1 客户端处理报文流程
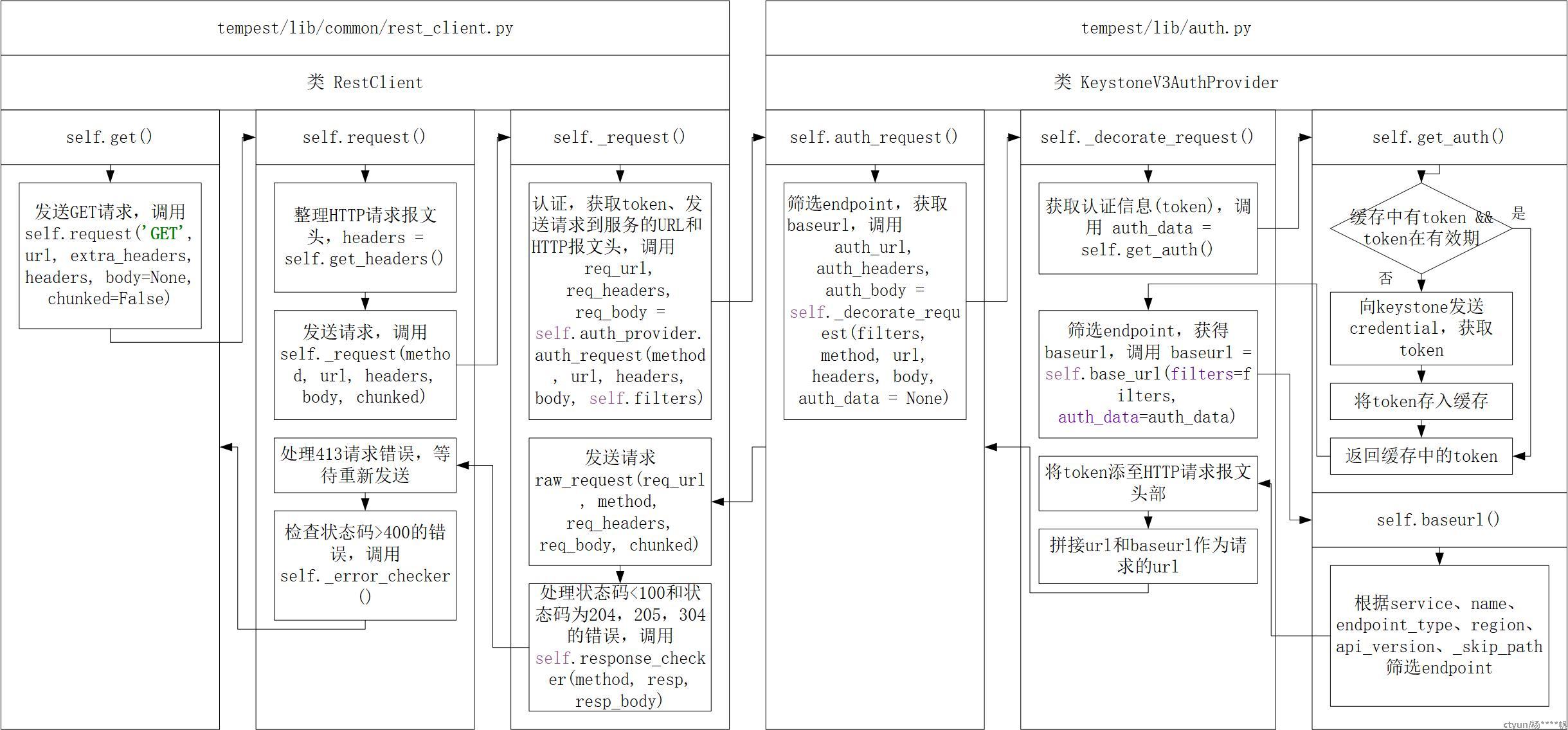
上图中RestClient类为客户端的基类,所有客户端发送及接收报文的机制都是大致相同的。
1.1 准备头部
发送HTTP报文需要URL、头部和主体这三部分。客户端调用RestClient.get()时,需传入URL和报文头部,如果是发送POST请求则还需传入主体部分。此时URL和报文头部都是不完整的。一些请求中需要包含额外的头部,通过调用self.get_headers()完成。
1.2 请求token、endpoint
发送请求到OpenStack时,头部需要添加’X-Auth-Token’字段。该字段值为token,需要预先向OpenStack请求。客户端传入的URL此时也并不是完整的URL,需要与endpoint拼接得到。
客户端中的self.auth_provider是KeystoneV3AuthProvider或KeystoneV2AuthProvider的实例,具体是哪个类的实例取决于环境中Keystone的版本和Tempest的配置。KeystoneV3AuthProvider提供了请求token和endpoint的功能,客户端的开发过程中就不用考虑认证部分了。
RestClient类中发送请求前调用了self.auth_provider.auth_request(),这个函数调用了self.decorate_request(),其代码如下:
def _decorate_request(self, filters, method, url, headers=None, body=None,
auth_data=None):
if auth_data is None:
auth_data = self.get_auth() #请求token和endpoint列表
token, _ = auth_data
base_url = self.base_url(filters=filters, auth_data=auth_data) #筛选endpoint
_headers = copy.deepcopy(headers) if headers is not None else {}
_headers['X-Auth-Token'] = str(token) #将token添加至头部
if url is None or url == "":
_url = base_url
else:
_url = "/".join([base_url, url]) #拼接endpoint和URL
parts = [x for x in urlparse.urlparse(_url)]
parts[2] = re.sub("/{2,}", "/", parts[2])
_url = urlparse.urlunparse(parts)
return str(_url), _headers, body
self.decorate_request()完成了以下几件事情:
- 请求token和endpoint列表
- 筛选endpoint
- 添加token至头部
- 拼接URL
请求token和endpoint列表通过self.get_auth()完成,该函数调用了OpenStack的/v3/auth/tokens,向OpenStack发送了认证信息以请求token,返回的响应body如下:
{
"token": {
"audit_ids": [
"3T2dc1CGQxyJsHdDu1xkcw"
],
"catalog": [
{
"endpoints": [
{
"id": "068d1b359ee84b438266cb736d81de97",
"interface": "public",
"region": "RegionOne",
"region_id": "RegionOne",
"url": "example.com/identity"
},
{
"id": "8bfc846841ab441ca38471be6d164ced",
"interface": "admin",
"region": "RegionOne",
"region_id": "RegionOne",
"url": "example.com/identity"
},
{
"id": "beb6d358c3654b4bada04d4663b640b9",
"interface": "internal",
"region": "RegionOne",
"region_id": "RegionOne",
"url": "example.com/identity"
}
],
"type": "identity",
"id": "050726f278654128aba89757ae25950c",
"name": "keystone"
}
],
"expires_at": "2015-11-07T02:58:43.578887Z",
"is_domain": false,
"issued_at": "2015-11-07T01:58:43.578929Z",
"methods": [
"password"
],
"project": {
"domain": {
"id": "default",
"name": "Default"
},
"id": "a6944d763bf64ee6a275f1263fae0352",
"name": "admin"
},
"roles": [
{
"id": "51cc68287d524c759f47c811e6463340",
"name": "admin"
}
],
"user": {
"domain": {
"id": "default",
"name": "Default"
},
"id": "ee4dfb6e5540447cb3741905149d9b6e",
"name": "admin",
"password_expires_at": "2016-11-06T15:32:17.000000"
}
}
}
请求得到的token在头部的‘X-Subject-Token’字段中,body中包含endpoint信息。
self.get_auth()返回的auth_data中包含的是token和endpoint两部分信息。
1.3 发送报文
URL、头部准备好后就可以发送报文了,RestClient类中self.raw_request()负责发送报文:
def raw_request(self, url, method, headers=None, body=None, chunked=False):
if headers is None:
headers = self.get_headers()
return self.http_obj.request(url, method, headers=headers,
body=body, chunked=chunked)
self.raw_request()是对self.http_obj.request()的封装,self.http是Tempest中ClosingHttp类或ClosingProxyHttp类的实例,而这两个类又分别是urllib3中urllib3.PoolManager和urllib3.ProxyManager的继承。发送请求最终是由urllib3完成的。
1.4 错误检查
返回响应的错误检查由self.response_check()和self.error_checker()完成:
def response_checker(self, method, resp, resp_body):
if (resp.status in set((204, 205, 304)) or resp.status < 200 or
method.upper() == 'HEAD') and resp_body:
raise exceptions.ResponseWithNonEmptyBody(status=resp.status)
# NOTE(afazekas):
# If the HTTP Status Code is 205
# 'The response MUST NOT include an entity.'
# A HTTP entity has an entity-body and an 'entity-header'.
# In the HTTP response specification (Section 6) the 'entity-header'
# 'generic-header' and 'response-header' are in OR relation.
# All headers not in the above two group are considered as entity
# header in every interpretation.
if (resp.status == 205 and
0 != len(set(resp.keys()) - set(('status',)) -
self.response_header_lc - self.general_header_lc)):
raise exceptions.ResponseWithEntity()
# NOTE(afazekas)
# Now the swift sometimes (delete not empty container)
# returns with non json error response, we can create new rest class
# for swift.
# Usually RFC2616 says error responses SHOULD contain an explanation.
# The warning is normal for SHOULD/SHOULD NOT case
# Likely it will cause an error
if method != 'HEAD' and not resp_body and resp.status >= 400:
self.LOG.warning("status >= 400 response with empty body")
self.response_check()主要检查当HTTP状态码为204、205、304时返回响应中是否有body。
def _error_checker(self, resp, resp_body):
# NOTE(mtreinish): Check for httplib response from glance_http. The
# object can't be used here because importing httplib breaks httplib2.
# If another object from a class not imported were passed here as
# resp this could possibly fail
if str(type(resp)) == "<type 'instance'>":
ctype = resp.getheader('content-type')
else:
try:
ctype = resp['content-type']
# NOTE(mtreinish): Keystone delete user responses doesn't have a
# content-type header. (They don't have a body) So just pretend it
# is set.
except KeyError:
ctype = 'application/json'
# It is not an error response
if resp.status < 400:
return
# NOTE(zhipengh): There is a purposefully duplicate of content-type
# with the only difference is with or without spaces, as specified
# in RFC7231.
JSON_ENC = ['application/json', 'application/json; charset=utf-8',
'application/json;charset=utf-8']
# NOTE(mtreinish): This is for compatibility with Glance and swift
# APIs. These are the return content types that Glance api v1
# (and occasionally swift) are using.
# NOTE(zhipengh): There is a purposefully duplicate of content-type
# with the only difference is with or without spaces, as specified
# in RFC7231.
TXT_ENC = ['text/plain', 'text/html', 'text/html; charset=utf-8',
'text/plain; charset=utf-8', 'text/html;charset=utf-8',
'text/plain;charset=utf-8']
if ctype.lower() in JSON_ENC:
parse_resp = True
elif ctype.lower() in TXT_ENC:
parse_resp = False
else:
raise exceptions.UnexpectedContentType(str(resp.status),
resp=resp)
if resp.status == 401:
if parse_resp:
resp_body = self._parse_resp(resp_body)
raise exceptions.Unauthorized(resp_body, resp=resp)
if resp.status == 403:
if parse_resp:
resp_body = self._parse_resp(resp_body)
raise exceptions.Forbidden(resp_body, resp=resp)
if resp.status == 404:
if parse_resp:
resp_body = self._parse_resp(resp_body)
raise exceptions.NotFound(resp_body, resp=resp)
if resp.status == 400:
if parse_resp:
resp_body = self._parse_resp(resp_body)
raise exceptions.BadRequest(resp_body, resp=resp)
if resp.status == 410:
if parse_resp:
resp_body = self._parse_resp(resp_body)
raise exceptions.Gone(resp_body, resp=resp)
if resp.status == 409:
if parse_resp:
resp_body = self._parse_resp(resp_body)
raise exceptions.Conflict(resp_body, resp=resp)
if resp.status == 412:
if parse_resp:
resp_body = self._parse_resp(resp_body)
raise exceptions.PreconditionFailed(resp_body, resp=resp)
if resp.status == 413:
if parse_resp:
resp_body = self._parse_resp(resp_body)
if self.is_absolute_limit(resp, resp_body):
raise exceptions.OverLimit(resp_body, resp=resp)
else:
raise exceptions.RateLimitExceeded(resp_body, resp=resp)
if resp.status == 415:
if parse_resp:
resp_body = self._parse_resp(resp_body)
raise exceptions.InvalidContentType(resp_body, resp=resp)
if resp.status == 422:
if parse_resp:
resp_body = self._parse_resp(resp_body)
raise exceptions.UnprocessableEntity(resp_body, resp=resp)
if resp.status in (500, 501):
message = resp_body
if parse_resp:
try:
resp_body = self._parse_resp(resp_body)
except ValueError:
# If response body is a non-json string message.
# Use resp_body as is and raise InvalidResponseBody
# exception.
raise exceptions.InvalidHTTPResponseBody(message)
else:
if isinstance(resp_body, dict):
# I'm seeing both computeFault
# and cloudServersFault come back.
# Will file a bug to fix, but leave as is for now.
if 'cloudServersFault' in resp_body:
message = resp_body['cloudServersFault']['message']
elif 'computeFault' in resp_body:
message = resp_body['computeFault']['message']
elif 'error' in resp_body:
message = resp_body['error']['message']
elif 'message' in resp_body:
message = resp_body['message']
else:
message = resp_body
if resp.status == 501:
raise exceptions.NotImplemented(resp_body, resp=resp,
message=message)
else:
raise exceptions.ServerFault(resp_body, resp=resp,
message=message)
if resp.status >= 400:
raise exceptions.UnexpectedResponseCode(str(resp.status),
resp=resp)
self.error_checker()主要是根据几种错误的状态码抛出异常。
2 micro version检查
Nova等服务的客户端还会检查返回响应是否符合micro version。如下是server的客户端中查询server的函数:
def show_server(self, server_id):
"""Get server details.
For a full list of available parameters, please refer to the official
API reference:
developer.openstack.org/api-ref/compute/#show-server-details
"""
resp, body = self.get("servers/%s" % server_id)
body = json.loads(body)
schema = self.get_schema(self.schema_versions_info)
self.validate_response(schema.get_server, resp, body)
return rest_client.ResponseBody(resp, body)
self.get(“servers/%s” % server_id)调用了RestClient的self.get()发送报文,过程如上节所述。
body = json.loads(body)将返回内容反序列化。
schema = self.get_schema(self.schema_versions_info)获取对应micro version下响应的schema。
self.schema_versions_info中保存有schema的列表:
schema_versions_info = [
{'min': None, 'max': '2.2', 'schema': schema},
{'min': '2.3', 'max': '2.5', 'schema': schemav23},
{'min': '2.6', 'max': '2.7', 'schema': schemav26},
{'min': '2.8', 'max': '2.8', 'schema': schemav28},
{'min': '2.9', 'max': '2.15', 'schema': schemav29},
{'min': '2.16', 'max': '2.18', 'schema': schemav216},
{'min': '2.19', 'max': '2.25', 'schema': schemav219},
{'min': '2.26', 'max': '2.46', 'schema': schemav226},
{'min': '2.47', 'max': '2.47', 'schema': schemav247},
{'min': '2.48', 'max': '2.53', 'schema': schemav248},
{'min': '2.54', 'max': '2.56', 'schema': schemav254},
{'min': '2.57', 'max': '2.62', 'schema': schemav257},
{'min': '2.63', 'max': None, 'schema': schemav263}]
def get_schema(self, schema_versions_info):
"""Get JSON schema
This method provides the matching schema for requested
microversion.
:param schema_versions_info: List of dict which provides schema
information with range of valid versions.
Example::
schema_versions_info = [
{'min': None, 'max': '2.1', 'schema': schemav21},
{'min': '2.2', 'max': '2.9', 'schema': schemav22},
{'min': '2.10', 'max': None, 'schema': schemav210}]
"""
schema = None
version = api_version_request.APIVersionRequest(COMPUTE_MICROVERSION)
for items in schema_versions_info:
min_version = api_version_request.APIVersionRequest(items['min'])
max_version = api_version_request.APIVersionRequest(items['max'])
# This is case where COMPUTE_MICROVERSION is None, which means
# request without microversion So select base v2.1 schema.
if version.is_null() and items['min'] is None:
schema = items['schema']
break
# else select appropriate schema as per COMPUTE_MICROVERSION
elif version.matches(min_version, max_version):
schema = items['schema']
break
if schema is None:
raise exceptions.JSONSchemaNotFound(
version=version.get_string(),
schema_versions_info=schema_versions_info)
return schema
self.get_schema()根据micro version返回schema,如果客户端的micro version为None,则返回最低micro version也就是v2.1的schema。没找到对应的micro version则会触发异常。