概述
高可用(HA)
高可用性是指提供在本地系统单个组件故障情况下,能继续访问应用的能力,无论这个故障是业务流程、物理设施、IT软/硬件的故障。当发生故障时,对应的服务要做故障切换(failover),切换有两个维度的成本:RTO (Recovery Time Objective)和 RPO(Recovery Point Objective)。
RTO 是服务恢复的时间,最佳的情况是 0,这意味着服务立即恢复;最坏是无穷大意味着服务永远恢复不了;
RPO 是切换时向前恢复的数据的时间长度,0 意味着使用同步的数据,大于 0 意味着有数据丢失,比如 RPO = 1 天 意味着恢复时使用一天前的数据,那么一天之内的数据就丢失了。
对 HA 来说,往往使用共享存储,这样的话,RPO =0 ;同时往往使用 Active/Active (双活集群) 模式来使得 RTO 几乎0,HA 的计算公式是[ 1 - (宕机时间)/(宕机时间 + 运行时间)],我们常常用几个 9 表示可用性:
- 2 个9(99%) = 1% * 365 = 3.65 * 24 小时/年 = 87.6 小时/年的宕机时间
- 4 个9(99%) = 0.01% * 365 * 24 * 60 = 52.56 分钟/年
- 5 个9(999%) = 0.001% * 365 * 24 * 60 = 5.265 分钟/年的宕机时间,也就意味着每次停机时间在一到两分钟
云的高可用
云包括一个广泛的系统,包括硬件设施、IaaS层、虚拟机和应用等。以 OpenStack 云为例,高可用包括:
- 应用的 HA
- 虚拟机的 HA
- 云控制服务的 HA
- 物理IT层:包括网络设备比如交换机和路由器,存储设备等
- 基础设施,比如电力、空调和防火设施等
本文主要介绍OpenStack的控制层面服务的高可用及测试方法
OpenStack控制面高可用
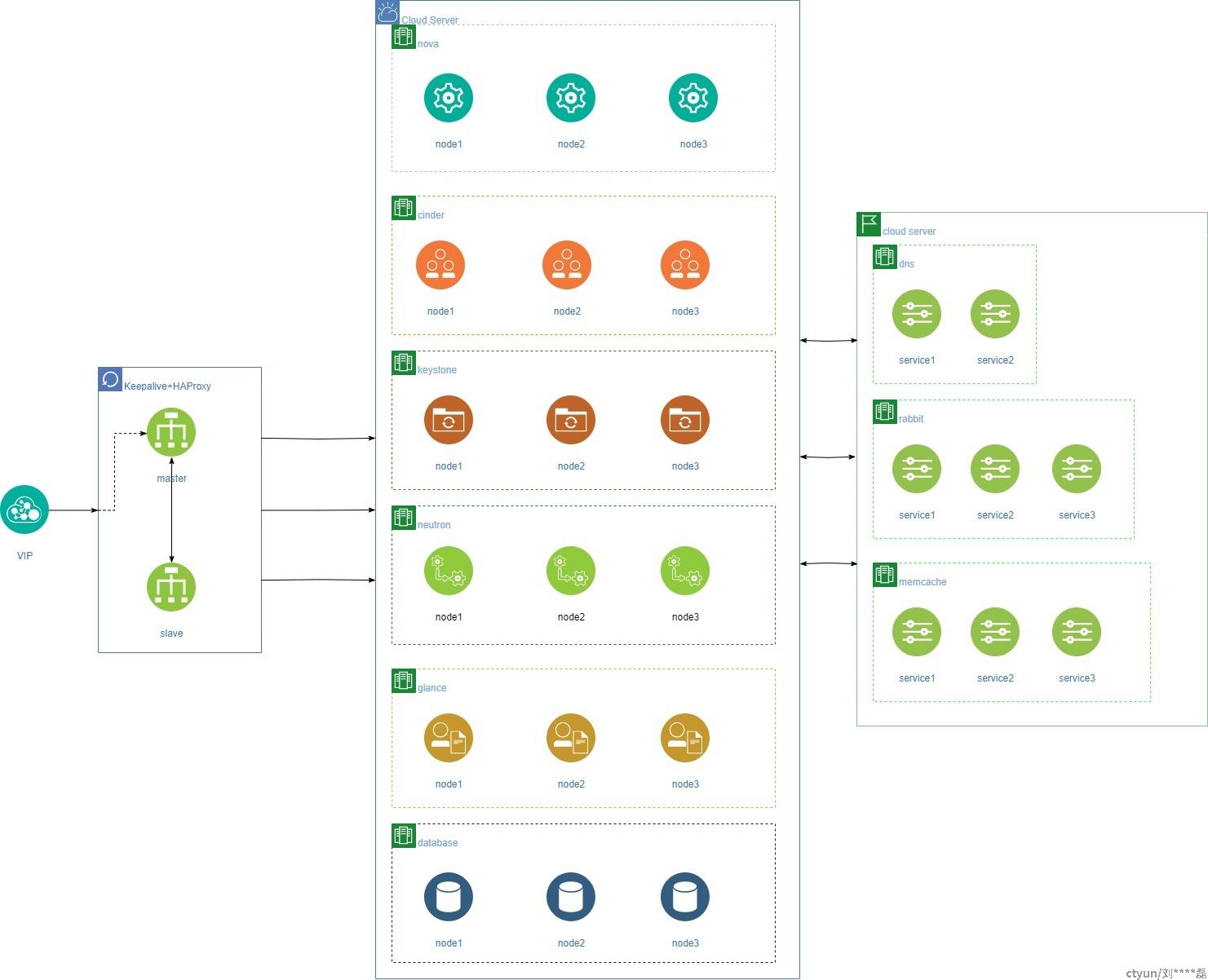
Keepalive+HAProxy
目前资源池部署OpenStack时,控制面的各个组件一般采用3节点,并使用keepalive和HAProxy来实现健康检查与故障转移
HAProxy
HAProxy 是一种免费、快速且可靠的高可用解决方案,它可为基于 TCP 和 HTTP 的应用程序提供高可用性、负载平衡和代理服务,特别适用于流量非常高的网站。
多年来,它已成为事实上的标准开源负载均衡器,现在随大多数主流 Linux 发行版一起提供,并且通常默认部署在云平台中。
Keepalive
keepalived是集群管理中保证集群高可用的一个服务软件,用来防止单点故障。
keepalived是以VRRP(虚拟路由冗余)协议为实现基础,即将N台提供相同功能的路由器组成一个路由器组,这个组里面有一个master和多个backup,master上面有一个对外提供服务的vip(该路由器所在局域网内其他机器的默认路由为该vip),master会发组播,当backup收不到vrrp包时就认为master宕掉了,这时就需要根据VRRP的优先级来选举一个backup当master。这样的话就可以保证路由器的高可用了。
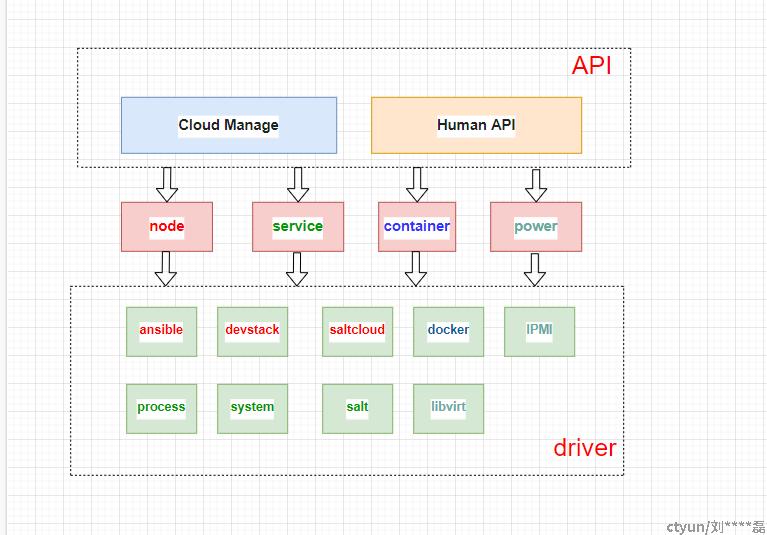
os-faults
社区开发os-faults项目,同时在rally中加入hook机制,形成了一套高可用的自动化测试解决方案。项目链接:https://opendev.org/performa/os-faults
os-faults可以对OpenStack执行破坏性操作,它为不同类型的云部署提供了一个抽象层。这些操作作为驱动程序实现(例如DevStack驱动程序、Salt驱动程序、Ansible驱动程序、IPMI驱动程序、Universal驱动程序,Docker驱动程序等)
安装
pip install os-faults配置
os-faults的操作对象,包括:
- service
- container
- node
支持通过yaml/json来进行配置
举例:
cloud_config = {
'cloud_management': {
'driver': 'universal',
},
'node_discover': {
'driver': 'node_list',
'args': [
{
'ip': '192.168.5.127',
'auth': {
'username': 'root',
'private_key_file': 'openstack_key',
}
},
{
'ip': '192.168.5.128',
'auth': {
'username': 'root',
'private_key_file': 'openstack_key',
}
}
]
},
'services': {
'memcached': {
'driver': 'system_service',
'args': {
'service_name': 'memcached',
'grep': 'memcached',
}
}
},
'containers': {
'neutron_api': {
'driver': 'docker_container',
'args': {
'container_name': 'nova_api',
}
}
},
'power_managements': [
{
'driver': 'libvirt',
'args': {
'connection_uri': 'qemu+unix:///system',
}
},
]
}
上述配置包含所有具有凭据的OpenStack节点,服务和容器。os-faults将自动确定服务、容器与节点之间的映射。同时电源管理的配置支持混合裸机和虚拟化部署。
通过如下接口建立到云的连接
cloud_management = os_faults.connect(cloud_config)
cloud_management.verify()
通过如下命令可进行一些破坏性测试
cloud_management.get_service(name='memcached').kill()
cloud_management.get_container(name='nova_api').restart()
human api
human api是自描述性的,它包括多个类型的命令:
service
<action> <service> service [on (random|one|single|<fqdn>|<node-number>|all node[s])]支持对节点上的服务,做如下操作:
- start - start Service
- terminate - terminate Service gracefully
- restart - restart Service
- kill - terminate Service abruptly
- unplug - unplug Service out of network
- plug - plug Service into network
举例:
restart keystone service:restarts Keystone service on all nodes.
kill openstack-nova-api service on one node:restarts Nova API on one randomly-picked node
node
<action> [random|one|single|<fqdn>] node[s] [with <service> service]
<action> <network> network on [random|one|single|<fqdn>] node[s] [with <service> service]
支持对节点做如下操作:
- reboot - reboot all nodes gracefully
- poweroff - power off all nodes abruptly
- reset - reset (cold restart) all nodes
- disconnect - disable network with the specified name on all nodes
- connect - enable network with the specified name on all nodes
举例:
reboot one node with mysql : reboots one random node with MySQL.
container
<action> <container> container [on (random|one|single|<fqdn>|<node-number>|all node[s])]支持对容器做如下操作:
- start - start Container
- terminate - terminate Container gracefully
- restart - restart Container
举例:
terminate nova_api container on one node : stops Neutron API container on one randomly-picked node.
rally fault injection hook
os-faults和rally的结合为测试OpenStack的高可用性和负载下的故障转移提供了自动化的工具。
rally利用hook来实现故障注入,注入的时刻可以指定为迭代次数或相对于测试开始的时间
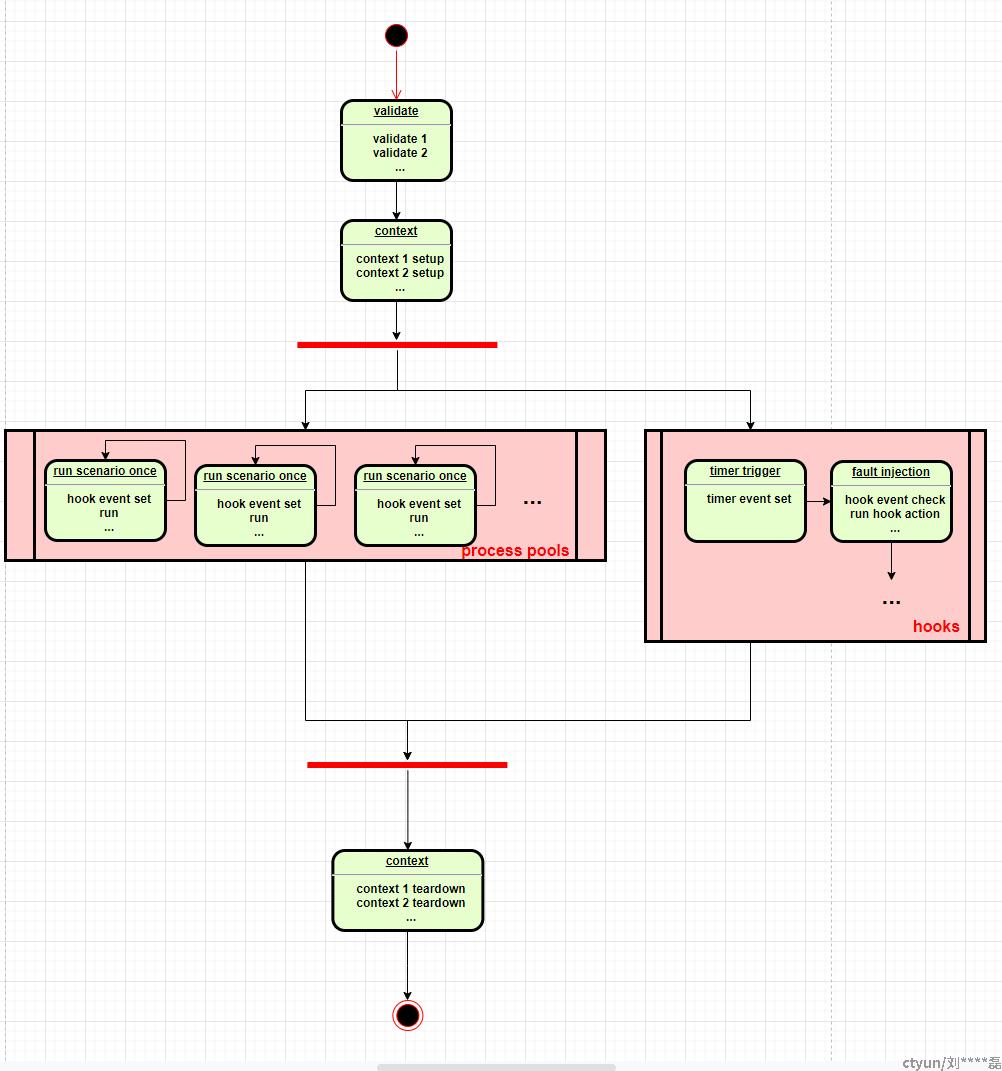
例如 重新启动nova-api服务来执行创建虚机的示例:
{% set flavor_name = flavor_name or "rally-1c2g" %}
{% set image_name = image_name or "CentOS7.6" %}
{% set size = size or 40 %}
{% set volume_type = volume_type or "default_volume_type" %}
{% set concurrency = concurrency or 5 %}
{% set nodes = nodes or ("11.5.72.73", "11.5.72.74", "11.5.72.75") %}
---
version: 2
title: Task for SDK test
description: >
Test suit for HA test.
subtasks:
-
title: SDK ComputeServers.boot_server_from_volume_and_delete
scenario:
ComputeServers.boot_server_from_volume_and_delete:
flavor:
name: "{{flavor_name}}"
image:
name: "{{image_name}}"
size: {{size}}
volume_type: "{{volume_type}}"
force_delete: false
auto_assign_nic: true
runner:
constant_for_duration:
duration: 300
concurrency: {{concurrency}}
contexts:
network: {}
users:
tenants: 1
users_per_tenant: 1
hooks:
- description: restart service openstack-nova-api
action:
fault_injection:
action: "restart openstack-nova-api service on one node"
auth:
private_key_file: "~/.rally/extra/os_pkey"
nodes:
{% for node in nodes %}
- {{node}}
{% endfor %}
services:
openstack-nova-api:
driver: "system_service"
args:
service_name: "openstack-nova-api"
grep: "nova-api"
trigger:
event:
unit: time
at: [50, 150]
fault_injection的实现 rally-openstack\rally_openstack\hook\fault_injection.py
# Copyright 2021: CTyun Inc.
# All Rights Reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may
# not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain
# a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT
# WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the
# License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations
# under the License.
import os.path
from rally.common import logging
from rally.common import validation
from rally.task import hook
from rally_openstack import consts
LOG = logging.getLogger(__name__)
@validation.configure("check_fault_injection_cloud_config")
class CheckFaultInjectionCloudConfigValidator(validation.Validator):
def __init__(self):
"""Validates the config of ansible worker context"""
super(CheckFaultInjectionCloudConfigValidator, self).__init__()
def validate(self, context, config, plugin_cls, plugin_cfg):
if plugin_cfg.get("cloud_file"):
cloud_file = plugin_cfg.get("cloud_file")
config_filename = os.path.realpath(os.path.expanduser(cloud_file))
if not os.path.exists(config_filename):
return self.fail(
"cloud_config file not exists, please check!")
else:
if plugin_cfg.get("auth", {}).get("private_key_file"):
pkf = plugin_cfg.get("auth").get("private_key_file")
pkf_path = os.path.realpath(os.path.expanduser(pkf))
if not os.path.exists(pkf_path):
return self.fail(
"private_key_file not exists, please check!")
@validation.add(name="check_fault_injection_cloud_config")
@hook.configure(name="fault_injection", platform="openstack")
class FaultInjectionHook(hook.HookAction):
"""Performs fault injection using os-faults library.
Configuration:
* action - string that represents an action (more info in [1])
* verify - whether to verify connection to cloud nodes or not
* config_file - the config file of cloud, the priority is highest
* auth - the auth config of ansible
* nodes - the nodes list
* services - the service on the nodes
This plugin discovers the config of cloud_config
and looks for "cloud_config" field. If cloud_config is present then
it will be used to connect to the cloud by os-faults.
Another option is to provide os-faults config file through
OS_FAULTS_CONFIG env variable. Format of the config can
be found in [1].
[1] http://os-faults.readthedocs.io/en/latest/usage.html
"""
CONFIG_SCHEMA = {
"type": "object",
"$schema": consts.JSON_SCHEMA,
"properties": {
"action": {"type": "string"},
"verify": {"type": "boolean"},
"cloud_file": {"type": "string"},
"auth": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
'username': {"type": "string"},
'private_key_file': {"type": "string"},
'ssh_port': {'type': 'integer'},
'become_username': {'type': 'string'},
'password': {'type': 'string'},
'become_password': {'type': 'string'},
},
"additionalProperties": False,
},
"nodes": {
"type": "array",
"items": {"type": "string"},
},
"services": {
"type": "object",
"pattenProperties": {
'.*': {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
'driver': {'type': 'string'},
'args': {
'type': 'object',
"properties": {
'service_name': {'type': 'string'},
'grep': {'type': 'string'},
'start_cmd': {'type': 'string'},
'terminate_cmd': {'type': 'string'},
'restart_cmd': {'type': 'string'},
},
'required': ['grep'],
"additionalProperties": True,
},
},
'required': ['driver'],
"additionalProperties": False,
},
},
}
},
"required": ["action"],
"additionalProperties": False,
}
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super(FaultInjectionHook, self).__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.cloud_file = self.config.get("cloud_file")
self.auth = None
self.cloud_config = None
self.get_cloud_config()
def get_cloud_config(self):
if self.cloud_file:
self.cloud_file = os.path.realpath(os.path.expanduser(
self.cloud_file))
else:
self.auth = {
"username": "secure",
"ssh_port": 10000,
}
self.cloud_config = {
'cloud_management': {
'driver': 'universal'
},
'node_discover': {
'driver': 'node_list',
},
}
self.auth.update(self.config.get("auth", {}))
pkf = self.config.get("auth", {}).get("private_key_file")
if pkf:
pkf_path = os.path.realpath(os.path.expanduser(pkf))
self.auth["private_key_file"] = pkf_path
nodes_args = []
for node_ip in self.config.get("nodes"):
nodes_args.append({
"ip": node_ip,
"auth": self.auth,
})
self.cloud_config["node_discover"]["args"] = nodes_args
self.cloud_config["services"] = self.config.get("services")
def run(self):
import os_faults
if self.cloud_file:
cloud_config = (None, self.cloud_file)
else:
cloud_config = (self.cloud_config, None)
# connect to the cloud
injector = os_faults.connect(*cloud_config)
# verify that all nodes are available
if self.config.get("verify"):
injector.verify()
LOG.debug("Injecting fault: %s" % self.config["action"])
try:
os_faults.human_api(injector, self.config["action"])
self.set_status(consts.HookStatus.SUCCESS)
except Exception as e:
self.set_status(consts.HookStatus.FAILED)
self.set_error(exception_name=type(e),
description='Fault injection failure',
details=str(e))
报告
高可用参数
- MTTR (Mean time to repair)- 故障后恢复服务性能的平均时间
- Service Downtime - 服务失效时间
- Absolute performance degradation - 绝对性能下降是指恢复期间操作持续时间的平均值与基线之间的绝对差值
- Relative performance degradation -相对性能下降—恢复期间的平均运行时间与基线之间的比率。
报告生成
使用rally-runners生成报告,方法如下:
1.安装python包
pip install sphinx
pip install rally-runners
2.获取本次测试的rally task的uuid,根据uuid生成测试结果的json文件
rally task results uuid > output.json3.通过rally_runner 脚本中的report函数 根据json文件生成index..rst文件
from rally_runners.reliability.report import make_report
if __name__ == "__main__":
folderPath = "/root/testscript/test/"
#测试的yaml文件
caseName = "testcase"
raw_file_names = [folderPath + 'output.json']
make_report(caseName, raw_file_names, folderPath)
ps:因为原生的脚本不匹配与当前版本了,需要修改部分代码 rally_runners包下的analytics.py
if hooks:
# when the hook started
#hook_start_time = hooks[0]['started_at'] - start
hook_start_time = hooks[0]['results'][0]['started_at'] - start
4.使用sphinx把rst转成html
sphinx-build -b html test/ result/举例
某项目中组件的高可用测试,发现了DNS组件部署实施时的问题
测试例yaml文件
{% set flavor_name = flavor_name or "rally-1c2g" %}
{% set image_name = image_name or "CentOS7.6" %}
{% set size = size or 40 %}
{% set volume_type = volume_type or "default_volume_type" %}
{% set concurrency = concurrency or 5 %}
{% set nodes = nodes or ("14.129.215.31", "14.129.215.32") %}
---
version: 2
title: Task for SDK test
description: >
Test suit for HA test.
subtasks:
-
title: SDK ComputeServers.boot_server_from_volume_and_delete
scenario:
ComputeServers.boot_server_from_volume_and_delete:
flavor:
name: "{{flavor_name}}"
image:
name: "{{image_name}}"
size: {{size}}
volume_type: "{{volume_type}}"
force_delete: false
auto_assign_nic: true
runner:
constant_for_duration:
duration: 300
concurrency: {{concurrency}}
contexts:
network: {}
users:
tenants: 1
users_per_tenant: 1
hooks:
- description: terminate service named
action:
fault_injection:
action: "terminate named service on one node"
auth:
private_key_file: "~/.rally/extra/os_pkey"
nodes:
{% for node in nodes %}
- {{node}}
{% endfor %}
services:
named:
driver: "system_service"
args:
service_name: "named"
grep: "named"
trigger:
event:
unit: time
at: [50]
- description: start service named
action:
fault_injection:
action: "start_systemctl_service named service on all nodes"
auth:
private_key_file: "~/.rally/extra/os_pkey"
nodes:
{% for node in nodes %}
- {{node}}
{% endfor %}
services:
named:
driver: "system_service"
args:
service_name: "named"
grep: "named"
trigger:
event:
unit: time
at: [200]
第一次测试,发现dns服务失效时间达130s,跟预期差距较大,经过定位发现2个dns服务与nova-api等服务部署在一起,且宿主机并没有配置nameserver或者主机名查询静态表(/etc/hosts),导致当dns服务被关闭后,该节点的nova请求的域名解析失败
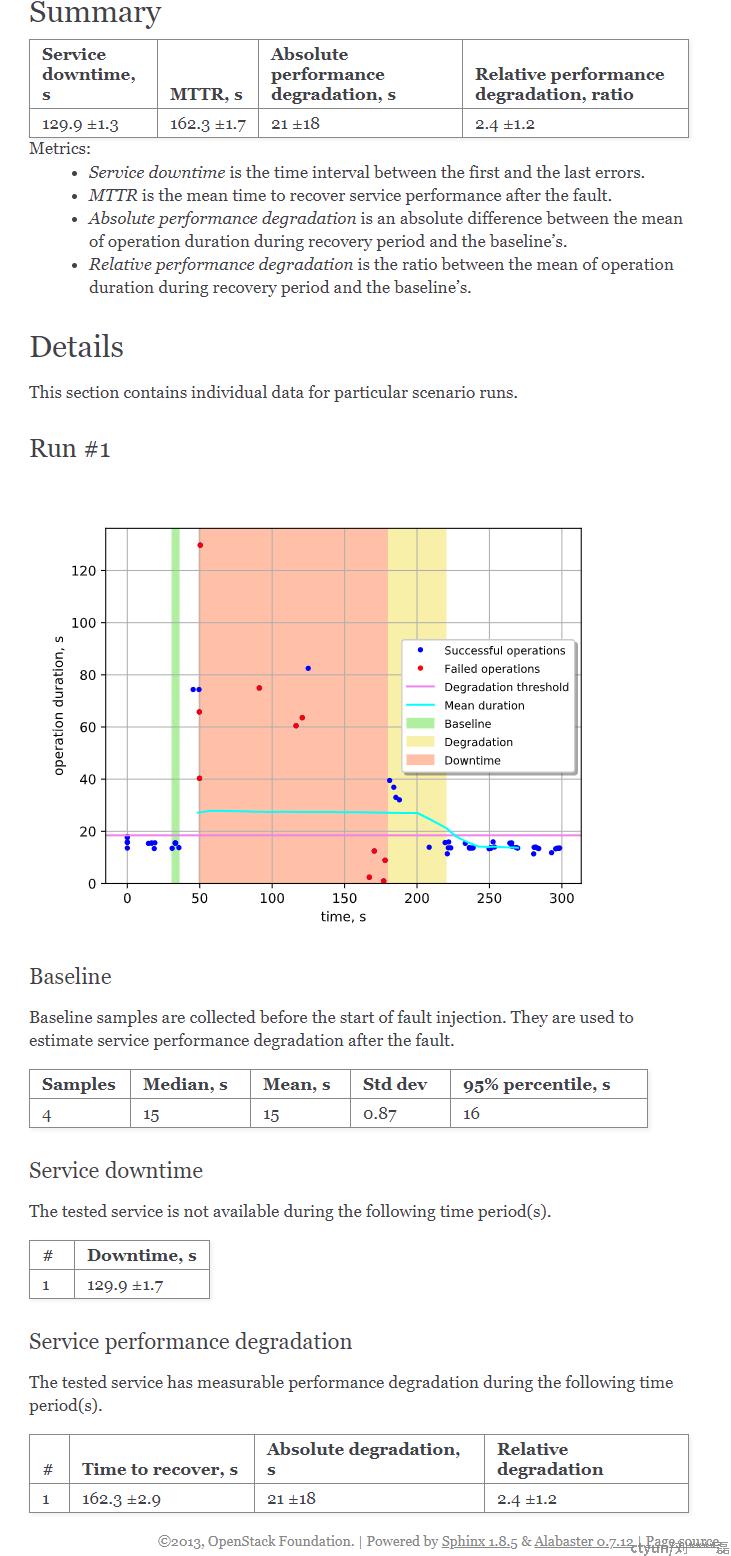
部署变更后,重新测试:关闭一个dns服务,未对整体性能造成影响(并发5,创建虚机)
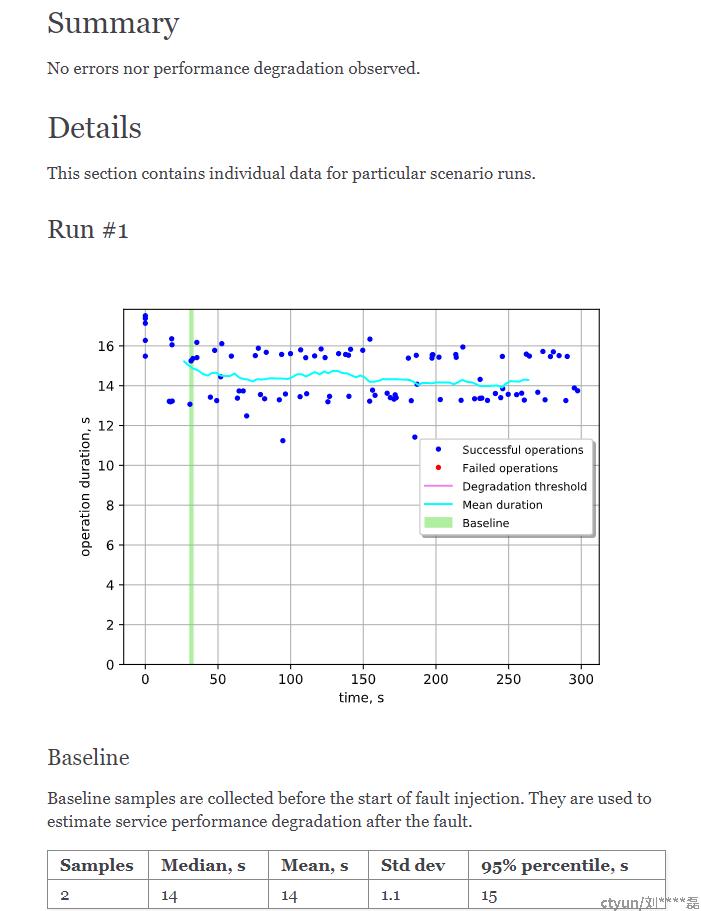
总结
本文介绍了高可用的概念及云环境的高可用场景,结合os-faults及rally hook插件,设计并组织了OpenStack控制面组件的高可用测试,在测试中收集相关数据并在报告中展示了服务失效时间,服务性能恢复时间等关键参数,为各类高可用方案的评估提供了测试依据。
参考文档
- https://docs.openstack.org/ha-guide/
- https://docs.openstack.org/rally/latest/