1. pg_unlock_check_deadlock函数中的优化改动
pg_unlock_check_deadlock函数是pg_unlock插件中用来查询死锁数量的函数,其中包含的重要过程函数为
GetAllTransInfo();
InitAllEdge();
DetectDeadlock();GetAllTransInfo函数利用sql语句,从每个节点得到事务的信息,并且保存在结构pgxc_transaction结构体中。InitAllEdge利用pgxc_transaction中锁等待信息,构建出每个事务之间的等待图DetectDeadlock函数使用深度搜索策略,遍历等待图中所有的死锁环,将其中非重复的死锁路径保存起来
其中进行了优化改动的函数为GetAllTransInfo和DetectDeadlock函数,在改动过后,出现了一个bug:新旧版本的代码相同死锁环境下,检测到的死锁数量不同。首先排查GetAllTransInfo函数在改动过后是否正确:由于在调用该函数后,会将所有的依赖信息保存起来,经过InitAllEdge函数后生成事务依赖的邻接矩阵pgxc_edge,因此在InitAllEdge函数的最后,分别输出新旧版本代码获取到的邻接矩阵的信息,代码如下:
void InitAllEdge(void)
{
int i;
int j;
pgxc_edge = (int **)palloc(pgxc_transaction_count * sizeof(int *));
for (i = 0; i < pgxc_transaction_count; i++)
{
pgxc_edge[i] = (int *)palloc(pgxc_transaction_count * sizeof(int));
for (j = 0; j < pgxc_transaction_count; j++)
{
pgxc_edge[i][j] = 0;
}
}
/*search for all edges*/
for (i = 0; i < pgxc_transaction_count; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < pgxc_transaction_count; j++)
{
if (i == j)
{
continue;
}
InitEdge(i, j);
}
}
fp = fopen(deadlock_pgxc_edge, "a+");
for(i = 0; i < pgxc_transaction_count; ++i){
for(j = 0; j < pgxc_transaction; ++j){
if(pgxc_edge[i][j] == 1){
fprintf(fp, "%d\t", pgxc_edge[i][j]);
}
}
fprintf(fp, "\n");
}
fclose(fp);
}通过
clion中Compare with Clipboard工具对比,新旧版本构造的邻接矩阵是相同的。接下来分析DetectDeadlock函数。下面是该函数的整体流程图。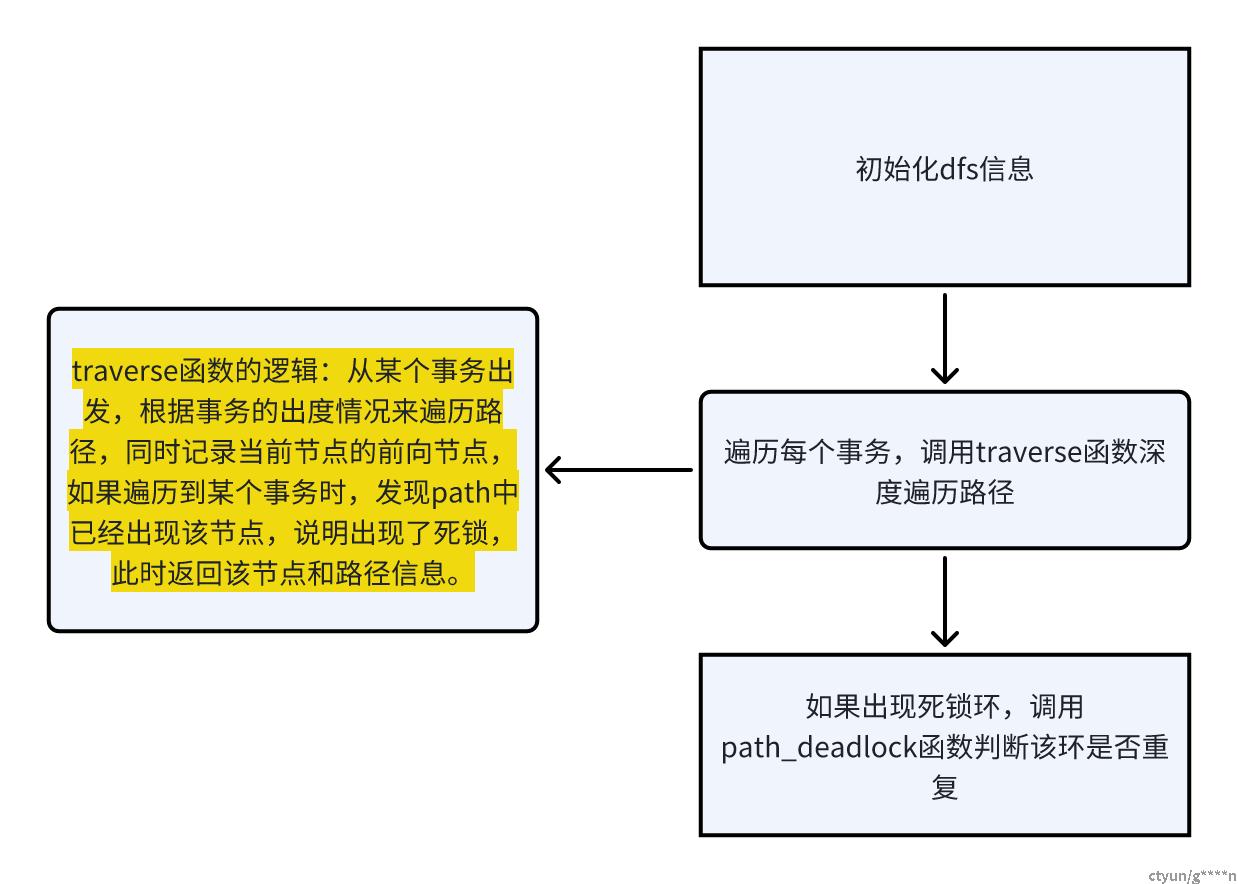 函数代码为:
函数代码为:
void DetectDeadlock(void)
{
int i;
deeplist dfs;
int loop_start;
InitDeeplist(&dfs);
InitHashtable();
for (i = 0; i < pgxc_transaction_count; i++) // 遍历所有事务
{
if (pgxc_deadlock_count > MAX_DEADLOCK)
{
break;
}
/*we can find all the deadlocks that conclude the transaction through tranvers it*/
if (pgxc_transaction[i].searched == true)
{
continue;
}
else
{
/*push i into stack*/
PALLOC(dfs.stack, i);
PALLOC(dfs.stackpre, -1);
}
while (dfs.stack_count != 0 ) // 处理dfs信息
{
if (pgxc_deadlock_count > MAX_DEADLOCK)
{
break;
}
/* 深度遍历dfs,如果存在死锁环,则返回开始事务节点 */
loop_start = traverse(&dfs);
if (loop_start > -1)
{
/* 检测当前死锁环是否重复 */
path_deadlock(&dfs, loop_start);
}
}
ClearDeeplist(&dfs);
}
DropDeeplist(&dfs);
DropHashtable();
}代码中修改过的部分为
path_deadlock函数,即traverse函数检测到了一个死锁环,并且将环中的路径保存在了dfs栈中,并且返回死锁环的起始事务节点,接下来由path_deadlock函数检测这个死锁环是否已经出现过,如果没有则保留。path_deadlock函数优化前
保存所有路径;判断路径重复过程使用方法为:双层for循环遍历,判断两个死锁环的相同与否,时间复杂度很高
/*first check whether the deadlock is exits*/
for (i = 0; i < pgxc_deadlock_count; i++)
{
if (pgxc_deadlock[i].txns_count == total_count)
{
isexist = true;
ii_txns_count = pgxc_deadlock[i].txns_count;
ij_txns_count = loop->txns_count * 2 - 1;
for (ii = 0, ij = 0; ii < ii_txns_count && ij < ij_txns_count;)
{
if (pgxc_deadlock[i].txns[ii] != loop->txns[ij % loop->txns_count])
{
if (ii == 0 && ij < loop->txns_count)
{
ij++;
}
else
{
/*deadlock not exist*/
isexist = false;
break;
}
}
else
{
ii++;
ij++;
}
}
if (isexist == true)
{
break;
}
/*deadlock in list[start~path_count-1] is already exist*/
}
}path_deadlock函数优化后
死锁环中各个节点互达,对于同一条死锁路径(可能起始节点不同)只需保存最小序列;判断死锁重复:使用哈希表,降低时间复杂度,哈希表中保存链表来避免
hash碰撞导致新的死锁环路径无法保存。/* 下面的两个for循环保证当前死锁环是上升序列,即最小状态 */
for (i = pathmin_index; i < list->path_count; i++)
{
PALLOC(loop->txns, list->path[i]);
pg_itoa(list->path[i], numstr);
deadlock_txn_path = (char *)repalloc(deadlock_txn_path, sizeof(char) * (strlen(deadlock_txn_path) + strlen(numstr) + 2));
strcat(deadlock_txn_path, numstr);
strcat(deadlock_txn_path, ",");
}
for (i = start; i < pathmin_index; i++)
{
PALLOC(loop->txns, list->path[i]);
pg_itoa(list->path[i], numstr);
deadlock_txn_path = (char *)repalloc(deadlock_txn_path, sizeof(char) * (strlen(deadlock_txn_path) + strlen(numstr) + 2));
strcat(deadlock_txn_path, numstr);
strcat(deadlock_txn_path, ",");
}
/* 使用MurmurHash2算法,将当前的死锁环路径转换成32位无符号整数 */
hash = MurmurHash2(deadlock_txn_path, strlen(deadlock_txn_path), 0);
if(deadlock_hashtable != NULL)
{
/* 使用hash_search判断哈希桶中是否保存了当前的hash值,found变量呈现其结果 */
dl_entry = (DeadlockPathEntry *)hash_search(deadlock_hashtable, (void *)&hash, HASH_ENTER, &found);
}
/* 如果不存在,为了避免hash碰撞,将hash值和对应的死锁环路径都保存在哈希桶中,形成hash对应的链表 */
if (!found)
{
dl_entry->entry = (DeadlockPathList *) palloc(sizeof(DeadlockPathList));
dl_entry->entry->path_str = deadlock_txn_path;
dl_entry->entry->next = NULL;
pgxc_deadlock_count++;
}
/* 否则还需判断:是否由hash碰撞导致的hash值相同但是死锁环路径不同 */
else
{
DeadlockPathList *head = dl_entry->entry;
while(dl_entry->entry != NULL)
{
/* 死锁环路径也相同,直接跳过 */
if(strcmp(dl_entry->entry->path_str, deadlock_txn_path) == 0)
{
break;
}
else
{
dl_entry->entry = dl_entry->entry->next;
}
}
/* 没有发现相同的死锁环路径,创建新节点(头插法) */
if(dl_entry->entry == NULL)
{
dl_entry->entry = (DeadlockPathList *) palloc(sizeof(DeadlockPathList));
dl_entry->entry->path_str = deadlock_txn_path;
dl_entry->entry->next = head;
pgxc_deadlock_count++;
}
else
{
RFREE(loop->txns);
}
}使用MurmurHash2算法的目的
hashtable中keysize参数表示保存的key的长度,在初始化的时候需要确定下来,如果直接保存死锁环,则长度需要设置为事务数量,而事务数量是不确定的(有可能很大)。MurmurHash2算法能通过char*类型生成固定长度的hash值(32、64、128位无符号整数);同时为了避免由于hash碰撞,导致两条不同的死锁环生成的hash值相同,则将hash对应的死锁环也保存到哈希表内。对应的数据结构如下:其中DeadlockPathList中保存死锁环具体信息并形成链表,DeadlockPathEntry中保存该链表和对应的hash值。
typedef struct DeadlockPathList{
struct DeadlockPathList *next;
char *path_str;
} DeadlockPathList;
typedef uint32 DeadlockPathKey;
typedef struct DeadlockPathEntry{
DeadlockPathKey key;
struct DeadlockPathList *entry;
} DeadlockPathEntry;哈希表的创建
需要指定
hash参数类型和hash函数,否则默认使用string比较方法,上面的bug出现的原因即为:输入的uint32类型的被转换为了char*类型去比较,导致对应的死锁环路径并没有出现,但是判断的结果是已经出现过了,导致死锁环漏检。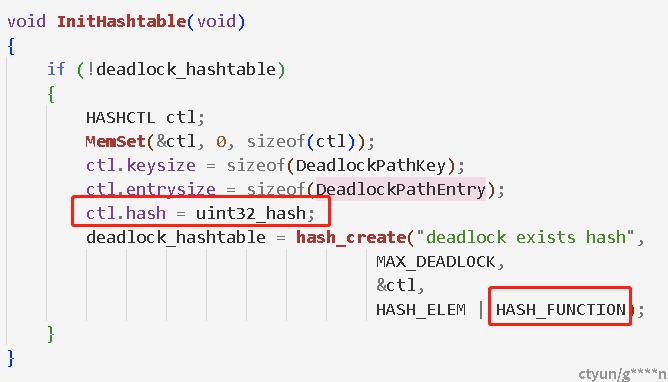
哈希表的销毁
hash_destroy函数只能销毁哈希表本身,但是由于其无法得知内部保存的信息,因此需要手动销毁内部的对象。具体代码如下:void DropHashtable(void)
{
if(deadlock_hashtable)
{
HASH_SEQ_STATUS seq;
DeadlockPathEntry *entry;
hash_seq_init(&seq, deadlock_hashtable);
while((entry = hash_seq_search(&seq)) != NULL)
{
DeadlockPathList * list = entry->entry;
DeadlockPathList * next = list;
while(list != NULL)
{
pfree(list->path_str);
next = list->next;
pfree(list);
list = next;
}
}
hash_destroy(deadlock_hashtable);
deadlock_hashtable = NULL;
}
}2. 测试方式:并行创建多连接构成分布式节点间的大量死锁
teledbx中,如果死锁发生在同一个dn节点内,会被系统发现并自动回滚事务来解锁,因此为了测试pg_unlock插件优化后的性能,需要构建不同cn、dn节点之间的死锁,同时死锁数量也需要大量增加。以两个dn节点为例,一种朴素的分布式死锁构建思路为:开启两个事务,第一个事务更新表A的第i行,第二个事务更新表A的第j行,此时让第一个事务更新表A的第j行,让第二个事务更新表A的第i行,则产生了分布式节点间的死锁环,并且这个死锁无法被系统检测到。按照这个思路,利用多线程同时开启多个事务,每个事务更新多行数据,即可迅速产生大量死锁。代码如下:#define RANGE_NUM 100
#define TRANS_NUM_PER_RAGE 15 /* 每个数据段分布15个事务 */
#define UPDATE_NUM_PER_TRANS 10 /* 每个事务更新十行数据 */
/* 不同的cn节点 */
enum cn_port {
cn01 = 11111,
cn02,
cn03,
cn04,
cn05
};
void *thread_func(void *arg) {
PGconn *conn;
PGresult *res;
char conn_info[100];
int cur_port = rand() % 5 + cn01;
snprintf(conn_info, sizeof(conn_info),
"dbname = postgres user = wanxdz password = 129212351GTFgtf_ host = 127.0.0.1 port = %d", cur_port);
conn = PQconnectdb(conn_info);
if (PQstatus(conn) != CONNECTION_OK) {
fprintf(stderr, "%lu connection to database failed: %s", pthread_self(), PQerrorMessage(conn));
PQfinish(conn);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
/* 开启事务 */
res = PQexec(conn, "BEGIN");
if (PQresultStatus(res) != PGRES_COMMAND_OK) {
fprintf(stderr, "%lu BEGIN failed: %s", pthread_self(), PQerrorMessage(conn));
PQclear(res);
PQfinish(conn);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
PQclear(res);
int begin_id = (int) arg;
int row_id;
for (int i = 0; i < UPDATE_NUM_PER_TRANS; ++i) {
char new_uuid[37];
uuid_t uuid;
char update_query[100];
uuid_generate_random(uuid);
uuid_unparse(uuid, new_uuid);
row_id = rand() % 100 + begin_id; //从 begin_id 开始到 begin_id + 100 - 1的范围取一个随机数值
snprintf(update_query, sizeof(update_query), "UPDATE foo SET str = '%s' WHERE id = %d", new_uuid, row_id);
res = PQexec(conn, update_query);
/* 更新成功后,将更新信息保存到日志内 */
if (PQresultStatus(res) == PGRES_COMMAND_OK) {
pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&rwlock);
fp = fopen(update_log, "a+");
fprintf(fp, "%lu\t\t%d\t\t%s\n", pthread_self(), row_id, new_uuid); /* 线程id 更新的行id 更新的uuid */
fclose(fp);
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rwlock);
} else {
fprintf(stderr, "%lu UPDATE failed: %s", pthread_self(), PQerrorMessage(conn));
PQclear(res);
PQfinish(conn);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
PQclear(res);
}
res = PQexec(conn, "END");
if (PQresultStatus(res) != PGRES_COMMAND_OK) {
fprintf(stderr, "%lu END failed: %s", pthread_self(), PQerrorMessage(conn));
PQclear(res);
PQfinish(conn);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
PQclear(res);
PQfinish(conn);
return NULL;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
/* 初始化写锁 */
int err = pthread_rwlock_init(&rwlock, NULL);
if (err != 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Can't init rwlock, the err result is %d", err);
return 0;
}
/* 初始化pthread数组 */
pthread_t **tid;
tid = (pthread_t **) malloc(sizeof(pthread_t *) * RANGE_NUM);
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i) { /* 分100段 */
tid[i] = (pthread_t *) malloc(sizeof(pthread_t) * TRANS_NUM_PER_RAGE);
int begin_row = i + 1;
for (int j = 0; j < TRANS_NUM_PER_RAGE; ++j) { /* 每段15个事务 */
pthread_create(&tid[i][j], NULL, (void *) thread_func, (void *) (begin_row * RANGE_NUM + 1));
pthread_detach(tid[i][j]);
}
}
while (1) {
/* 这里防止main退出 */
}
return 0;
}