1 工人和计算机
CPU
工人,干活的,判断以及逻辑处理。
内存
车间,工人干活的地方,在车间中加工原料,当车间中没原料了,就从仓库中取。
磁盘
仓库,存储原料的地方。
2 基础知识
2.1 专业术语
内存
应用程序地址空间(address space)的一部分,通常由RAM或swap支持。
块(chunk)
可以分配、释放或与相邻块组合成更大范围的一小段内存,是对应用程序内存块的一个包装,存在 于一个堆中,属于一个arana。
堆
一个连续的内存区域,被划分为chunk,每个堆都属于唯一的arana。
arena
在一个或多个线程之间共享的一种结构,包含对一个或多个堆的引用,以及这些堆中“空闲”的块的链表。分配给每个arena的线程将从该arena的空闲列表中分配内存。
从定义上来看,如果对它们从范围上做个排序,那么arena > heap > chunk > memory.
2.2 虚拟内存地址
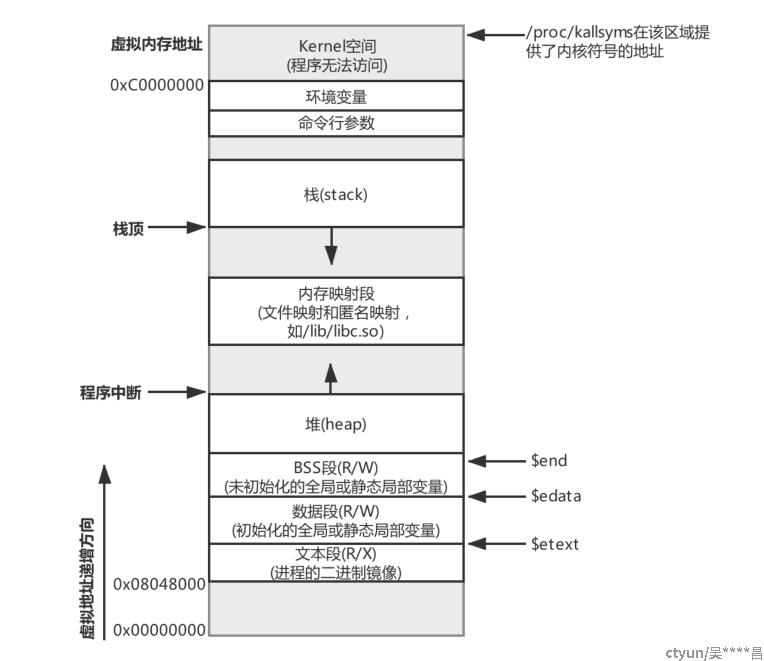
指针数据都是存储在堆上的,而字面量(string literal)都放在所谓的“文字常量区”。
让我们来看一段C代码的程序
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int add(int a, int b){
return a+b;
}
int del(int a, int b){
return a-b;
}
int (*fPointer)(int a, int b);
int global = 0;
int global_uninitialized;
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
int var = 0;
char *chOnHeap = "test";
int *nOnHeap = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*1);
*nOnHeap = 200;
fPointer = add;
while(1)
{
sleep(1);
printf("---------------------------------------------------------------------\n");
printf("global address = %p\n",(void*)&global);
printf("global uninitialized address = %p\n", (void*)&global_uninitialized);
printf("var value = %d, address = %p\n",var,(void*)&var);
printf("chOnHeap value = %s, pointer address = %p, pointed address =%p\n",chOnHeap,(void*)&chOnHeap,chOnHeap);
printf("nOnHeap value = %d, pointer address = %p, pointed address =%p\n",*nOnHeap,(void*)&nOnHeap,nOnHeap);
printf("main address = %p\n",(void*)&main);
for(int i = 0; i < argc; i++){
printf("argument address = %p\n",(void*)&argv[i]);
}
printf("add address = %p\n", (void *)&add);
printf("del address = %p\n", (void *)&del);
printf("function pointer address = %p, pointed address = %p ,value =%d\n",(void *)&fPointer,fPointer,(*fPointer)(10,20));
printf("--------------------------------------------------------------------------------\n");
}
free(nOnHeap);
return 1;
}程序的结果输出
global address = 0x601054
global uninitialized address = 0x601058
var value = 0, address = 0x7fff282697e8
chOnHeap value = test, pointer address = 0x7fff282697e0, pointed address =
0x400860
nOnHeap value = 200, pointer address = 0x7fff282697d8, pointed address =
0xfd2010
main address = 0x400637
argument address = 0x7fff282698d8
argument address = 0x7fff282698e0
add address = 0x40060d
del address = 0x400621
function pointer address = 0x601060, pointed address = 0x40060d ,value = 30查看系统中进程的内存分布
00400000-00401000 r-xp 00000000 08:02 31611366
/home/teledb/showVM
00600000-00601000 r--p 00000000 08:02 31611366
/home/teledb/showVM
00601000-00602000 rw-p 00001000 08:02 31611366
/home/teledb/showVM
00fd2000-00ff3000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0 [heap]
2b11fcc89000-2b11fccaa000 r-xp 00000000 08:02 9701073
/usr/lib64/ld-2.17.so
2b11fccaa000-2b11fccac000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0
2b11fccc1000-2b11fccc4000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0
2b11fceaa000-2b11fceab000 r--p 00021000 08:02 9701073
/usr/lib64/ld-2.17.so
2b11fceab000-2b11fceac000 rw-p 00022000 08:02 9701073
/usr/lib64/ld-2.17.so
2b11fceac000-2b11fcead000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0
2b11fcead000-2b11fd065000 r-xp 00000000 08:02 9701081
/usr/lib64/libc-2.17.so
2b11fd065000-2b11fd265000 ---p 001b8000 08:02 9701081
/usr/lib64/libc-2.17.so
2b11fd265000-2b11fd269000 r--p 001b8000 08:02 9701081
/usr/lib64/libc-2.17.so
2b11fd269000-2b11fd26b000 rw-p 001bc000 08:02 9701081
/usr/lib64/libc-2.17.so
2b11fd26b000-2b11fd270000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0
7fff2824b000-7fff2826f000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0 [stack]
7fff28308000-7fff2830a000 r-xp 00000000 00:00 0 [vdso]
ffffffffff600000-ffffffffff601000 r-xp 00000000 00:00 0
[vsyscall]2.3 堆内存的分配
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/malloc-vs-new/
| 编号 | new | malloc() |
| 1 | calls constructor | does not calls constructors |
| 2 | It is an operator | It is a function |
| 3 | supported by C++ | supported by standard library |
| 4 | Returns exact data type | Returns void * |
| 5 | on failure, Throws | On failure, returns NULL |
| 6 | Memory allocated from free store | Memory allocated from heap |
| 7 | can be overloaded | can not be overloaded |
| 8 | size is calculated by compiler | size is calculated manually |
| 9 | memory deallocate by delete | memory deallocate by free() function |
思考题
mysql源码里,从底层申请堆内存的时候,用的是new还是malloc?为什么要这样做?
2.4 内存碎片
当程序需要内存的时候,会向内存管理器提出内存申请,程序使用完成后会将其归还给内存管理器,以供后续使用。随着程序的运行以及内存的分配与释放,大块连续的空闲内存会被分割成不连续的小块的空闲内存。当程序再次请求分配大块连续的内存时,虽然此时空闲内存的总量大于所请求的内存大小,但是由于没有连续大块的内存存在,导致请求得不到满足,这就是内存碎片问题。
1 内部碎片
已经被分配的却不能被利用的内存空间。(内存对齐,导致浪费,在64位操作系统上,glibc内存分配器会对程序请求的内存按照16对齐,当程序请求23字节的时候,实际分配的是32字节,多分配的9字节会被浪费)
2 外部碎片
还没有被分配出去,但是由于太小而无法满足程序的大块连续内存申请的空闲内存。
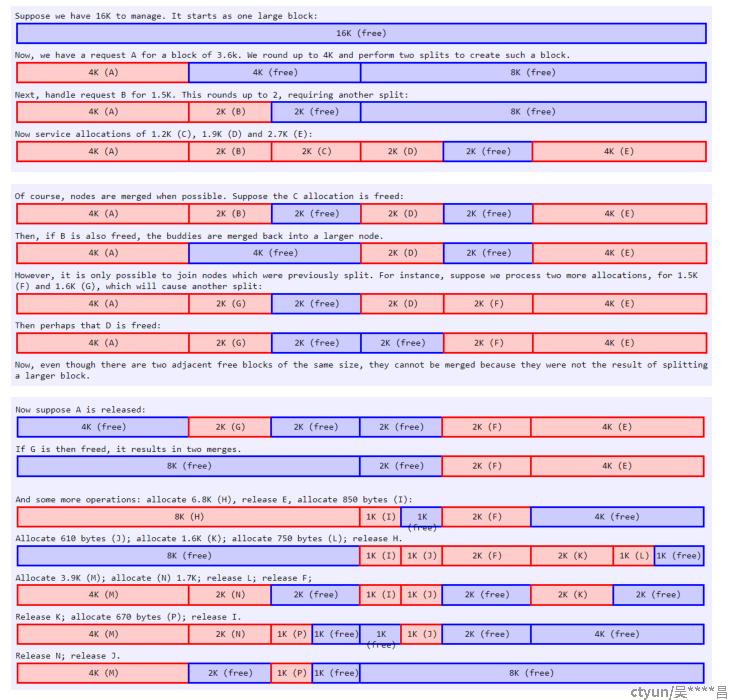
3 伙伴系统算法
在程序中,频繁调用malloc来申请内存,也会导致外部碎片问题。Linux内核通过伙伴系统算法( https://www.halolinux.us/kernel-reference/the-buddy-system-algorithm.html)解决了外部碎片问题。
3 MEM_ROOT介绍
mysql内部直接向底层申请内存,用的是glibc的malloc()方法。
在glibc里面,内存管理器用的是ptmalloc,ptmalloc同样采用了伙伴系统算法来管理空闲的内存。
The GNU C library's (glibc's) malloc library contains a handful of functions that manage
allocated memory in the application's address space. The glibc malloc is derived from
ptmalloc (pthreads malloc), which is derived from dlmalloc (Doug Lea malloc). This malloc is
a "heap" style malloc, which means that chunks of various sizes exist within a larger region
of memory (a "heap") as opposed to, for example, an implementation that uses bitmaps
and arrays, or regions of same-sized blocks, etc. In ancient times, there was one heap per
application, but glibc's malloc allows for multiple heaps, each of which grows within its
address space.——https://sourceware.org/glibc/wiki/MallocInternals而在进程内部,通常都是内部碎片问题。为了避免内部碎片问题,一个可以的策略就是向内存管理器请
求4、8或者16倍数大小的大块内存,减少非对齐小块内存的申请。
mysql中内存分配的策略
用MEM_ROOT替换malloc直接向内存分配器申请大块对齐的内存;应用程序向MEM_ROOT申请小块的内存。这样的管理方式,减少了在堆中的内存申请操作次数,可以提升性能。
3.1 内部结构
my_alloc.h
//内存空间的最小结构体
typedef struct st_used_mem
{ /* struct for once_alloc (block) */
struct st_used_mem *next; /* 下一个块 */
unsigned int left; /* 当前块中剩余的字节数 */
unsigned int size; /* 当前块的大小 */
} USED_MEM;
typedef struct st_mem_root
{
USED_MEM *free; /* 空闲内存块链表 */
USED_MEM *used; /* 已用内存块链表 */
USED_MEM *pre_alloc; /* 初始化时预分配的内存块 */
/* if block have less memory it will be put in 'used' list */
size_t min_malloc;
size_t block_size; /* initial block size */
unsigned int block_num; /* allocated blocks counter */
/*
first free block in queue test counter (if it exceed
MAX_BLOCK_USAGE_BEFORE_DROP block will be dropped in 'used' list)
*/
unsigned int first_block_usage;
/*
Maximum amount of memory this mem_root can hold. A value of 0
implies there is no limit.
*/
size_t max_capacity;
/* Allocated size for this mem_root */
size_t allocated_size;
/* Enable this for error reporting if capacity is exceeded */
my_bool error_for_capacity_exceeded;
void (*error_handler)(void);
PSI_memory_key m_psi_key;
} MEM_ROOT;3.2 MEM_ROOT的使用
1 内存初始化
void init_alloc_root(PSI_memory_key key,
MEM_ROOT *mem_root, size_t block_size,
size_t pre_alloc_size MY_ATTRIBUTE((unused)))
{
DBUG_ENTER("init_alloc_root");
DBUG_PRINT("enter",("root: 0x%lx", (long) mem_root));
mem_root->free= mem_root->used= mem_root->pre_alloc= 0;
mem_root->min_malloc= 32;
mem_root->block_size= block_size - ALLOC_ROOT_MIN_BLOCK_SIZE;
mem_root->error_handler= 0;
mem_root->block_num= 4; /* We shift this with >>2 */
mem_root->first_block_usage= 0;
mem_root->m_psi_key= key;
mem_root->max_capacity= 0;
mem_root->allocated_size= 0;
mem_root->error_for_capacity_exceeded= FALSE;
if (pre_alloc_size)
{
if ((mem_root->free= mem_root->pre_alloc=
(USED_MEM*) my_malloc(key,
pre_alloc_size+ ALIGN_SIZE(sizeof(USED_MEM)),
MYF(0))))
{
mem_root->free->size= (uint)(pre_alloc_size+ALIGN_SIZE(sizeof(USED_MEM)));
mem_root->free->left= (uint)pre_alloc_size;
mem_root->free->next= 0;
mem_root->allocated_size+= pre_alloc_size+ ALIGN_SIZE(sizeof(USED_MEM));
}
}
DBUG_VOID_RETURN;
}
#define MY_ALIGN(A,L) (((A) + (L) - 1) & ~((L) - 1))
#define ALIGN_SIZE(A) MY_ALIGN((A),sizeof(double))2 内存分配
void *alloc_root(MEM_ROOT *mem_root, size_t length)
{
length= ALIGN_SIZE(length);
if ((*(prev= &mem_root->free)) != NULL)
{
/*1、如果可用内存不够 2、已分配次数大于10 3、剩余内存小于4k 同时满足这3个条件,则将该内存
块置为已使用*/
if ((*prev)->left < length &&
mem_root->first_block_usage++ >= ALLOC_MAX_BLOCK_USAGE_BEFORE_DROP &&
(*prev)->left < ALLOC_MAX_BLOCK_TO_DROP)
{
next= *prev;
*prev= next->next; /* Remove block from list */
next->next= mem_root->used;
mem_root->used= next;
mem_root->first_block_usage= 0;
}
for (next= *prev ; next && next->left < length ; next= next->next)
prev= &next->next;
}
//没有找到合适的块,则分配新的内存块
if (! next)
{ /* Time to alloc new block */
block_size= mem_root->block_size * (mem_root->block_num >> 2);
get_size= length+ALIGN_SIZE(sizeof(USED_MEM));
get_size= MY_MAX(get_size, block_size); //计算新的内存块大小
//判断MEM_ROOT中内存是否可用,因为max_capacity设置为0,所以正常情况下检测都会成功
if (!is_mem_available(mem_root, get_size))
{
if (mem_root->error_for_capacity_exceeded)
my_error(EE_CAPACITY_EXCEEDED, MYF(0),
(ulonglong) mem_root->max_capacity);
else
DBUG_RETURN(NULL);
}
//实际开始分配内存
if (!(next = (USED_MEM*) my_malloc(mem_root->m_psi_key,
get_size,MYF(MY_WME | ME_FATALERROR))))
{
if (mem_root->error_handler)
(*mem_root->error_handler)();
DBUG_RETURN((void*) 0); /* purecov: inspected */
}
//更新MEMROOT属性
mem_root->allocated_size+= get_size;
mem_root->block_num++;
next->next= *prev;
next->size= (uint)get_size;
next->left= (uint)(get_size-ALIGN_SIZE(sizeof(USED_MEM)));
*prev=next;
}
//1 找到了合适大小的内存块
point= (uchar*) ((char*) next+ (next->size-next->left));
/*TODO: next part may be unneded due to mem_root->first_block_usage counter*/
/*2 分配内存后,更新left属性,同时如果当前块的left小于min_malloc,则将此内存快放到used列
表中,否则继续存在于free列表中*/
if ((next->left-= (uint)length) < mem_root->min_malloc)
{ /* Full block */
*prev= next->next; /* Remove block from list */
next->next= mem_root->used;
mem_root->used= next;
mem_root->first_block_usage= 0;
}
DBUG_PRINT("exit",("ptr: 0x%lx", (ulong) point));
DBUG_RETURN((void*) point);
}
判断当前MEMROOT是否可用
static inline my_bool is_mem_available(MEM_ROOT *mem_root, size_t size)
{
if (mem_root->max_capacity)
{
if ((mem_root->allocated_size + size) > mem_root->max_capacity)
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
开始请求内存
void * my_malloc(PSI_memory_key key, size_t size, myf flags)
{
my_memory_header *mh;
size_t raw_size;
compile_time_assert(sizeof(my_memory_header) <= HEADER_SIZE);
raw_size= HEADER_SIZE + size;
mh= (my_memory_header*) my_raw_malloc(raw_size, flags);
if (likely(mh != NULL))
{
void *user_ptr;
mh->m_magic= MAGIC;
mh->m_size= size;
mh->m_key= PSI_MEMORY_CALL(memory_alloc)(key, size, & mh->m_owner);
user_ptr= HEADER_TO_USER(mh);
MEM_MALLOCLIKE_BLOCK(user_ptr, size, 0, (flags & MY_ZEROFILL));
return user_ptr;
}
return NULL;
}
实际从系统请求内存
static void *my_raw_malloc(size_t size, myf my_flags)
{
/* Safety */
if (!size)
size=1;
point= malloc(size);
if (point == NULL)
{
set_my_errno(errno);
if (my_flags & MY_FAE)
error_handler_hook=fatal_error_handler_hook;
if (my_flags & (MY_FAE+MY_WME))
my_error(EE_OUTOFMEMORY, MYF(ME_ERRORLOG + ME_FATALERROR),size);
DBUG_EXECUTE_IF("simulate_out_of_memory",
DBUG_SET("-d,simulate_out_of_memory"););
if (my_flags & MY_FAE)
exit(1);
}
DBUG_PRINT("exit",("ptr: %p", point));
DBUG_RETURN(point);
}
mysqld在打印帮助信息时用到了MEMROOT初始化
static void print_help()
{
MEM_ROOT mem_root;
init_alloc_root(key_memory_help, &mem_root, 4096, 4096);
all_options.pop_back();
sys_var_add_options(&all_options, sys_var::PARSE_EARLY);
for (my_option *opt= my_long_early_options;
opt->name != NULL;
opt++)
{
all_options.push_back(*opt);
}
//插件的帮助信息
add_plugin_options(&all_options, &mem_root);
std::sort(all_options.begin(), all_options.end(), std::less<my_option>());
add_terminator(&all_options);
my_print_help(&all_options[0]);
my_print_variables(&all_options[0]);
free_root(&mem_root, MYF(0));
vector<my_option>().swap(all_options); // Deletes the vector contents.
}3 内存释放
void free_root(MEM_ROOT *root, myf MyFlags)
{
USED_MEM *next,*old;
//1 将所有的内存块设置为空闲状态
if (MyFlags & MY_MARK_BLOCKS_FREE)
{
mark_blocks_free(root);
DBUG_VOID_RETURN;
}
//2 是否保留预分配的内存块
if (!(MyFlags & MY_KEEP_PREALLOC))
root->pre_alloc=0;
//3 释放已使用链表中的所有内存块
for (next=root->used; next ;)
{
old=next; next= next->next ;
if (old != root->pre_alloc)
{
old->left= old->size;
TRASH_MEM(old);
my_free(old);
}
}
//释放空闲链表中的所有内存块
for (next=root->free ; next ;)
{
old=next; next= next->next;
if (old != root->pre_alloc)
{
old->left= old->size;
TRASH_MEM(old);
my_free(old);
}
}
root->used=root->free=0;
//重置预分配块
if (root->pre_alloc)
{
root->free=root->pre_alloc;
root->free->left=root->pre_alloc->size-(uint)ALIGN_SIZE(sizeof(USED_MEM));
root->allocated_size= root->pre_alloc->size;
TRASH_MEM(root->pre_alloc);
root->free->next=0;
}
else
root->allocated_size= 0;
root->block_num= 4;
root->first_block_usage= 0;
DBUG_VOID_RETURN;
}
static inline void mark_blocks_free(MEM_ROOT* root)
{
USED_MEM *next;
USED_MEM **last;
/* iterate through (partially) free blocks, mark them free */
last= &root->free;
for (next= root->free; next; next= *(last= &next->next))
{
next->left= next->size - (uint)ALIGN_SIZE(sizeof(USED_MEM));
TRASH_MEM(next);
}
/* Combine the free and the used list */
*last= next=root->used;
/* now go through the used blocks and mark them free */
for (; next; next= next->next)
{
next->left= next->size - (uint)ALIGN_SIZE(sizeof(USED_MEM));
TRASH_MEM(next);
}
/* Now everything is set; Indicate that nothing is used anymore */
root->used= 0;
root->first_block_usage= 0;
}3.3 总结
通过标准库的malloc函数申请的内存在使用完之后,需要调用free函数来将其释放。而用户向MEM_ROOT申请的内存,不需要执行相应的free操作,只需要在最后将MEM_ROOT中的所有内存块置为空闲或者释放即可。这样的好处是处理起来非常简单,不需要跟踪每个已分配内存在什么时候进行回收。但这样也限制了MEM_ROOT的使用场景——使用同一个MEM_ROOT实例的所有对象必须具有相同的生命周期。(具有相同生命周期的变量向同一个MEM_ROOT实例申请内存)