1、KVM概述
由以色列qumranet公司研发,后被RedHad公司收购,依赖于 HVM、inter VT、AMD-v。
KVM是(Kernel-based Virtual Machine)的简称,是一个开源的系统虚拟化模块,自Linux
2.6.20之后集成在Linux的各个主要发行版本中。它使用Linux自身的调度器进行管理,所以相对于Xen,其核心源码很少。
KVM的虚拟化需要硬件支持(如Intel VT技术或者AMD
V技术)。是基于硬件的完全虚拟化。而Xen早期则是基于软件模拟的Para-Virtualization,新版本则是基于硬件支持的完全虚拟化。但Xen本身有自己的进程调度器,存储管理模块等,所以代码较为庞大。广为流传的商业系统虚拟化软件VMware
ESX系列是基于软件模拟的Full-Virtualization。
1.1 工作原理
KVM 是基于虚拟化扩展(Intel VT 或者 AMD-V)的 X86 硬件的开源的 Linux 原生的全虚拟化解决方案。KVM 中,虚拟机被实现为常规的 Linux 进程,由标准 Linux 调度程序进行调度;虚机的每个虚拟 CPU 被实现为一个常规的 Linux 进程。这使得 KMV 能够使用 Linux 内核的已有功能。
但是,KVM 本身不执行任何硬件模拟,需要客户空间程序通过 /dev/kvm 接口设置一个客户机虚拟服务器的地址空间,向它提供模拟的 I/O,并将它的视频显示映射回宿主的显示屏。目前这个应用程序是 QEMU。
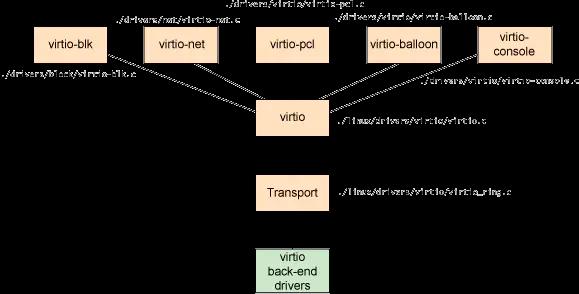
1.2 核心组件
(1)kvm.ko内核模块
(kvm.ko)/dev/kvm:工作为hypervisor,在用户空间可通过系统调用ioctl()与内核中的kvm模块交互,从而完成虚拟机的创建、启动、停止、删除等各种管理功能;
(2)qemu-kvm:用户空间的工具程序
qemu-kvm进程:工作于用户空间,用于实现IO设备模拟;用于实现一个虚拟机实例;
(3)libvirt:工具箱用于与主流操作系统虚拟化进行交互工具
(4)virt-manager:图像化工具
2 桥接网络配置
2.1 安装 bridge-utils 软件包,它提供 brctl 工具来配置网桥
yum install bridge-utils2.2 加载 tun 和 bridge 模块
[root@localhost ~]# lsmod | grep tun
tun 36164 2 vhost_net
[root@localhost ~]#
[root@localhost ~]# lsmod | grep bridge
bridge 151336 1 ebtable_broute
stp 12976 1 bridge
llc 14552 2 stp,bridge2.3 创建 brdige
将物理机工作的网口绑定到 brdige 上,将网口 IP 清除,让 bridge 获取 IP
root@localhost:~# brctl addbr br0
root@localhost:~# brctl addif br0 enp3s0
root@localhost:~# brctl show br0
bridge name bridge id STP enabled interfaces
br0 8000.eef79549afe7 no enp3s0
root@localhost:~#
root@localhost:~# brctl stp br0 on
root@localhost:~#
root@localhost:~# brctl show br0
bridge name bridge id STP enabled interfaces
br0 8000.eef79549afe7 yes enp3s0
root@localhost:~#
root@localhost:~#
root@localhost:~# ifconfig enp3s0
enp3s0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet xx.xxx.xxx.111 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast xx.xxx.xxx.255
inet6 fe80::401c:b143:3935:a3e prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether ee:f7:95:49:af:e7 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 5597473 bytes 7095008949 (6.6 GiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 15 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 2065687 bytes 153950765 (146.8 MiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
device interrupt 41
root@localhost:~#
root@localhost:~# ifconfig br0
br0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
ether ee:f7:95:49:af:e7 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
root@localhost:~# ifconfig enp3s0 0 up
root@localhost:~# ifconfig br0 up
root@localhost:~# dhclient br0
root@localhost:~#
root@localhost:~# ifconfig br0
br0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet xx.xxx.xxx.111 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast xx.xxx.xxx.255
inet6 fe80::ecf7:95ff:fe49:afe7 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether ee:f7:95:49:af:e7 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 703 bytes 65605 (64.0 KiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 92 bytes 15483 (15.1 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
root@localhost:~# ifconfig enp3s0
enp3s0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet6 fe80::401c:b143:3935:a3e prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether ee:f7:95:49:af:e7 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 5597473 bytes 7095008949 (6.6 GiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 15 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 2065687 bytes 153950765 (146.8 MiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
device interrupt 41
root@localhost:~# 此时, 作为网桥借口的附庸(slave),物理网口 enp3s0 借口没有自己的 IP 地址, 网桥寄生在它身上,网桥与物理网口 MAC 地址相同。
当有虚拟机启动时,QEMU 创建的 tap 设备绑定到 bridge 上,虚拟机就能和外部网络连通了。
创建网桥后的接口逻辑图如下:

2.4 准备 qemu-ifup/qemu-ifdown 脚本
在虚拟机启动网络前执行的脚本由 script 参数配置(默认 /etc/qemu-ifup)。该脚本时将 QEMU 自动创建的 TAP 设备绑定到网桥上。
虚拟机关闭时,QEMU 会自动解除 TAP 设备的绑定,删除 TAP 设备。所以 qemu-ifdown 是不用配置的。
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/qemu-ifup
#!/bin/bash
switch=br0
ifconfig $1 up
brctl addif $switch $12.5 启动虚拟机
[root@localhost ~]#
[root@localhost ~]# /usr/libexec/qemu-kvm centos70-64.qcow2 -enable-kvm -smp 2 -m 2G -device virtio-net-pci,netdev=vnet0 -netdev tap,id=vnet0 -monitor telnet::3333,server,nowait -serial stdio
VNC server running on ::1:5900
CentOS Linux 7 (Core)
Kernel 3.10.0-1127.el7.x86_64 on an x86_64
localhost login: root
Password:
Last login: Thu May 13 23:05:33 on ttyS0
[root@localhost ~]#
[root@localhost ~]# ifconfig
eth0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet xx.xxx.xxx.122 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast xx.xxx.xxx.255
inet6 fe80::e940:5ead:bd61:cde5 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether 52:54:00:12:34:56 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 62 bytes 5733 (5.5 KiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 22 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 48 bytes 4481 (4.3 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
lo: flags=73<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING> mtu 65536
inet xx.xxx.xxx.xx netmask 255.0.0.0
inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x10<host>
loop txqueuelen 1000 (Local Loopback)
RX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
[root@localhost ~]#
[root@localhost ~]# route -n
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
0.0.0.0 xx.xxx.xxx.254 0.0.0.0 UG 100 0 0 eth0
xx.xxx.xxx.0 0.0.0.0 xx.xxx.xxx.0 U 100 0 0 eth0
[root@localhost ~]#
[root@localhost ~]#