpus_allowed))
6182 continue;
6183 if (available_idle_cpu(cpu))
6184 return cpu;
6185 }
6186
6187 return -1;
6188 }
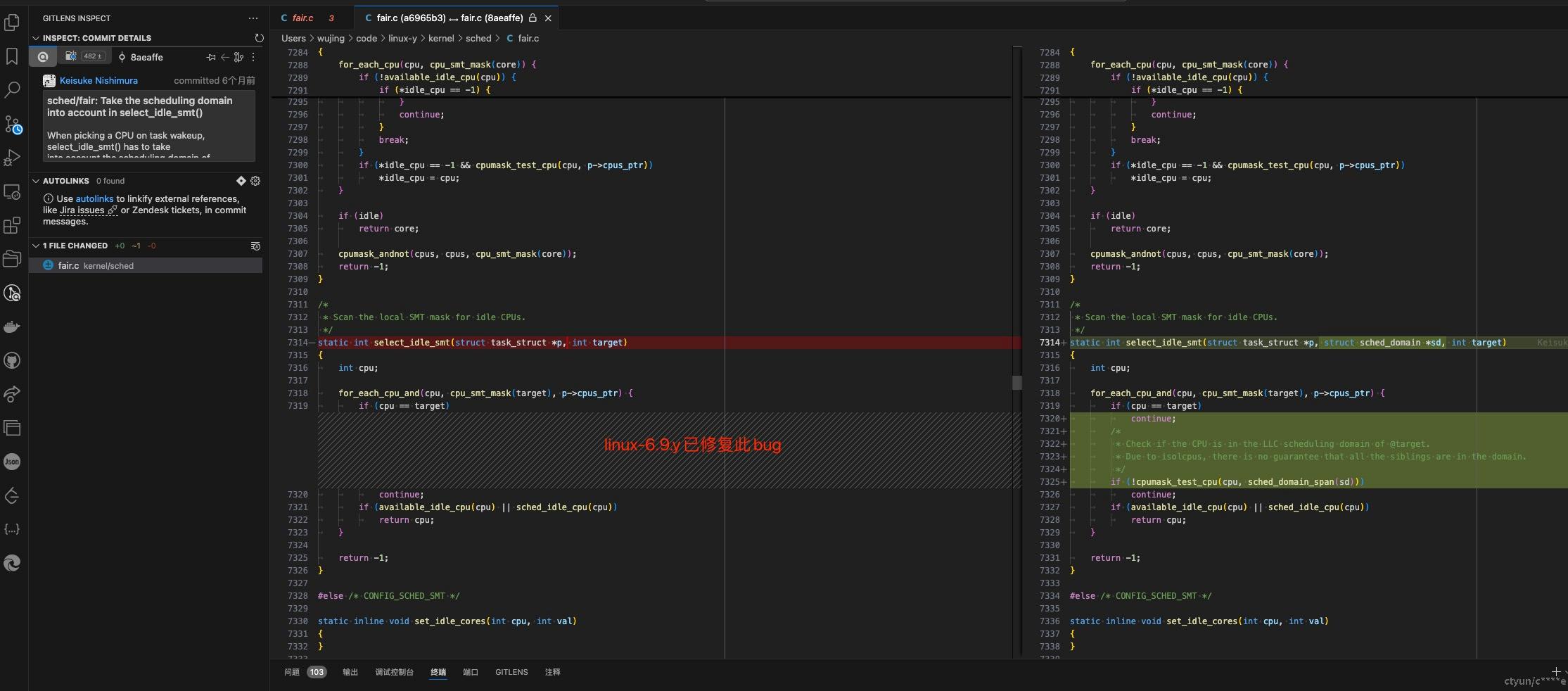
修改源码修复bug
改一行代码,隔离cpu的时候可以不考虑超线程逻辑,可修复此问题:
git show HEAD
commit a90c573c74f55930f3b770ec67d7a84528e8dac8 (HEAD -> master)
Author: QiLiang Yuan <yuanql9@chinatelecom.cn>
Date: Thu Jul 18 23:18:24 2024 +0800
sched/fair: Fix wrong cpu selecting from isolated domain
Signed-off-by: QiLiang Yuan <yuanql9@chinatelecom.cn>
diff --git a/kernel/sched/fair.c b/kernel/sched/fair.c
index f58f13545450..30f32641a45c 100644
--- a/kernel/sched/fair.c
+++ b/kernel/sched/fair.c
@@ -6178,7 +6178,7 @@ static int select_idle_smt(struct task_struct *p, struct sched_domain *sd, int t
return -1;
for_each_cpu(cpu, cpu_smt_mask(target)) {
- if (!cpumask_test_cpu(cpu, &p->cpus_allowed))
+ if (!cpumask_test_cpu(cpu, &p->cpus_allowed) || !cpumask_test_cpu(cpu, sched_domain_span(sd)))
continue;
if (available_idle_cpu(cpu))
return cpu;
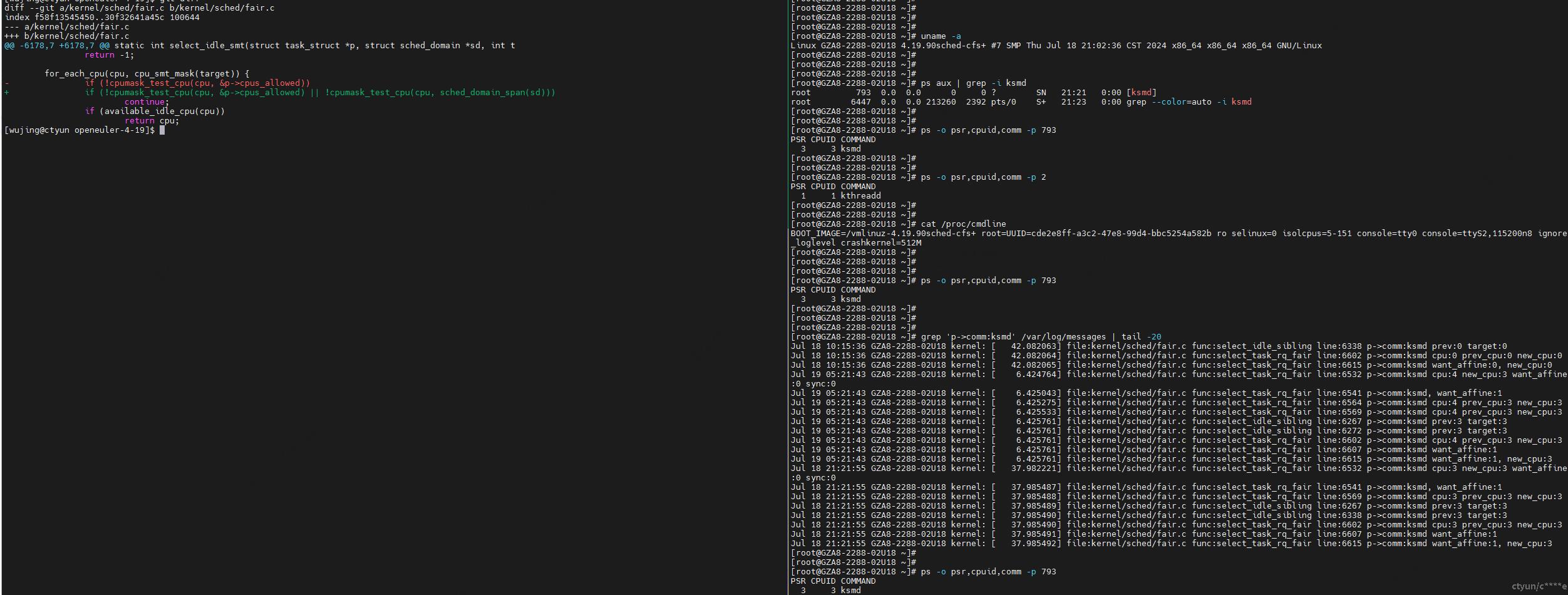
历史上select_idle_smt、cpumask_test_cpu(cpu, sched_domain_span(sd))多次删除再合入,最近一次在6个月前:
git log -S 'cpumask_test_cpu(cpu, sched_domain_span(sd))' --oneline kernel/sched/fair.c
8aeaffef8c6e sched/fair: Take the scheduling domain into account in select_idle_smt()
3e6efe87cd5c sched/fair: Remove redundant check in select_idle_smt()
3e8c6c9aac42 sched/fair: Remove task_util from effective utilization in feec()
c722f35b513f sched/fair: Bring back select_idle_smt(), but differently
6cd56ef1df39 sched/fair: Remove select_idle_smt()
df3cb4ea1fb6 sched/fair: Fix wrong cpu selecting from isolated domain
进一步使用git show 查看上述所有commit的具体内容:
git log -S 'cpumask_test_cpu(cpu, sched_domain_span(sd))' --oneline kernel/sched/fair.c | awk {'print $1'} | xargs git show > sched_domain_span.log
不修改源码避开此bug
隔离核心考虑超线程调度域
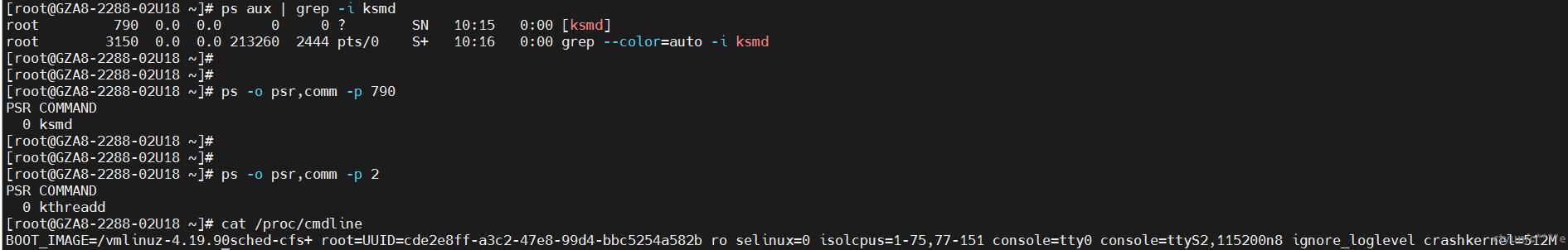
查看逻辑cpu0的超线程调度域下的兄弟节点:
cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/topology/thread_siblings_list
76
从下图可以看出isolcpus=1-75,77-151的时候ksmd不会被调度上去。
手动将ksmd迁走
此方案适用于线上不停机的情况,可直接将ksmd迁至非隔离核心上。
- [PF_NO_SETAFFINITY校验值]
在内核源码中查看PF_NO_SETAFFINITY定义:
#linux/sched.h
#define PF_NO_SETAFFINITY 0x04000000 /* Userland is not allowed to meddle with cpus_allowed */
在物理机上查看ksmd进程号:
ps aux | grep -i ksmd
root 510 11.1 0.0 0 0 ? RN Jan19 26874:37 [ksmd]
root 1979672 0.0 0.0 213952 1600 pts/16 S+ 16:13 0:00 grep -i ksmd
进一步查看ksmd进程的状态:
```bash
[root@gzinf-kunpeng-55e235e17e57 yql]# cat /proc/510/stat
510 (ksmd) S 2 0 0 0 -1 2097216 0 0 0 0 3 161248078 0 0 25 5 1 0 13 0 0 18446744073709551615 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2147483647 0 1 0 0 17 69 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
查看ksmd进程的标志位(flags):
[root@gzinf-kunpeng-55e235e17e57 yql]# flags=$(cut -f 9 -d ' ' /proc/510/stat)
查看ksmd进程的标志位(flags)是否包含PF_NO_SETAFFINITY(0x04000000):
[root@gzinf-kunpeng-55e235e17e57 yql]# echo $(($flags & 0x40000000))
0
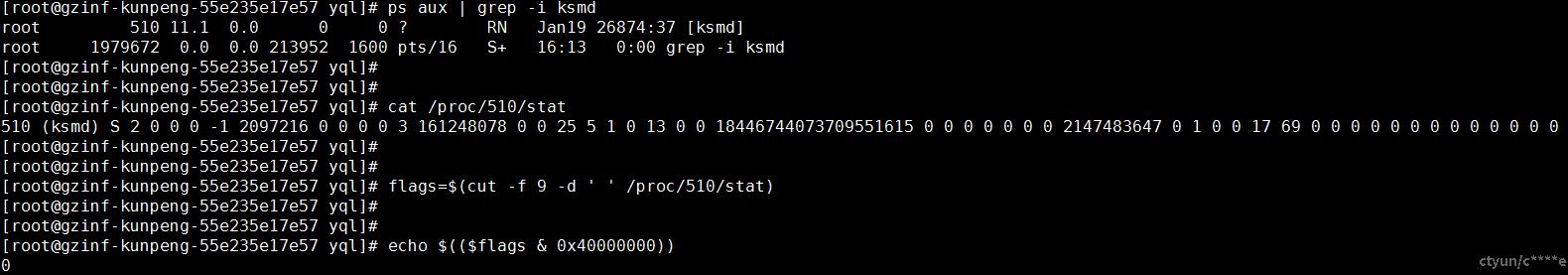
可以看到ksmd进程的标志位(flags)不包含PF_NO_SETAFFINITY(0x04000000)。故可以通过taskset或者cgroups设置ksmd的cpu亲和性,将起绑定到非客户虚拟机所在的cpu上。
将ksmd的亲和性设置为10号cpu:
taskset -pc 10 510
将ksmd的亲和性设置为非隔离核心:
此场景需要刨去超线程调度域下的兄弟节点,假设0号逻辑cpu、76号逻辑cpu位于同一个物理cpu上,即0号逻辑cpu跟76号逻辑cpu是一个超线程调度域下的兄弟节点。假设0号逻辑cpu是隔离核心,那设置ksmd亲核心的时候需要排除掉掉76号逻辑cpu。
taskset -pc 0-63 510
通过上述两步即可将ksmd从隔离的cpu上迁走,同时保障ksmd不会再被调度到隔离核心上。
cicd运维一键迁
已经打成了rpm包,安装ksmd-taskset.rpm包即可一键迁移,详细步骤可以参考ksmd-taskset打包说明。
stress-ng压测
从github clone stress-ng源码:
cd stress-ng
make
make install
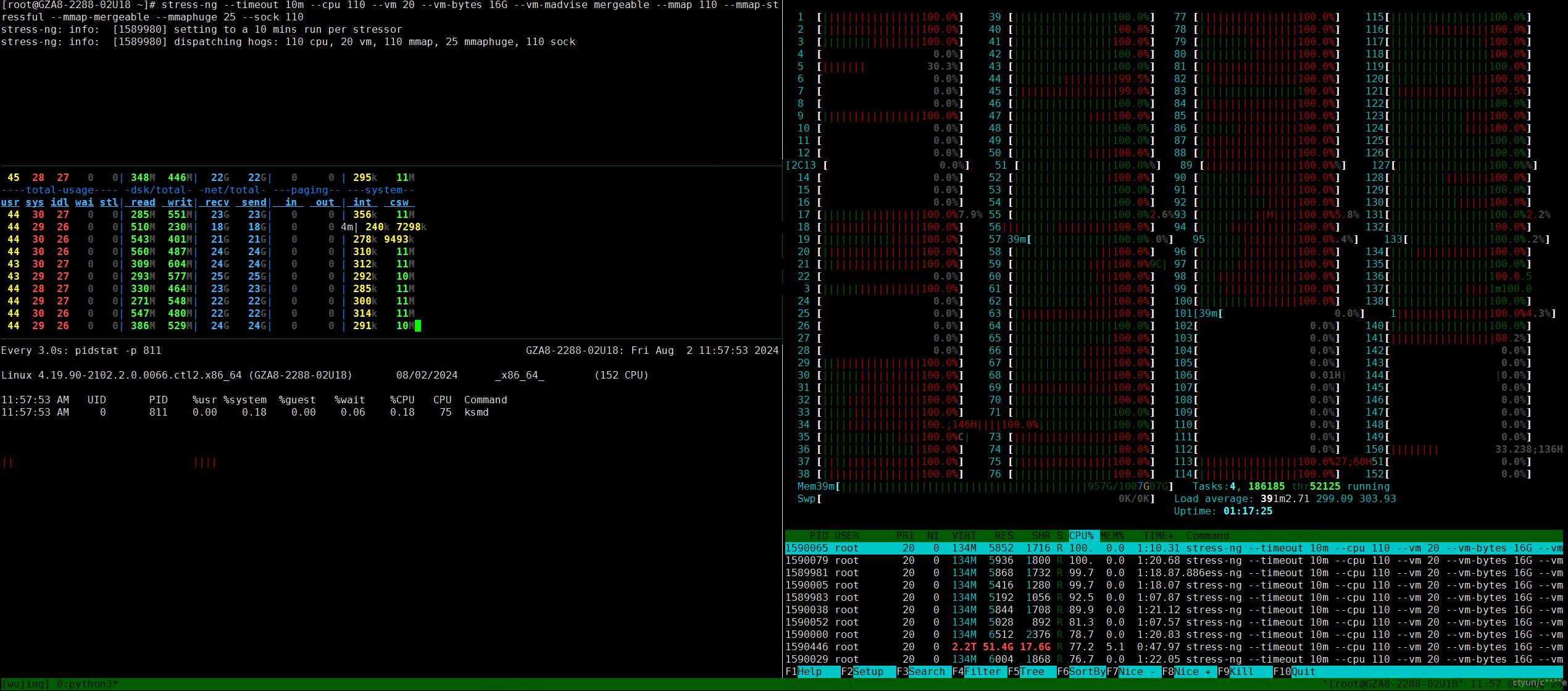
stress-ng --timeout 10m --cpu 110 --vm 20 --vm-bytes 16G --vm-madvise mergeable --mmap 110 --mmap-stressful --mmap-mergeable --mmaphuge 25 --sock 110
stress-ng --timeout 10m --cpu 110 --vm 20 --vm-bytes 16G --vm-madvise mergeable --mmap 110 --mmap-stressful --mmap-mergeable --mmaphuge 25 --sock 110 --ksm
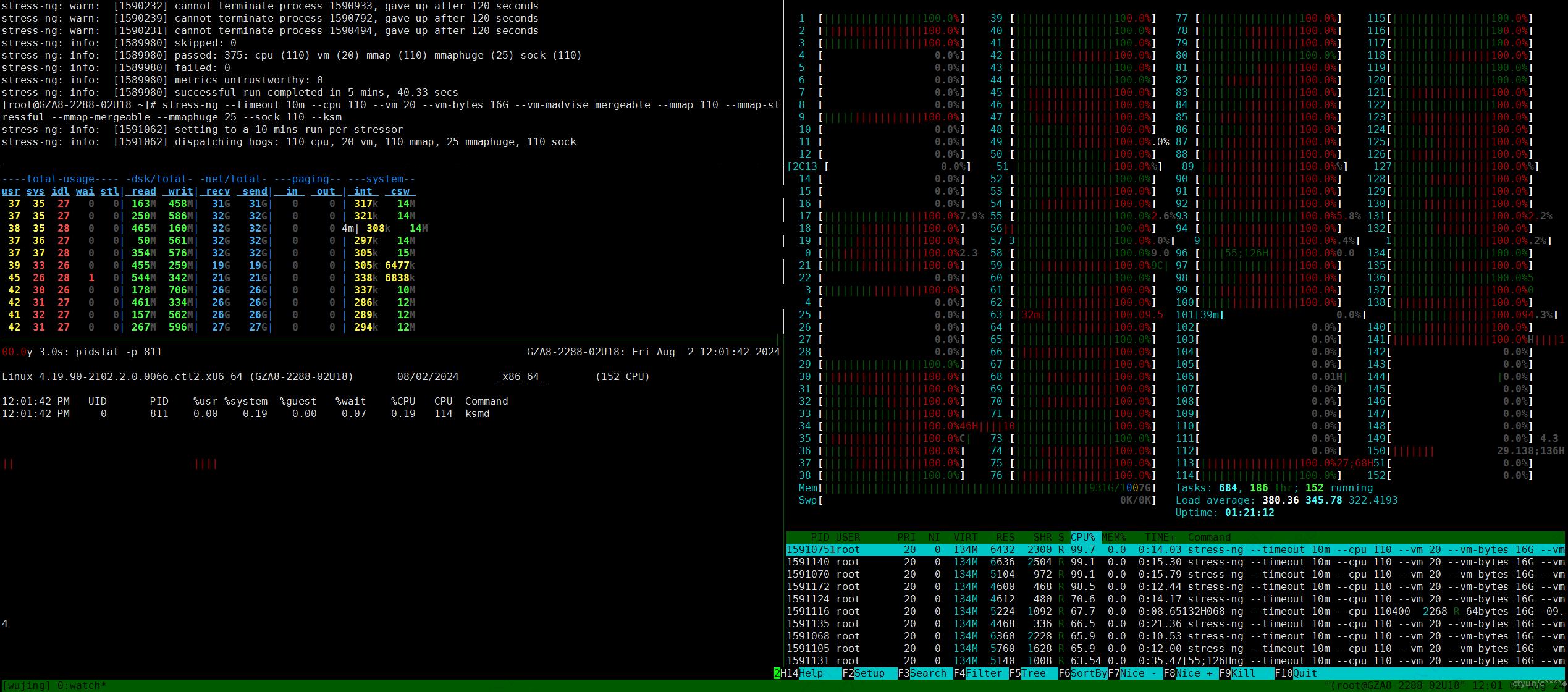
实测将ksmd迁移到非隔离核心没有太大影响,从pidstat结果来看ksmd消耗了整体cpu占比为0.19%。
总结
下一个发行版合修复源码。
线上机器通过设置kpatch方式进行热修复,通过设置ksmd的cpu亲和性,将其绑定到非客户虚拟机所在的cpu上。
进一步可以通过调整ksmd参数来提高虚拟机的性能。